
Sun scald vs sunburn Illustration
Sun scald occurs when intense, direct sunlight damages the bark of trees, leading to cracking and tissue death, primarily affecting the plant's structural integrity. Sunburn affects both plants and humans, causing superficial skin or leaf damage due to excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure, resulting in redness, blistering, or leaf discoloration. Understanding the difference between sun scald and sunburn is essential for effective prevention and treatment, as sun scald targets woody tissues while sunburn impacts softer surfaces.
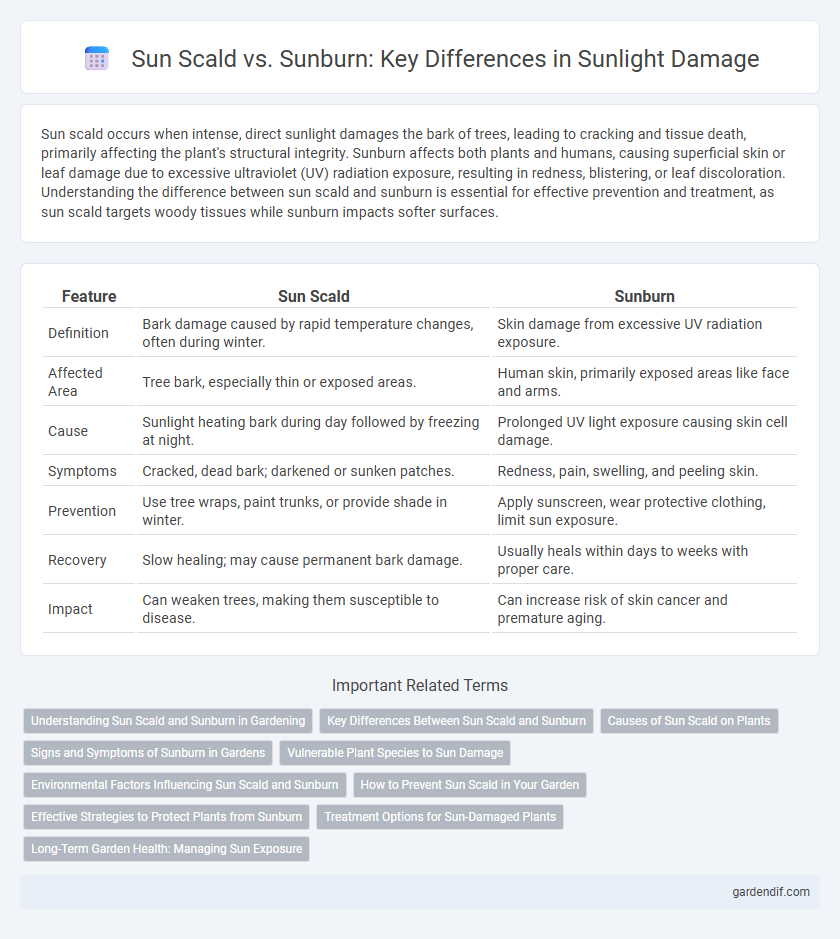
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sun Scald | Sunburn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bark damage caused by rapid temperature changes, often during winter. | Skin damage from excessive UV radiation exposure. |
| Affected Area | Tree bark, especially thin or exposed areas. | Human skin, primarily exposed areas like face and arms. |
| Cause | Sunlight heating bark during day followed by freezing at night. | Prolonged UV light exposure causing skin cell damage. |
| Symptoms | Cracked, dead bark; darkened or sunken patches. | Redness, pain, swelling, and peeling skin. |
| Prevention | Use tree wraps, paint trunks, or provide shade in winter. | Apply sunscreen, wear protective clothing, limit sun exposure. |
| Recovery | Slow healing; may cause permanent bark damage. | Usually heals within days to weeks with proper care. |
| Impact | Can weaken trees, making them susceptible to disease. | Can increase risk of skin cancer and premature aging. |
Understanding Sun Scald and Sunburn in Gardening
Sun scald in gardening occurs when plant tissues are damaged by sudden temperature fluctuations after exposure to intense sunlight, often causing bark cracks or sunken lesions on fruits. Sunburn, on the other hand, results from direct ultraviolet radiation damaging the plant's surface, leading to bleached or necrotic patches on leaves and fruit. Recognizing the differences between sun scald and sunburn helps gardeners implement targeted protective measures such as shade covers or reflective mulches to minimize crop damage.
