
Balanced NPK vs High-phosphorus Illustration
Balanced NPK fertilizers provide an optimal ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to support overall plant growth, root development, and nutrient uptake. High-phosphorus fertilizers specifically enhance root strength and flower production but may lead to nutrient imbalances if used excessively. Proper selection depends on soil testing and crop requirements to ensure efficient nutrient use and maximize yield.
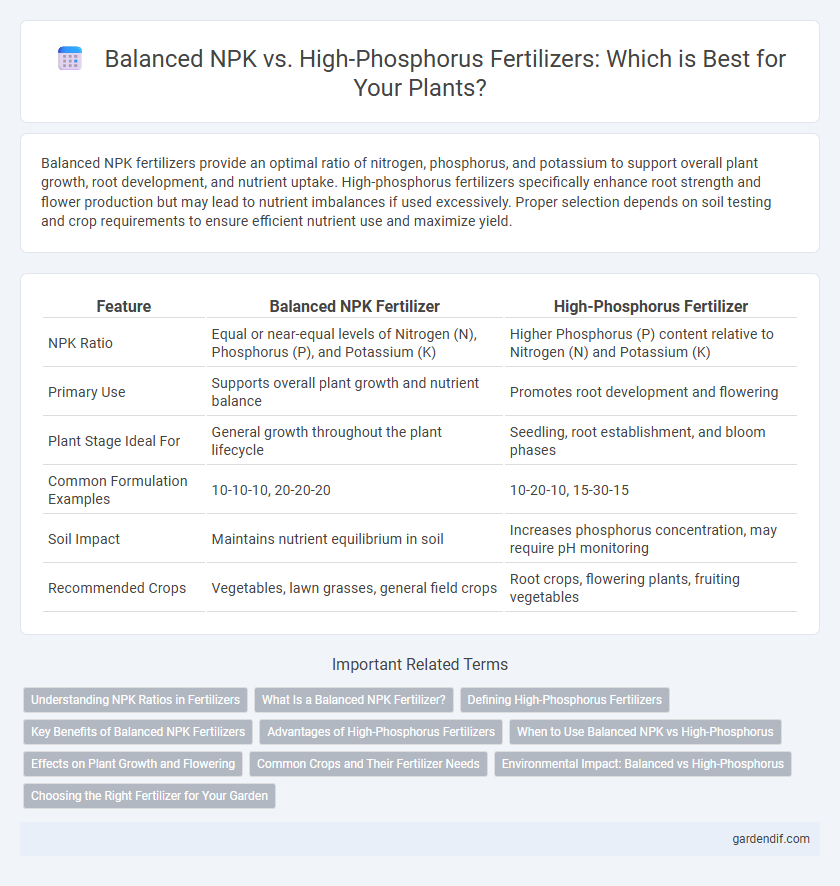
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Balanced NPK Fertilizer | High-Phosphorus Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| NPK Ratio | Equal or near-equal levels of Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) | Higher Phosphorus (P) content relative to Nitrogen (N) and Potassium (K) |
| Primary Use | Supports overall plant growth and nutrient balance | Promotes root development and flowering |
| Plant Stage Ideal For | General growth throughout the plant lifecycle | Seedling, root establishment, and bloom phases |
| Common Formulation Examples | 10-10-10, 20-20-20 | 10-20-10, 15-30-15 |
| Soil Impact | Maintains nutrient equilibrium in soil | Increases phosphorus concentration, may require pH monitoring |
| Recommended Crops | Vegetables, lawn grasses, general field crops | Root crops, flowering plants, fruiting vegetables |
Understanding NPK Ratios in Fertilizers
Balanced NPK fertilizers contain equal or nearly equal proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), ideal for overall plant growth and soil fertility maintenance. High-phosphorus fertilizers feature elevated phosphorus content, crucial for root development and flowering, especially during early planting stages. Understanding NPK ratios helps in selecting the right fertilizer based on specific crop nutrient needs and soil conditions for optimal growth and yield.
What Is a Balanced NPK Fertilizer?
