
Seed coating vs Seed priming Illustration
Seed coating enhances seed protection by applying a physical layer that improves handling, disease resistance, and nutrient delivery, while seed priming activates metabolic processes to accelerate germination and improve seedling vigor. Unlike seed priming, which involves soaking seeds to initiate early growth stages before planting, seed coating does not alter seed metabolism but optimizes the seed's environment for better germination conditions. Choosing between seed coating and seed priming depends on specific crop needs, environmental conditions, and desired outcomes in crop establishment.
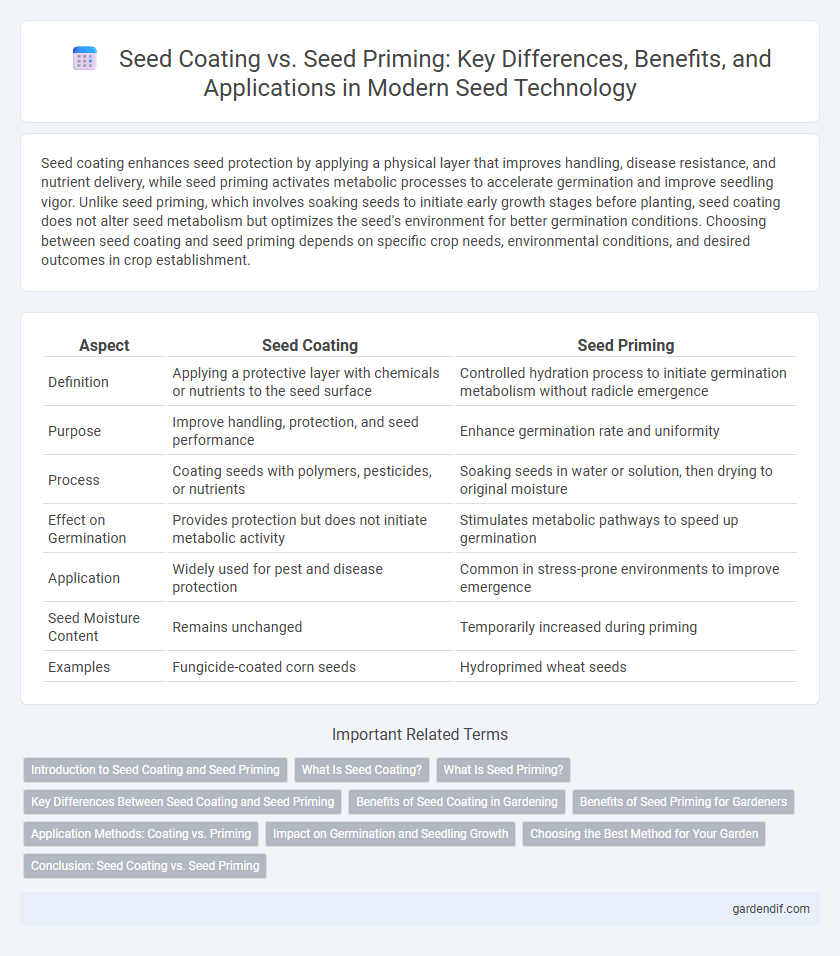
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Seed Coating | Seed Priming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying a protective layer with chemicals or nutrients to the seed surface | Controlled hydration process to initiate germination metabolism without radicle emergence |
| Purpose | Improve handling, protection, and seed performance | Enhance germination rate and uniformity |
| Process | Coating seeds with polymers, pesticides, or nutrients | Soaking seeds in water or solution, then drying to original moisture |
| Effect on Germination | Provides protection but does not initiate metabolic activity | Stimulates metabolic pathways to speed up germination |
| Application | Widely used for pest and disease protection | Common in stress-prone environments to improve emergence |
| Seed Moisture Content | Remains unchanged | Temporarily increased during priming |
| Examples | Fungicide-coated corn seeds | Hydroprimed wheat seeds |
Introduction to Seed Coating and Seed Priming
Seed coating enhances seed performance by applying a protective layer containing nutrients, pesticides, or growth stimulants, improving handling, sowing precision, and early seedling vigor. Seed priming involves controlled hydration of seeds to initiate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, leading to faster germination and uniform seedling emergence. Both techniques optimize seed quality and crop establishment but target different physiological aspects of seed preparation.
