
Primed seeds vs Unprimed seeds Illustration
Primed seeds undergo a controlled hydration process that accelerates germination and improves uniformity compared to unprimed seeds, which germinate more slowly and irregularly. Priming enhances seed vigor, resulting in stronger seedlings and higher crop yields, especially under stress conditions. Choosing primed seeds optimizes growth potential and ensures more reliable field establishment.
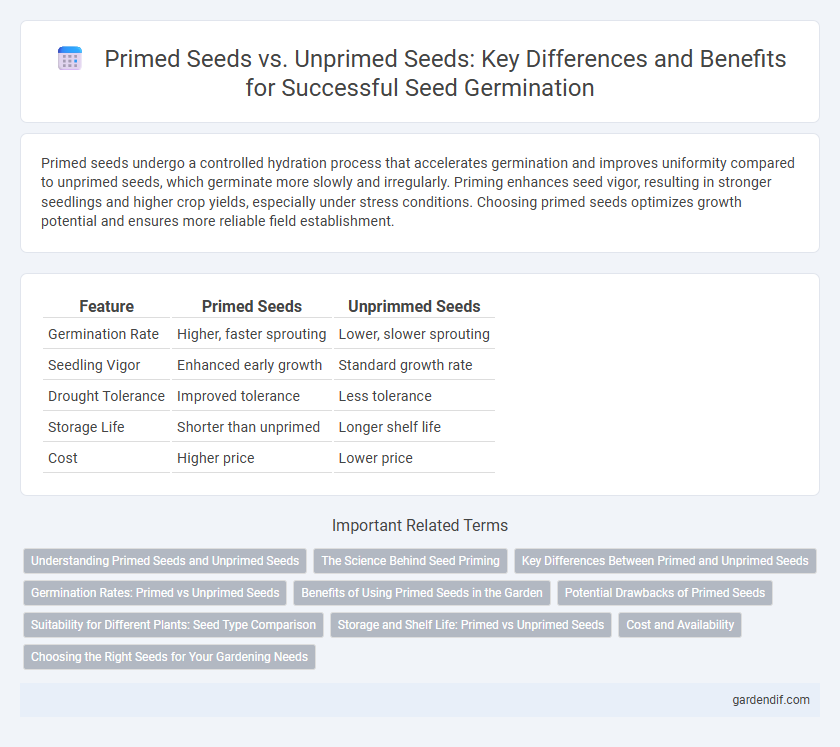
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Primed Seeds | Unprimmed Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Germination Rate | Higher, faster sprouting | Lower, slower sprouting |
| Seedling Vigor | Enhanced early growth | Standard growth rate |
| Drought Tolerance | Improved tolerance | Less tolerance |
| Storage Life | Shorter than unprimed | Longer shelf life |
| Cost | Higher price | Lower price |
Understanding Primed Seeds and Unprimed Seeds
Primed seeds undergo a controlled hydration process to initiate germination, resulting in faster and more uniform seedling emergence compared to unprimed seeds, which are in their natural, dormant state. This priming technique improves seed vigor, enhances stress tolerance, and can significantly boost crop yield under suboptimal growing conditions. Understanding the differences helps farmers select the appropriate seed type for optimized planting schedules and improved agricultural productivity.
The Science Behind Seed Priming
Seed priming enhances germination by initiating metabolic processes before sowing, leading to faster and more uniform seedling emergence. This controlled hydration activates enzymes that repair DNA, synthesize proteins, and mobilize stored nutrients without allowing radicle protrusion. Scientific studies demonstrate primed seeds exhibit improved stress tolerance and higher vigor due to optimized cellular repair and metabolism during early germination stages.
Key Differences Between Primed and Unprimed Seeds
Primed seeds undergo a controlled hydration process to initiate germination, resulting in faster and more uniform seedling emergence compared to unprimed seeds, which lack pre-germination treatment. Priming enhances seed vigor, improves stress tolerance, and increases germination rates, whereas unprimed seeds typically exhibit slower germination and variable seedling growth. Seed priming techniques include hydropriming, osmopriming, and biopriming, all aimed at improving early seedling establishment in agricultural production.
Germination Rates: Primed vs Unprimed Seeds
Primed seeds exhibit significantly higher germination rates compared to unprimed seeds due to enhanced metabolic readiness and improved water uptake. Studies show primed seeds can achieve germination rates exceeding 90%, while unprimed seeds often fall below 70%, particularly in suboptimal environmental conditions. This increased vigor reduces the time needed for seedling emergence, optimizing overall crop establishment and yield potential.
Benefits of Using Primed Seeds in the Garden
Primed seeds deliver accelerated germination and uniform seedling emergence, enhancing overall crop establishment. These seeds improve stress tolerance against drought and temperature fluctuations, resulting in higher survival rates. Using primed seeds boosts garden productivity by promoting faster growth cycles and stronger, healthier plants.
Potential Drawbacks of Primed Seeds
Primed seeds often face a shorter shelf life compared to unprimed seeds due to their enhanced metabolic activity, which accelerates aging and reduces storability. The increased moisture content during priming can elevate the risk of fungal infections, negatively impacting seed health and germination rates. Moreover, improper priming protocols may cause uneven seed treatment, leading to variability in seedling vigor and crop stand uniformity.
Suitability for Different Plants: Seed Type Comparison
Primed seeds exhibit enhanced germination rates and uniformity, making them ideal for fast-growing vegetables like lettuce and carrots, which benefit from precise planting schedules. Unprimed seeds, retaining their natural dormancy, suit plants with longer germination periods such as beans and peas that thrive in varied environmental conditions. Selecting seed type according to plant species ensures optimal growth performance and resource efficiency in agriculture and gardening.
Storage and Shelf Life: Primed vs Unprimed Seeds
Primed seeds have a shorter shelf life compared to unprimed seeds due to their increased metabolic activity, which accelerates aging during storage. Unprimed seeds maintain dormancy longer and exhibit greater longevity under proper storage conditions, typically cool and dry environments. Optimal storage for primed seeds requires stricter moisture and temperature controls to preserve viability and germination rates.
Cost and Availability
Primed seeds undergo pre-germination treatments that enhance germination speed and uniformity, but they typically cost more due to specialized processing. Unprimed seeds are generally more affordable and widely available in bulk, making them suitable for large-scale planting where cost efficiency is crucial. Availability of primed seeds may be limited depending on the crop type and supplier, while unprimed seeds remain the standard choice for most farmers seeking cost-effective solutions.
Choosing the Right Seeds for Your Gardening Needs
Primed seeds undergo a controlled hydration process to accelerate germination and ensure uniform sprouting, making them ideal for gardeners seeking faster crop establishment. Unprimed seeds remain dry and require natural moisture to initiate growth, offering longer shelf life and greater flexibility for varying planting schedules. Selecting primed or unprimed seeds depends on your climate, planting timeline, and specific crop requirements to optimize garden productivity.
Primed seeds vs Unprimed seeds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com