Key Differences Between Sun Scald and Sunburn
Sun scald primarily affects plants, causing damage to bark and underlying tissues due to rapid temperature fluctuations and intense sunlight exposure, whereas sunburn refers to skin damage in humans caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Sun scald symptoms include splitting, discoloration, and cracking of plant bark, while sunburn manifests as redness, pain, and blistering of human skin. The key difference lies in the affected organism and the nature of damage--thermal and tissue injury in plants versus UV-induced skin inflammation in humans.
Causes of Sun Scald on Plants
Sun scald on plants primarily results from rapid temperature fluctuations, particularly when intense sunlight heats the bark during the day followed by sudden cooling at night, leading to cell damage. This condition often occurs on the south or southwest sides of trees, where exposure to winter sun is strongest. Unlike sunburn caused by ultraviolet radiation damaging leaf tissue, sun scald targets the bark, causing cracking and cankers that compromise plant health.
Signs and Symptoms of Sunburn in Gardens
Sunburn in gardens appears as reddish, inflamed leaves that may develop brown, dry, or crispy patches, especially on plants exposed to intense sunlight. Signs include leaf curling, wilting, and premature leaf drop, indicating cellular damage due to excessive UV radiation. These symptoms differ from sun scald, which typically manifests as white or pale areas on bark or stems caused by rapid temperature fluctuations.
Vulnerable Plant Species to Sun Damage
Sun scald primarily affects thin-barked trees such as maples, cherries, and apples, causing bark injury during rapid temperature fluctuations. Sunburn targets fruits like apples, grapes, and tomatoes, leading to tissue damage and reduced yield. Both sun scald and sunburn intensify under intense sunlight and drought conditions, making vulnerable species more susceptible.
Environmental Factors Influencing Sun Scald and Sunburn
Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and wind exposure significantly influence the occurrence of sun scald and sunburn in plants and skin. Rapid temperature changes combined with intense solar radiation can cause sun scald by damaging cell tissues, while prolonged UV exposure primarily leads to sunburn. Vegetation type, altitude, and local microclimates also play critical roles in the severity and frequency of these sun-related injuries.
How to Prevent Sun Scald in Your Garden
Sun scald occurs when intense sunlight damages plant bark or fruit, often during abrupt temperature changes, distinct from sunburn which affects skin or leaves. To prevent sun scald in your garden, apply protective wraps around tree trunks, use shading techniques such as shade cloths during peak sunlight hours, and maintain adequate soil moisture to reduce stress on plants. Planting sun-tolerant species and avoiding late-season pruning also helps minimize exposure and vulnerability to sun scald.
Effective Strategies to Protect Plants from Sunburn
Sun scald occurs when intense sunlight damages the bark or outer layer of plants, while sunburn affects leaves and fruit through excessive UV exposure. Effective strategies to protect plants from sunburn include applying shade cloths to reduce UV intensity, using anti-transpirant sprays to minimize moisture loss, and selecting plant varieties with natural sun tolerance. Mulching and maintaining optimal soil moisture also help mitigate heat stress and prevent sunburn damage.
Treatment Options for Sun-Damaged Plants
Treatment options for sun-damaged plants vary depending on whether the damage is sun scald or sunburn. Sun scald, caused by intense heat leading to bark damage, requires pruning of affected areas and application of protective wraps or tree guards to prevent further exposure. Sunburn, characterized by leaf scorch and tissue damage, benefits from shading, regular watering to reduce plant stress, and the use of anti-transpirants or foliar sprays that enhance UV protection.
Long-Term Garden Health: Managing Sun Exposure
Sun scald occurs when plant bark or fruit is exposed to intense sunlight, causing damaged tissues that can lead to cracking and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases, impacting long-term garden health. Sunburn primarily affects leaves and fruits, resulting in discolored, scorched spots that reduce photosynthesis and yield quality over time. Effective management of sun exposure through strategic planting, using shade cloths, and mulching is essential to protect plants from both sun scald and sunburn, ensuring sustained growth and productivity.
Sun scald vs sunburn Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com