
F1 Hybrid Seeds vs F2 Generation Seeds Illustration
F1 hybrid seeds are produced by cross-breeding two genetically distinct parent plants, resulting in offspring with uniform traits such as enhanced vigor, disease resistance, and higher yields. In contrast, F2 generation seeds come from self-pollinating F1 hybrids, leading to genetic variability and a mixture of characteristics that may not consistently express the desired qualities. Gardeners and farmers often prefer F1 hybrids for reliable performance, while F2 seeds are suitable for seed saving and breeding new plant varieties.
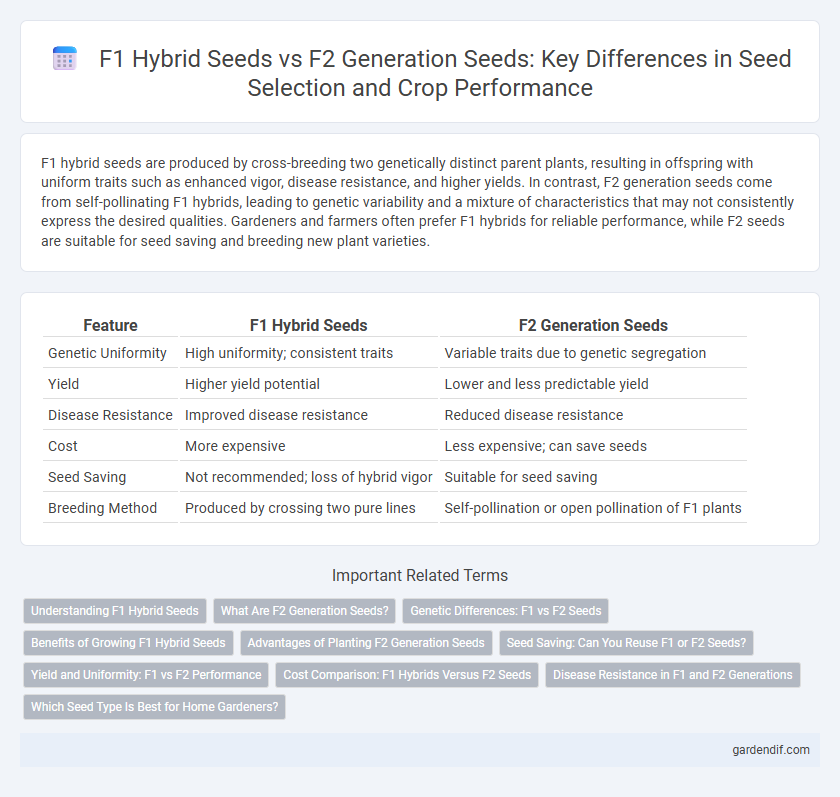
Table of Comparison
| Feature | F1 Hybrid Seeds | F2 Generation Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Uniformity | High uniformity; consistent traits | Variable traits due to genetic segregation |
| Yield | Higher yield potential | Lower and less predictable yield |
| Disease Resistance | Improved disease resistance | Reduced disease resistance |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive; can save seeds |
| Seed Saving | Not recommended; loss of hybrid vigor | Suitable for seed saving |
| Breeding Method | Produced by crossing two pure lines | Self-pollination or open pollination of F1 plants |
Understanding F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds result from the controlled cross-pollination of two distinct, genetically stable parent lines, producing offspring with enhanced vigor, uniformity, and yield known as hybrid vigor or heterosis. These seeds deliver consistent traits such as disease resistance, growth rate, and fruit quality, making them highly preferred for commercial agriculture. However, seeds saved from F1 hybrids, called F2 generation seeds, exhibit genetic segregation, leading to variability in plant characteristics and reduced uniformity.
What Are F2 Generation Seeds?
F2 generation seeds result from self-pollinating or crossing plants grown from F1 hybrid seeds, inheriting a more diverse genetic mix and exhibiting greater variation in traits. Unlike uniform F1 hybrids, F2 seeds produce plants with unpredictable characteristics, which may include reduced vigor and inconsistent fruit quality. This genetic segregation can impact crop performance, making F2 seeds less reliable for commercial farming but valuable for plant breeding and seed saving.
Genetic Differences: F1 vs F2 Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds result from the controlled cross-pollination of two genetically distinct parent lines, exhibiting uniformity and hybrid vigor due to heterozygosity. F2 generation seeds come from self-pollination or interbreeding of F1 plants, displaying genetic segregation and increased variability in traits because of gene recombination and allele segregation. The genetic differences influence seed performance, with F1 hybrids offering consistency and F2 seeds showing diverse phenotypes.
Benefits of Growing F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds deliver uniformity, vigor, and higher yields due to their controlled crossbreeding, resulting in plants with enhanced disease resistance and improved tolerance to environmental stress. These seeds produce consistent crops with predictable traits, which is essential for commercial farming and gardeners seeking reliable performance. Growing F1 hybrids maximizes productivity and often reduces the need for chemical inputs, promoting sustainable cultivation practices.
Advantages of Planting F2 Generation Seeds
F2 generation seeds offer cost savings and greater seed availability compared to F1 hybrid seeds, making them ideal for budget-conscious growers. These seeds provide genetic diversity, which can enhance plant resilience against pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. Growing F2 seeds allows farmers to select and propagate traits best suited to their local conditions, supporting long-term sustainability and crop adaptation.
Seed Saving: Can You Reuse F1 or F2 Seeds?
F1 hybrid seeds produce uniform, high-yield crops but saving and reusing their seeds often leads to unpredictable traits in the F2 generation due to genetic segregation. F2 generation seeds, derived from F1 hybrids, exhibit greater genetic variability and reduced vigor, making them less reliable for consistent crop performance. For optimal seed saving and maintaining desired plant characteristics, gardeners and farmers typically prefer to purchase new F1 hybrid seeds instead of reusing F1 or F2 seeds.
Yield and Uniformity: F1 vs F2 Performance
F1 hybrid seeds deliver higher yield and greater uniformity due to their controlled, stable genetics, ensuring consistent plant vigor and productivity. F2 generation seeds exhibit more genetic variability, resulting in reduced yield potential and increased variation in plant traits. Farmers seeking reliable crop performance and uniform harvest should prefer F1 hybrids over F2 seeds for optimal results.
Cost Comparison: F1 Hybrids Versus F2 Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds typically cost more than F2 generation seeds due to the advanced breeding techniques required to produce uniform and high-yielding plants. F2 seeds, derived from self-pollinating F1 hybrids, are cheaper but often display genetic variability, resulting in inconsistent crop quality and lower yields. Investing in F1 hybrids can lead to higher upfront expenses but may offer better economic returns through improved plant vigor and productivity compared to the lower-cost, less predictable F2 seeds.
Disease Resistance in F1 and F2 Generations
F1 hybrid seeds exhibit strong disease resistance due to their uniform genetic makeup, resulting from controlled crossbreeding of two distinct parent lines. In contrast, F2 generation seeds often show reduced disease resistance as genetic segregation occurs, leading to variability and potential loss of hybrid vigor. Farmers seeking consistent protection against pathogens generally prefer F1 hybrids for their reliable resistance traits.
Which Seed Type Is Best for Home Gardeners?
F1 hybrid seeds offer uniformity, vigor, and disease resistance, making them ideal for home gardeners seeking consistent, high-quality crops. F2 generation seeds, derived from self-pollinating F1 plants, exhibit greater genetic variability, which may result in unpredictable traits and lower yields. For home gardeners prioritizing reliability and performance, F1 hybrid seeds are generally the best choice.
F1 Hybrid Seeds vs F2 Generation Seeds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com