
Sun exposure vs shade cover Illustration
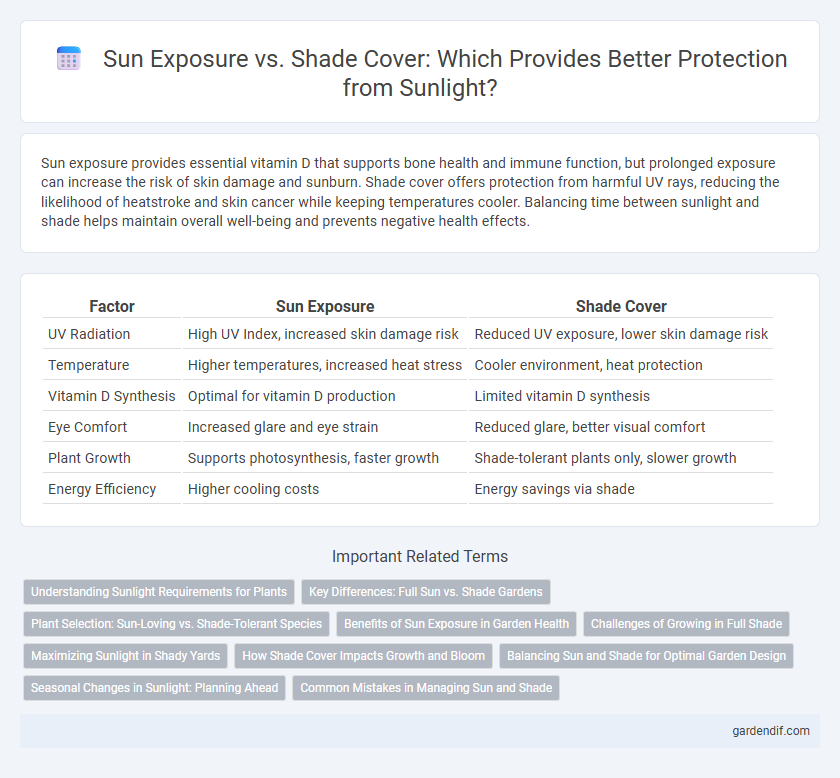
Sun exposure provides essential vitamin D that supports bone health and immune function, but prolonged exposure can increase the risk of skin damage and sunburn. Shade cover offers protection from harmful UV rays, reducing the likelihood of heatstroke and skin cancer while keeping temperatures cooler. Balancing time between sunlight and shade helps maintain overall well-being and prevents negative health effects.
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Sun Exposure | Shade Cover |
|---|---|---|
| UV Radiation | High UV Index, increased skin damage risk | Reduced UV exposure, lower skin damage risk |
| Temperature | Higher temperatures, increased heat stress | Cooler environment, heat protection |
| Vitamin D Synthesis | Optimal for vitamin D production | Limited vitamin D synthesis |
| Eye Comfort | Increased glare and eye strain | Reduced glare, better visual comfort |
| Plant Growth | Supports photosynthesis, faster growth | Shade-tolerant plants only, slower growth |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher cooling costs | Energy savings via shade |
Understanding Sunlight Requirements for Plants
Plants have varying sunlight requirements depending on their species, with some thriving under full sun exposure providing at least six hours of direct light, while others prefer partial shade to avoid leaf scorch and dehydration. Understanding the intensity and duration of sunlight in a garden area helps optimize plant health by matching species to their ideal light conditions. Shade cover reduces UV radiation and temperature stress, promoting growth in shade-tolerant plants like ferns and hostas that require filtered or indirect sunlight.
Key Differences: Full Sun vs. Shade Gardens
Full sun gardens receive at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, promoting vigorous growth in sun-loving plants like tomatoes and sunflowers, while shade gardens thrive with less than four hours of light, favoring shade-tolerant species such as ferns and hostas. Sun exposure increases photosynthesis, resulting in higher energy production and vibrant blooms, whereas shade cover reduces light intensity, minimizing water evaporation and protecting plants from heat stress. Soil temperature also varies, with full sun areas warming quickly and encouraging faster root development, while shaded areas maintain cooler conditions conducive to moisture retention.
Plant Selection: Sun-Loving vs. Shade-Tolerant Species
Sun-loving plants such as tomatoes, lavender, and sunflowers require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily to thrive and produce optimal blooms or fruit. Shade-tolerant species like ferns, hostas, and impatiens adapt well to low-light conditions, often flourishing in areas with filtered or indirect sunlight. Selecting plant species based on their sunlight preferences ensures healthier growth, higher resistance to stress, and better overall garden productivity.
Benefits of Sun Exposure in Garden Health
Sun exposure plays a crucial role in garden health by enhancing photosynthesis, which fuels plant growth and improves flower and fruit production. Exposure to sunlight increases the synthesis of essential nutrients such as vitamins and antioxidants, boosting the resilience of plants against diseases and pests. Properly sunlit gardens also promote beneficial soil microorganisms that support nutrient cycling and root development, leading to overall healthier plant ecosystems.
Challenges of Growing in Full Shade
Growing plants in full shade presents significant challenges due to limited sunlight, which restricts photosynthesis and reduces energy production necessary for growth. Shade-tolerant species may survive but often exhibit slower development, weaker structures, and lower yields compared to those grown under adequate sun exposure. Ensuring proper moisture levels and selecting shade-adapted varieties are essential strategies to mitigate the negative effects of insufficient sunlight.
Maximizing Sunlight in Shady Yards
Maximizing sunlight in shady yards requires strategic pruning to thin tree branches and increase light penetration by up to 30%. Planting reflective surfaces like light-colored mulch or garden stones can boost sunlight availability by redirecting rays into shaded areas. Selecting sun-loving, shade-tolerant plants ensures optimal growth despite limited direct sun exposure.
How Shade Cover Impacts Growth and Bloom
Shade cover significantly influences plant growth and bloom by regulating the intensity and duration of sunlight exposure. Reduced sunlight under shade cover can limit photosynthesis, leading to slower growth rates and fewer flowers, especially in sun-loving species. However, shade can protect plants from excessive heat and UV damage, promoting healthier foliage and extending bloom periods in certain shade-tolerant varieties.
Balancing Sun and Shade for Optimal Garden Design
Balancing sun exposure and shade cover is crucial for optimal garden design, as different plants require varying light intensities to thrive. Incorporating both sunny and shaded areas ensures diverse plant health, improves soil moisture retention, and reduces heat stress on sensitive species. Strategic placement of trees, shrubs, and shade structures creates microclimates that maximize photosynthesis while protecting delicate foliage from excessive ultraviolet radiation.
Seasonal Changes in Sunlight: Planning Ahead
Seasonal changes in sunlight impact the duration and intensity of sun exposure, requiring strategic planning for both outdoor activities and shade cover. During winter, shorter daylight hours and lower sun angles reduce UV exposure, while summer brings longer, more intense sunlight necessitating enhanced shade and sun protection measures. Incorporating adjustable shade solutions such as retractable awnings or seasonal landscaping helps optimize comfort and skin safety throughout the year.
Common Mistakes in Managing Sun and Shade
Many people underestimate the harmful effects of prolonged sun exposure, ignoring the need for regular application of high-SPF sunscreen and protective clothing. Common mistakes include staying in direct sunlight during peak UV hours without adequate hydration or shade breaks, which increases the risk of sunburn and heat-related illnesses. Conversely, excessive reliance on shade without any sun exposure can lead to vitamin D deficiency, highlighting the importance of balanced sun and shade management for optimal health.
Sun exposure vs shade cover Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com