
Open-pollinated seeds vs Genetically modified seeds Illustration
Open-pollinated seeds allow plants to reproduce naturally, maintaining genetic diversity and enabling gardeners to save seeds for future planting without loss of traits. Genetically modified seeds are engineered for specific traits such as pest resistance or increased yield, but they often require purchasing new seeds each season due to patent restrictions. Farmers choosing open-pollinated seeds benefit from sustainability and seed sovereignty, while genetically modified seeds offer targeted enhancements at the cost of dependency on biotech companies.
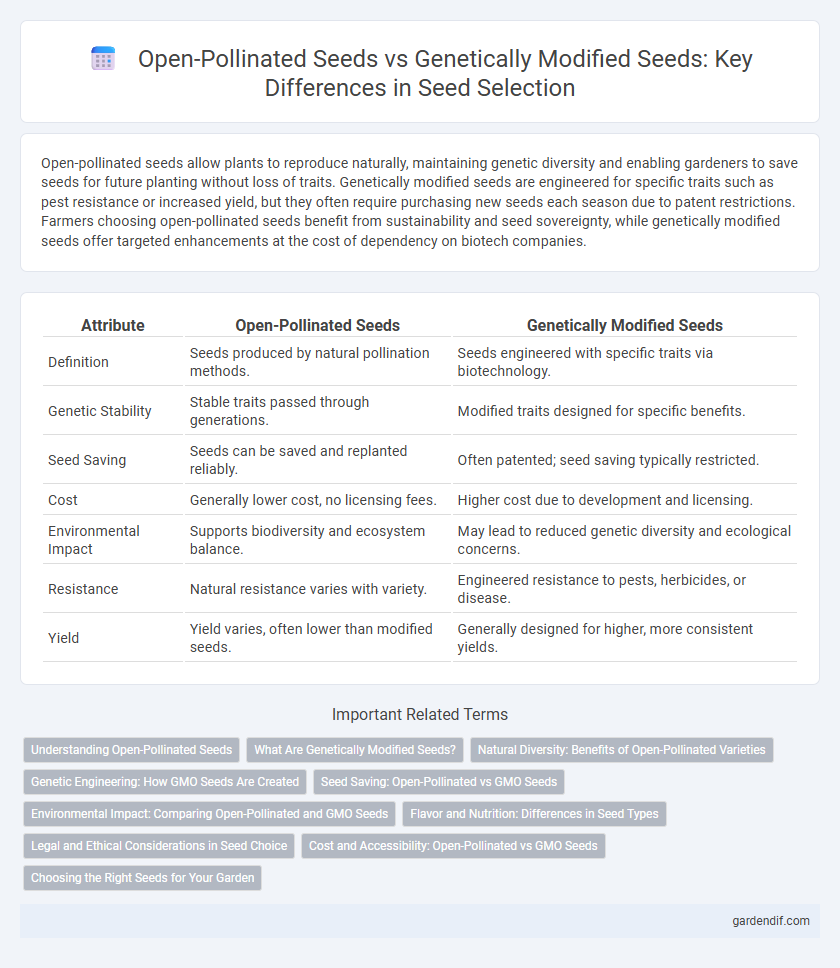
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Open-Pollinated Seeds | Genetically Modified Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seeds produced by natural pollination methods. | Seeds engineered with specific traits via biotechnology. |
| Genetic Stability | Stable traits passed through generations. | Modified traits designed for specific benefits. |
| Seed Saving | Seeds can be saved and replanted reliably. | Often patented; seed saving typically restricted. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, no licensing fees. | Higher cost due to development and licensing. |
| Environmental Impact | Supports biodiversity and ecosystem balance. | May lead to reduced genetic diversity and ecological concerns. |
| Resistance | Natural resistance varies with variety. | Engineered resistance to pests, herbicides, or disease. |
| Yield | Yield varies, often lower than modified seeds. | Generally designed for higher, more consistent yields. |
Understanding Open-Pollinated Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds are naturally pollinated by wind, insects, or birds, ensuring genetic diversity and stable traits passed down through generations. These seeds adapt well to local environments and allow farmers to save and replant seeds, preserving heirloom varieties and biodiversity. Unlike genetically modified seeds, open-pollinated seeds do not involve direct genetic manipulation, offering an organic, sustainable option for cultivation.
