
Sandy Soil vs Silt Soil Illustration
Sandy soil features large, coarse particles that promote excellent drainage but often lack nutrient retention, making it ideal for plants requiring well-aerated conditions. In contrast, silt soil contains finer particles that hold moisture and nutrients more effectively, enhancing fertility and supporting a wider range of crops. Understanding the differences in texture and water retention between sandy and silt soils is essential for optimizing plant growth and soil management practices.
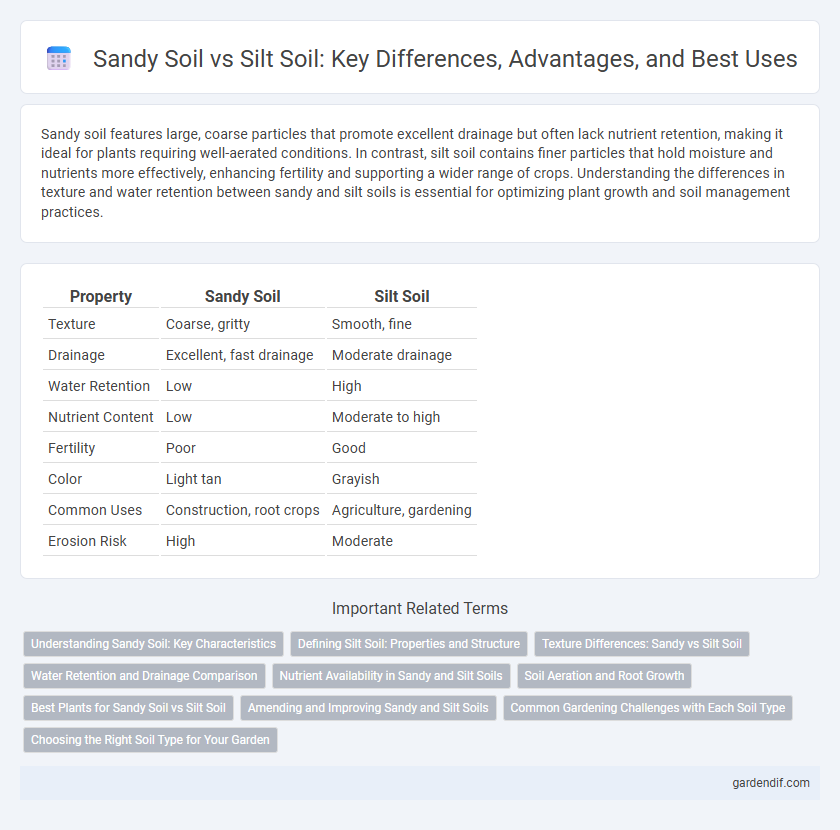
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandy Soil | Silt Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Coarse, gritty | Smooth, fine |
| Drainage | Excellent, fast drainage | Moderate drainage |
| Water Retention | Low | High |
| Nutrient Content | Low | Moderate to high |
| Fertility | Poor | Good |
| Color | Light tan | Grayish |
| Common Uses | Construction, root crops | Agriculture, gardening |
| Erosion Risk | High | Moderate |
Understanding Sandy Soil: Key Characteristics
Sandy soil features large, coarse particles that allow excellent drainage and aeration but result in low nutrient and water retention, making it less fertile compared to other soil types. Its gritty texture causes water to flow quickly, often requiring frequent irrigation to support plant growth. Sandy soil's high permeability makes it ideal for drought-resistant plants yet challenging for crops needing consistent moisture.
Defining Silt Soil: Properties and Structure
Silt soil is composed of fine particles smaller than sand but larger than clay, typically ranging from 0.002 to 0.05 millimeters in diameter, which gives it a smooth, flour-like texture. Its high water retention capacity and moderate drainage make it more fertile than sandy soil, supporting robust plant growth due to its nutrient-rich properties. Structurally, silt particles pack more tightly than sand, resulting in lower permeability and a higher likelihood of compaction, which can affect aeration and root penetration.
Texture Differences: Sandy vs Silt Soil
Sandy soil features large, coarse particles that create a gritty texture, allowing for excellent drainage but poor nutrient retention. In contrast, silt soil consists of finer, smooth particles that feel soft and floury, improving moisture retention and providing better fertility compared to sandy soil. The particle size distribution directly influences water holding capacity, aeration, and root penetration in these soil types.
Water Retention and Drainage Comparison
Sandy soil features large particles that create ample space for water to drain quickly, resulting in low water retention capacity, which can cause plants to dry out faster. In contrast, silt soil has smaller particles that hold water more effectively, providing moderate water retention while maintaining decent drainage to prevent waterlogging. Understanding these differences helps optimize irrigation practices and select appropriate crops for each soil type.
Nutrient Availability in Sandy and Silt Soils
Sandy soil has low nutrient availability due to its coarse texture and high drainage, which causes essential nutrients to leach away quickly. In contrast, silt soil retains more nutrients and moisture because of its finer particles and better water-holding capacity. This nutrient retention in silt soil promotes healthier plant growth and improved soil fertility compared to sandy soil.
Soil Aeration and Root Growth
Sandy soil offers excellent aeration due to its large particle size and loose texture, promoting healthy root growth by allowing oxygen to penetrate easily. In contrast, silt soil has smaller particles that retain moisture but can reduce soil aeration, potentially restricting root oxygen availability and slowing root development. Optimal plant growth requires balancing the high aeration of sandy soil with the moisture retention properties of silt soil.
Best Plants for Sandy Soil vs Silt Soil
Sandy soil, characterized by large particles and excellent drainage, supports plants like lavender, rosemary, and cactus that thrive in well-drained, nutrient-poor conditions. Silt soil, with finer particles and higher nutrient retention, is ideal for growing vegetables such as lettuce, spinach, and carrots, which require moisture and fertile soil. Selecting plants based on soil type improves growth, with sandy soil favoring drought-tolerant species and silty soil supporting moisture-loving crops.
Amending and Improving Sandy and Silt Soils
Amending sandy soil requires adding organic matter such as compost or peat moss to improve water retention and nutrient-holding capacity, while incorporating clay or silt particles enhances its structure. For silt soil, introducing coarse sand or organic materials helps increase drainage and aeration, preventing waterlogging and compaction. Both soil types benefit from mulching and regular addition of well-rotted manure to maintain fertility and improve soil texture effectively.
Common Gardening Challenges with Each Soil Type
Sandy soil drains quickly but struggles to retain nutrients, leading to frequent watering and fertilization needs that challenge gardeners. Silt soil retains moisture and nutrients better but tends to compact easily, causing poor aeration and root growth issues. Both soil types require tailored amendments: organic matter boosts nutrient retention in sandy soil, while regular tilling helps prevent silt soil compaction.
Choosing the Right Soil Type for Your Garden
Sandy soil offers excellent drainage and warms quickly in spring, making it ideal for plants that require well-aerated roots and dry conditions. Silt soil, richer in nutrients and better at retaining moisture, supports a wider variety of garden plants but may require improved drainage in wetter climates. Selecting between sandy and silt soil depends on your garden's plant types and local climate, ensuring optimal root health and growth.
Sandy Soil vs Silt Soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com