Balanced NPK fertilizer contains equal or nearly equal proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), typically represented as 10-10-10 or 20-20-20 formulations, promoting overall healthy plant growth by supplying essential macronutrients in equilibrium. High-phosphorus fertilizers, on the other hand, have an elevated phosphorus content, such as 10-30-10, specifically enhancing root development and flowering rather than supporting complete nutrition. Choosing between balanced NPK and high-phosphorus fertilizers depends on crop type, soil nutrient status, and specific growth stage requirements to optimize yield and plant health.
Defining High-Phosphorus Fertilizers
High-phosphorus fertilizers contain an elevated concentration of phosphorus (P), typically exceeding the balanced NPK ratio, to address specific crop requirements such as root development and flowering. These fertilizers can range from single nutrient formulations like superphosphate to complex blends with higher phosphorus content compared to nitrogen (N) and potassium (K). The increased phosphorus availability promotes early plant establishment and supports energy transfer processes critical for seed and fruit production.
Key Benefits of Balanced NPK Fertilizers
Balanced NPK fertilizers provide essential nutrients in optimal ratios, promoting overall plant health, enhanced root development, and improved nutrient uptake efficiency. They support sustained growth and higher crop yields by supplying nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in harmony, preventing nutrient imbalances often caused by high-phosphorus fertilizers. This balanced nutrient delivery reduces soil nutrient depletion and minimizes environmental risks such as phosphorus runoff.
Advantages of High-Phosphorus Fertilizers
High-phosphorus fertilizers enhance root development and improve early plant growth by supplying essential phosphorus during critical growth stages. These fertilizers boost flowering and fruiting processes, leading to increased crop yields and better-quality produce. Compared to balanced NPK formulations, high-phosphorus fertilizers are particularly advantageous in phosphorus-deficient soils, enabling targeted nutrient management for optimal plant performance.
When to Use Balanced NPK vs High-Phosphorus
Balanced NPK fertilizers, containing equal or near-equal proportions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are ideal for general crop growth and maintaining overall soil fertility. High-phosphorus fertilizers should be applied during early root development stages or to establish new plants, as phosphorus promotes strong root systems and flowering. Soil testing is essential to determine nutrient deficiencies and select the appropriate fertilizer type for optimal plant health and yield.
Effects on Plant Growth and Flowering
Balanced NPK fertilizers provide essential nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in optimal ratios, promoting overall healthy plant growth, strong root development, and sustained leaf and stem advancement. High-phosphorus fertilizers enhance flowering and fruiting by stimulating bud formation and accelerating bloom cycles but may limit vegetative growth if nitrogen is insufficient. Selecting the appropriate NPK ratio tailored to specific plant species and growth stages maximizes plant vigor and reproductive success.
Common Crops and Their Fertilizer Needs
Common crops like wheat, corn, and rice benefit from balanced NPK fertilizers that supply essential nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in optimal proportions for overall growth and yield. High-phosphorus fertilizers are particularly advantageous for root development and early plant establishment, especially in crops such as potatoes and legumes that require enhanced phosphorus during initial stages. Tailoring fertilizer types based on crop-specific nutrient demands ensures improved nutrient efficiency and maximizes agricultural productivity.
Environmental Impact: Balanced vs High-Phosphorus
Balanced NPK fertilizers, containing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in appropriate ratios, promote sustainable crop growth while minimizing nutrient runoff and soil degradation compared to high-phosphorus fertilizers. Excessive phosphorus from high-phosphorus fertilizers often leads to eutrophication in water bodies, causing harmful algal blooms and aquatic ecosystem damage. Implementing balanced NPK applications supports environmental health by reducing phosphorus leaching and maintaining soil nutrient equilibrium.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Garden
Choosing the right fertilizer for your garden depends on soil nutrient levels and plant needs, with balanced NPK fertilizers providing essential nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in equal proportions to support overall plant health. High-phosphorus fertilizers are ideal for promoting root development and flowering in phosphorus-deficient soils or during early growth stages. Soil testing helps determine which fertilizer type maximizes plant growth and yield by addressing specific nutrient deficiencies effectively.
Balanced NPK vs High-phosphorus Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com