What Are Genetically Modified Seeds?
Genetically modified seeds are engineered through biotechnology to incorporate specific traits such as pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, or improved nutritional content. These seeds contain altered DNA sequences that enable plants to thrive under adverse conditions and increase crop yield. Unlike open-pollinated seeds, genetically modified seeds produce uniform offspring with targeted genetic enhancements designed for commercial agriculture.
Natural Diversity: Benefits of Open-Pollinated Varieties
Open-pollinated seeds preserve natural genetic diversity by allowing plants to cross-pollinate freely, which enhances resilience to environmental stresses and pests. This genetic variety supports sustainable agriculture by promoting soil health and reducing dependency on chemical inputs. Farmers and gardeners benefit from saving seeds that remain true to type, ensuring stable crop traits over generations without the need for costly re-purchasing.
Genetic Engineering: How GMO Seeds Are Created
Genetically modified organism (GMO) seeds are created through genetic engineering, a precise process that involves inserting specific genes from one organism into the DNA of a plant to introduce desired traits such as pest resistance or drought tolerance. This technique contrasts with open-pollinated seeds, which rely on natural pollination processes without direct manipulation of genetic material, preserving genetic diversity. Genetic engineering enables targeted modifications at the molecular level, resulting in crops with enhanced performance and predictable outcomes.
Seed Saving: Open-Pollinated vs GMO Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds allow gardeners to save and reuse seeds year after year, maintaining genetic diversity and seed viability. In contrast, genetically modified (GMO) seeds often contain terminator technology or patent protections preventing seed saving and requiring annual repurchase. Seed saving from open-pollinated varieties supports sustainable gardening practices and preserves heirloom strains, while GMO seeds prioritize uniformity and yield at the cost of seed sovereignty.
Environmental Impact: Comparing Open-Pollinated and GMO Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds promote biodiversity and support ecosystem resilience by maintaining genetic diversity, which reduces the risk of crop failure and pest outbreaks. GMO seeds often require higher inputs of herbicides and pesticides, potentially leading to soil degradation and harming non-target organisms such as pollinators and beneficial insects. The environmental footprint of open-pollinated seeds is generally lower, making them a more sustainable choice for preserving soil health and ecological balance.
Flavor and Nutrition: Differences in Seed Types
Open-pollinated seeds typically produce vegetables and fruits with richer, more complex flavors and higher nutritional content due to natural genetic diversity and traditional breeding methods. Genetically modified seeds are engineered for specific traits like pest resistance or increased yield but may sometimes sacrifice taste and nutrient density. Studies highlight that open-pollinated varieties often retain superior antioxidant levels and vitamins compared to many genetically modified counterparts.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Seed Choice
Open-pollinated seeds preserve genetic diversity and farmers' rights to save and reuse seeds, aligning with traditional agricultural practices and biodiversity conservation laws. Genetically modified (GM) seeds often involve patented technology, restricting seed saving and requiring legal agreements that impact farmers' autonomy and raise ethical concerns regarding corporate control over food systems. Regulatory frameworks vary globally, balancing innovation incentives with safeguarding environmental risks, food safety, and farmers' socioeconomic rights.
Cost and Accessibility: Open-Pollinated vs GMO Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds are generally more affordable and widely accessible to small-scale farmers and home gardeners due to local availability and the ability to save seeds for future planting, reducing ongoing costs. Genetically modified (GMO) seeds tend to have higher upfront costs and often require purchase each season due to licensing restrictions and intellectual property protections. The cost-effectiveness and accessibility of open-pollinated seeds make them a preferred choice for sustainable agriculture in resource-limited settings.
Choosing the Right Seeds for Your Garden
Open-pollinated seeds preserve genetic diversity and produce plants true to type, making them ideal for gardeners seeking natural adaptation and seed saving. Genetically modified seeds offer enhanced traits such as pest resistance or herbicide tolerance, often resulting in higher yields and reduced chemical use. Selecting the right seeds depends on your gardening goals, environmental conditions, and preference for sustainability versus engineered crop performance.
Open-pollinated seeds vs Genetically modified seeds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com