
Sheet mulching vs Trench composting Illustration
Sheet mulching enhances soil fertility by layering organic materials directly on the soil surface, promoting moisture retention and weed suppression. Trench composting involves burying compostable materials underground, accelerating decomposition and enriching soil nutrients at root level. Both techniques improve soil health but differ in application depth and nutrient release timing.
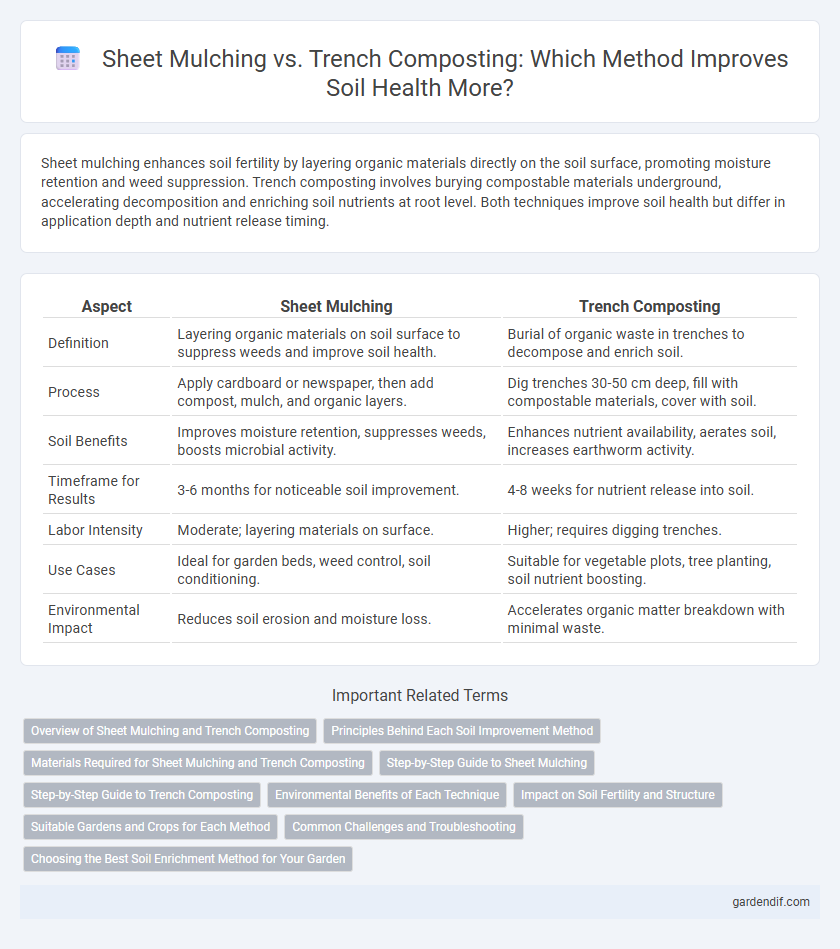
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sheet Mulching | Trench Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layering organic materials on soil surface to suppress weeds and improve soil health. | Burial of organic waste in trenches to decompose and enrich soil. |
| Process | Apply cardboard or newspaper, then add compost, mulch, and organic layers. | Dig trenches 30-50 cm deep, fill with compostable materials, cover with soil. |
| Soil Benefits | Improves moisture retention, suppresses weeds, boosts microbial activity. | Enhances nutrient availability, aerates soil, increases earthworm activity. |
| Timeframe for Results | 3-6 months for noticeable soil improvement. | 4-8 weeks for nutrient release into soil. |
| Labor Intensity | Moderate; layering materials on surface. | Higher; requires digging trenches. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for garden beds, weed control, soil conditioning. | Suitable for vegetable plots, tree planting, soil nutrient boosting. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces soil erosion and moisture loss. | Accelerates organic matter breakdown with minimal waste. |
Overview of Sheet Mulching and Trench Composting
Sheet mulching involves layering organic materials such as cardboard, mulch, and compost directly on the soil surface to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and improve soil fertility. Trench composting consists of digging a trench or hole, filling it with kitchen scraps and organic waste, and covering it with soil, allowing decomposition to occur underground and enhance nutrient availability. Both methods promote sustainable soil health by increasing organic matter and microbial activity, but sheet mulching primarily improves surface conditions while trench composting enriches subsurface layers.