What Is Seed Coating?
Seed coating involves applying a protective layer of materials such as polymers, nutrients, or pesticides to the exterior of seeds, enhancing sowing efficiency and seedling protection. This technique improves seed handling, uniformity, and resistance to pests and diseases during germination and early growth stages. Unlike seed priming, which involves pre-soaking seeds to trigger metabolic processes, seed coating primarily serves as a physical barrier to optimize seed performance and agricultural productivity.
What Is Seed Priming?
Seed priming is a pre-sowing treatment that involves partial hydration of seeds to initiate metabolic processes without allowing radicle emergence, enhancing germination rate and uniformity. This technique improves seed vigor by activating enzymes, repairing cellular damage, and increasing resistance to environmental stresses during early growth stages. Unlike seed coating, which adds physical or chemical layers to seeds for protection or nutrient delivery, seed priming directly boosts physiological improvements within the seed.
Key Differences Between Seed Coating and Seed Priming
Seed coating involves applying a physical layer of protective materials, such as polymers, nutrients, or pesticides, to the seed surface to enhance handling, protect against pests, and improve sowing precision. Seed priming, on the other hand, is a pre-sowing treatment that partially hydrates seeds to initiate metabolic processes without radical emergence, promoting faster and uniform germination. Key differences include seed coating's focus on external protection and seed handling improvement, whereas seed priming primarily targets physiological seed activation for enhanced germination performance.
Benefits of Seed Coating in Gardening
Seed coating enhances germination rates by providing a protective barrier against pests, diseases, and environmental stress, improving seedling vigor in gardening. It allows precise application of nutrients and growth stimulants directly to the seed, boosting early plant development and uniformity. This method also facilitates easier seed handling and sowing, resulting in more efficient garden management and higher crop yields.
Benefits of Seed Priming for Gardeners
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity, resulting in more consistent seedling emergence and healthier plant development. It improves stress tolerance against drought and temperature fluctuations, increasing the chances of successful growth in varying garden conditions. Gardeners benefit from higher seedling vigor and reduced seed wastage, leading to more efficient planting and better crop yields.
Application Methods: Coating vs. Priming
Seed coating involves applying a protective layer of polymers, nutrients, or pesticides directly onto the seed surface, enhancing handling, disease resistance, and controlled release of active ingredients. Seed priming, by contrast, entails partial hydration of seeds to initiate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, improving germination speed and uniformity under stressed conditions. Coating methods prioritize physical protection and delivery of beneficial agents, while priming focuses on physiological activation to boost seed vigor before sowing.
Impact on Germination and Seedling Growth
Seed coating enhances germination by providing physical protection and incorporating fungicides or nutrients that improve seedling vigor, while seed priming accelerates metabolic processes within the seed, leading to faster and more uniform germination. Seed priming significantly improves early seedling growth by optimizing water uptake and enzyme activation, which promotes robust root and shoot development. Unlike seed coating, priming directly influences the physiological state of the seed, resulting in higher germination rates and improved establishment under stress conditions.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Garden
Seed coating enhances germination by applying protective layers infused with nutrients, pesticides, or growth regulators, improving seed handling and disease resistance. Seed priming involves controlled seed hydration to initiate metabolic processes before planting, resulting in faster and more uniform sprouting, especially advantageous for crops in challenging soil conditions. Selecting the best method depends on garden goals: seed coating suits long-term protection and pest management, while priming optimizes germination speed and seedling vigor.
Conclusion: Seed Coating vs. Seed Priming
Seed coating enhances seed protection against pests and improves handling but may delay germination compared to seed priming, which accelerates germination and seedling vigor by pre-hydrating seeds. Seed priming is more effective for stress tolerance and faster crop establishment, while seed coating offers benefits in nutrient delivery and seed preservation. Choosing between seed coating and seed priming depends on specific crop requirements, environmental conditions, and desired outcomes in agricultural productivity.
Seed coating vs Seed priming Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com