
Perlite amendment vs Vermiculite amendment Illustration
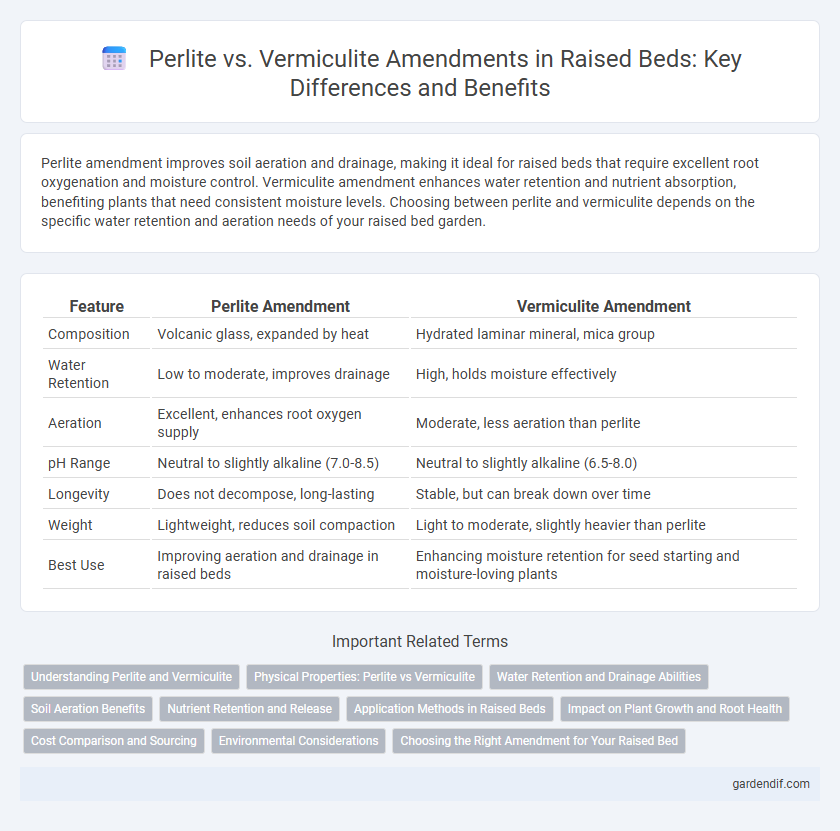
Perlite amendment improves soil aeration and drainage, making it ideal for raised beds that require excellent root oxygenation and moisture control. Vermiculite amendment enhances water retention and nutrient absorption, benefiting plants that need consistent moisture levels. Choosing between perlite and vermiculite depends on the specific water retention and aeration needs of your raised bed garden.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Perlite Amendment | Vermiculite Amendment |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Volcanic glass, expanded by heat | Hydrated laminar mineral, mica group |
| Water Retention | Low to moderate, improves drainage | High, holds moisture effectively |
| Aeration | Excellent, enhances root oxygen supply | Moderate, less aeration than perlite |
| pH Range | Neutral to slightly alkaline (7.0-8.5) | Neutral to slightly alkaline (6.5-8.0) |
| Longevity | Does not decompose, long-lasting | Stable, but can break down over time |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces soil compaction | Light to moderate, slightly heavier than perlite |
| Best Use | Improving aeration and drainage in raised beds | Enhancing moisture retention for seed starting and moisture-loving plants |
Understanding Perlite and Vermiculite
Perlite is a volcanic glass that expands when heated, providing excellent aeration and drainage in raised bed soil, which helps prevent root rot and promotes healthy plant growth. Vermiculite, a hydrated laminar magnesium-aluminum-iron silicate mineral, enhances moisture retention and nutrient exchange by absorbing and slowly releasing water and nutrients to plant roots. Understanding the distinct roles of perlite and vermiculite allows gardeners to amend raised bed soil effectively based on the specific water retention and aeration needs of their plants.
