
Soil Mix vs Native Soil Illustration
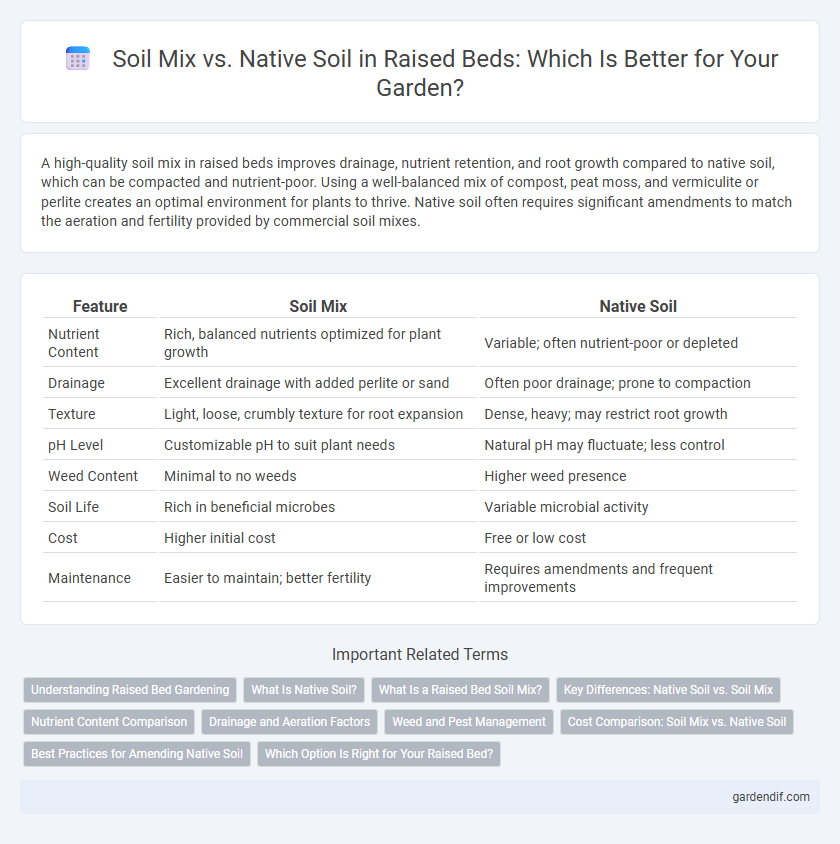
A high-quality soil mix in raised beds improves drainage, nutrient retention, and root growth compared to native soil, which can be compacted and nutrient-poor. Using a well-balanced mix of compost, peat moss, and vermiculite or perlite creates an optimal environment for plants to thrive. Native soil often requires significant amendments to match the aeration and fertility provided by commercial soil mixes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soil Mix | Native Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Content | Rich, balanced nutrients optimized for plant growth | Variable; often nutrient-poor or depleted |
| Drainage | Excellent drainage with added perlite or sand | Often poor drainage; prone to compaction |
| Texture | Light, loose, crumbly texture for root expansion | Dense, heavy; may restrict root growth |
| pH Level | Customizable pH to suit plant needs | Natural pH may fluctuate; less control |
| Weed Content | Minimal to no weeds | Higher weed presence |
| Soil Life | Rich in beneficial microbes | Variable microbial activity |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Free or low cost |
| Maintenance | Easier to maintain; better fertility | Requires amendments and frequent improvements |
Understanding Raised Bed Gardening
Raised bed gardening benefits from using a soil mix tailored for drainage, nutrient retention, and root growth, unlike native soil which often lacks these optimized qualities. A well-balanced soil mix typically includes components such as compost, peat moss, and vermiculite to enhance aeration and moisture control. Choosing the right soil mix over native soil promotes healthier plants and higher yields in raised bed systems.
What Is Native Soil?
Native soil refers to the existing ground earth present at a specific location, composed of natural minerals, organic matter, and microorganisms unique to the local environment. It typically varies in texture, fertility, and drainage properties depending on regional conditions, often requiring amendment for optimal plant growth in raised beds. Understanding native soil characteristics helps gardeners decide whether to enhance it or replace it with a specialized soil mix for raised bed gardening.
What Is a Raised Bed Soil Mix?
A raised bed soil mix is a specially formulated blend designed to provide optimal drainage, aeration, and nutrient availability for plants, differing significantly from native soil which can be compacted and nutrient-poor. Common components of raised bed mixes include compost, peat moss or coconut coir, and vermiculite or perlite, creating a lightweight, fertile medium tailored for vigorous root growth. This mix ensures better moisture retention and root penetration compared to native soil, promoting healthier, more productive plant growth in garden beds.
Key Differences: Native Soil vs. Soil Mix
Soil mix in raised beds offers superior drainage, aeration, and nutrient balance compared to native soil, which can be dense, compacted, and low in organic matter. Unlike native soil, soil mix typically includes compost, peat moss, and vermiculite or perlite, promoting healthier root development and higher yields. Native soil may contain pests and weeds, whereas soil mix provides a clean, controlled environment for optimal plant growth.
Nutrient Content Comparison
Raised bed soil mixes typically contain a balanced blend of organic matter, compost, and aeration materials, resulting in higher nutrient content and better retention compared to native soil. Native soil often lacks the rich organic components and may have poor structure, leading to lower fertility and nutrient availability for plants. Optimized soil mixes enhance nutrient delivery and root health, promoting greater plant growth in raised beds.
Drainage and Aeration Factors
Soil mix in raised beds typically offers superior drainage and aeration compared to native soil, promoting healthier root development and reducing waterlogging risks. Engineered blends often include components like peat moss, perlite, and compost, which enhance pore space and oxygen availability essential for microbial activity. Native soil may retain excess moisture and compact easily, limiting air circulation and negatively impacting plant growth.
Weed and Pest Management
Using a high-quality soil mix in raised beds significantly reduces weed infestation compared to native soil, as it is typically free from weed seeds and pathogens. Soil mixes with good drainage and nutrient content create an environment less favorable for pests, minimizing the need for chemical interventions. Native soil often harbors weed seeds and pest eggs, increasing the risk of infestations and complicating effective weed and pest management in raised bed gardening.
Cost Comparison: Soil Mix vs. Native Soil
Using native soil for raised beds significantly reduces upfront costs compared to purchasing a soil mix, as it eliminates the need to buy and transport large volumes of compost, peat moss, and other amendments. Soil mixes, while more expensive per cubic foot, provide optimized drainage and nutrient content that can enhance plant growth, potentially reducing expenses related to fertilizers and pest control over time. Evaluating local soil quality and amendment costs helps determine the most cost-effective option for sustainable raised bed gardening.
Best Practices for Amending Native Soil
Amending native soil for raised beds involves integrating organic matter such as compost, aged manure, and peat moss to enhance fertility and structure. Incorporating balanced proportions of sand and perlite improves aeration and drainage, preventing root rot and compaction. Regular soil testing guides nutrient adjustments, ensuring optimal pH and nutrient levels for healthy plant growth.
Which Option Is Right for Your Raised Bed?
Choosing between soil mix and native soil for your raised bed depends on factors like drainage, fertility, and local soil quality. Soil mix typically offers superior aeration, nutrient content, and water retention, promoting healthier plant growth compared to dense or clay-heavy native soil. Assess your native soil's composition and consider a custom soil mix blend tailored to your plants' needs for optimal results in raised bed gardening.
Soil Mix vs Native Soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com