Principles Behind Each Soil Improvement Method
Sheet mulching improves soil by layering organic materials like cardboard, mulch, and compost on the surface, which suppresses weeds, retains moisture, and promotes microbial activity through gradual decomposition. Trench composting involves burying organic waste directly into the soil, enhancing nutrient cycling by accelerating decomposition and integrating nutrients deeper into the root zone. Both methods optimize soil structure and fertility but differ in application depth and decomposition processes driving soil health improvement.
Materials Required for Sheet Mulching and Trench Composting
Sheet mulching requires layers of organic materials such as cardboard or newspaper, followed by compost, mulch, straw, and sometimes topsoil to create a nutrient-rich, weed-resistant barrier. Trench composting involves digging trenches filled with kitchen scraps, garden waste, and compostable materials that decompose directly in the soil, enriching it with minimal additional inputs. Both methods rely on organic matter but differ in material placement and decomposition dynamics to enhance soil fertility.
Step-by-Step Guide to Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching involves layering organic materials such as cardboard, compost, and mulch directly onto the soil surface to suppress weeds and enhance soil fertility. Begin by removing existing vegetation, then lay down a cardboard layer to block sunlight and decompose over time, followed by a thick application of compost and wood chips for moisture retention and nutrient supply. This method improves soil structure, promotes microbial activity, and reduces erosion compared to trench composting, which incorporates organic matter below ground.
Step-by-Step Guide to Trench Composting
Trench composting begins by digging a narrow trench about 12-18 inches deep where organic waste will decompose directly in the soil. Kitchen scraps and yard waste are layered into the trench, then covered with excavated soil to enhance microbial activity and nutrient absorption. This method improves soil fertility by slowly releasing nutrients, promoting healthy root growth and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Environmental Benefits of Each Technique
Sheet mulching enhances soil health by improving moisture retention, reducing erosion, and promoting beneficial microbial activity through layers of organic materials. Trench composting accelerates nutrient cycling and enriches soil fertility by directly incorporating decomposed organic matter into the subsoil, minimizing surface runoff and nutrient loss. Both techniques contribute to sustainable soil management, reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers and supporting carbon sequestration in agricultural ecosystems.
Impact on Soil Fertility and Structure
Sheet mulching enhances soil fertility by promoting organic matter accumulation and microbial activity, which improves nutrient availability and soil structure through layered decomposition. Trench composting accelerates nutrient cycling by directly incorporating compost into subsurface soil, boosting soil aeration and moisture retention while reducing erosion. Both methods enrich soil fertility and structure, but sheet mulching offers a surface-level, gradual improvement, whereas trench composting delivers deeper, more immediate nutrient integration.
Suitable Gardens and Crops for Each Method
Sheet mulching suits vegetable gardens and flower beds by improving soil structure and moisture retention, ideal for crops like tomatoes, lettuce, and herbs. Trench composting is better for larger gardens or orchards, supporting deep-rooted plants such as fruit trees and shrubs by enhancing nutrient availability directly to root zones. Both methods enrich soil fertility but target different plant root depths and garden scales for optimal growth.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Sheet mulching often faces challenges with uneven decomposition due to poor layering or insufficient moisture, leading to rodent attraction and weed growth. Trench composting can experience issues such as slow organic matter breakdown and soil disturbance if not properly aerated or if unsuitable materials are used. Both methods require careful material selection, moisture management, and monitoring to optimize nutrient cycling and prevent pest problems effectively.
Choosing the Best Soil Enrichment Method for Your Garden
Sheet mulching enhances soil fertility by layering organic materials directly on the garden surface, promoting moisture retention and weed suppression while improving microbial activity. Trench composting involves burying organic waste in deep soil trenches, accelerating decomposition and enriching soil nutrients at root level for robust plant growth. Selecting between these methods depends on garden size, soil condition, and desired nutrient delivery speed, with sheet mulching suited for surface improvement and trench composting ideal for deep soil nutrient infusion.
Sheet mulching vs Trench composting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com