Physical Properties: Perlite vs Vermiculite
Perlite exhibits a lightweight, porous structure that enhances soil aeration and drainage, preventing waterlogging in raised beds. Vermiculite holds moisture effectively due to its spongy, layered composition, promoting water retention and nutrient absorption. The choice between perlite and vermiculite depends on balancing soil drainage needs versus moisture retention for optimal plant growth.
Water Retention and Drainage Abilities
Perlite amendment enhances raised bed soil drainage by creating air pockets that prevent waterlogging, making it ideal for plants requiring well-drained conditions. Vermiculite amendment significantly improves water retention due to its high moisture-holding capacity, providing consistent hydration for moisture-loving plants. Balancing perlite and vermiculite in raised beds optimizes both drainage and moisture retention, promoting healthy root development.
Soil Aeration Benefits
Perlite amendment enhances soil aeration in raised beds by creating larger air spaces, improving oxygen availability to plant roots and promoting healthy root development. Vermiculite amendment retains moisture but provides less air circulation compared to perlite, which can lead to denser soil conditions. Optimal soil aeration achieved with perlite supports beneficial microbial activity and prevents root rot in raised bed gardening.
Nutrient Retention and Release
Perlite amendment in raised beds enhances soil aeration and drainage but has limited nutrient retention capacity, making it ideal for plants requiring fast-draining substrates. Vermiculite amendment significantly improves nutrient retention and moisture holding, gradually releasing nutrients to plants over time and supporting steady growth. Choosing vermiculite is beneficial for nutrient-demanding crops, while perlite suits plants needing quick drainage and less nutrient hold.
Application Methods in Raised Beds
Perlite amendment in raised beds is applied by mixing it thoroughly into the soil to enhance aeration and drainage, usually at a ratio of 10-20% by volume. Vermiculite amendment is incorporated similarly but focuses more on moisture retention and nutrient holding capacity, often mixed at about 5-10% with the soil. Both application methods involve blending these amendments into the top 6-12 inches of raised bed soil to optimize root health and plant growth.
Impact on Plant Growth and Root Health
Perlite amendment in raised beds enhances aeration and drainage, promoting strong root development and preventing root rot by reducing water retention. Vermiculite amendment improves moisture retention and nutrient absorption, supporting consistent hydration and nutrient availability for healthy plant growth. Selecting between perlite and vermiculite depends on the specific crop's water needs and soil conditions to optimize root health and overall plant vigor.
Cost Comparison and Sourcing
Perlite is generally more affordable than vermiculite, making it a cost-effective choice for raised bed soil amendments, with prices often ranging between $10 to $20 per cubic foot compared to vermiculite's $15 to $30. Perlite is widely sourced from volcanic glass deposits, primarily in the United States and Greece, whereas vermiculite is mined from expanded mica deposits, with major suppliers including South Africa and the United States. The availability and lower cost of perlite contribute to its popularity for improving aeration and drainage in raised bed gardening.
Environmental Considerations
Perlite amendment in raised beds enhances aeration and drainage while being an inert, non-toxic volcanic glass, posing minimal environmental risks and offering long-term stability without chemical leaching. Vermiculite amendment improves moisture retention and nutrient exchange by expanding into a lightweight mineral, but its mining and processing have a higher environmental footprint due to energy use and potential dust emissions. Choosing perlite supports sustainable gardening practices by conserving water and reducing soil compaction, whereas vermiculite's environmental impact necessitates mindful sourcing and usage to mitigate ecological effects.
Choosing the Right Amendment for Your Raised Bed
Perlite amendment enhances soil aeration and drainage, making it ideal for raised beds requiring quick water dispersion and root oxygenation. Vermiculite amendment retains moisture and nutrients effectively, benefiting plants that thrive in consistently moist conditions. Choosing the right amendment depends on plant type and soil moisture needs, with perlite best for succulents and vermiculite for moisture-loving vegetables.
Perlite amendment vs Vermiculite amendment Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com