
Sided raised beds vs open-bottom beds Illustration
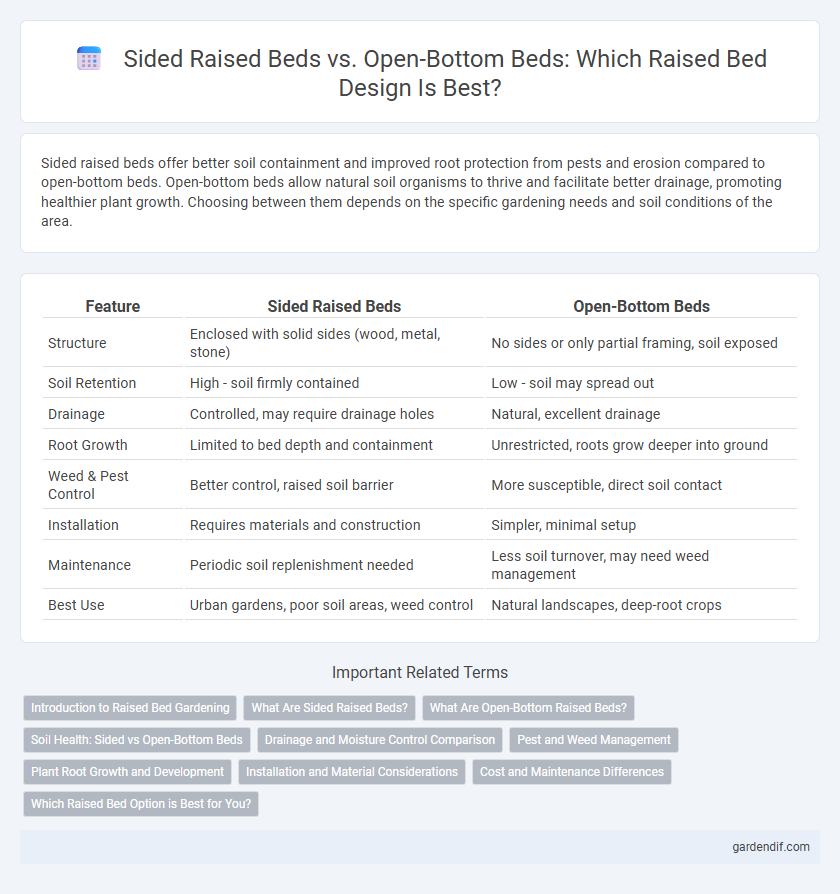
Sided raised beds offer better soil containment and improved root protection from pests and erosion compared to open-bottom beds. Open-bottom beds allow natural soil organisms to thrive and facilitate better drainage, promoting healthier plant growth. Choosing between them depends on the specific gardening needs and soil conditions of the area.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sided Raised Beds | Open-Bottom Beds |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Enclosed with solid sides (wood, metal, stone) | No sides or only partial framing, soil exposed |
| Soil Retention | High - soil firmly contained | Low - soil may spread out |
| Drainage | Controlled, may require drainage holes | Natural, excellent drainage |
| Root Growth | Limited to bed depth and containment | Unrestricted, roots grow deeper into ground |
| Weed & Pest Control | Better control, raised soil barrier | More susceptible, direct soil contact |
| Installation | Requires materials and construction | Simpler, minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Periodic soil replenishment needed | Less soil turnover, may need weed management |
| Best Use | Urban gardens, poor soil areas, weed control | Natural landscapes, deep-root crops |
Introduction to Raised Bed Gardening
Sided raised beds feature sturdy walls made from wood, stone, or metal that retain soil and define garden boundaries, promoting better soil structure and moisture retention. Open-bottom beds allow direct contact with the native soil, enhancing root growth and natural drainage while benefiting from soil microorganisms. Choosing between sided and open-bottom raised beds depends on garden goals, soil quality, and desired plant health outcomes.
What Are Sided Raised Beds?
Sided raised beds are garden structures with vertical barriers made from materials like wood, metal, or stone, designed to contain soil and enhance growing conditions. These raised beds improve drainage, prevent soil compaction, and allow for better root development compared to open-bottom beds. Unlike open-bottom beds that lie directly on the ground, sided raised beds provide structural support and help control soil quality and temperature.
What Are Open-Bottom Raised Beds?
Open-bottom raised beds are garden beds constructed with side walls but no solid base, allowing plant roots to grow directly into the native soil beneath. This design promotes natural drainage and greater root expansion while enhancing soil biodiversity by integrating existing microorganisms. Unlike sided raised beds with a closed bottom, open-bottom beds reduce the risk of waterlogging and provide better access to deeper mineral deposits essential for plant health.
Soil Health: Sided vs Open-Bottom Beds
Sided raised beds help maintain soil structure by reducing soil erosion and compaction, promoting better root growth and moisture retention compared to open-bottom beds. Open-bottom beds allow direct contact with native soil, enhancing natural drainage and beneficial soil organism activity, which improves soil fertility over time. Both systems influence soil microbial diversity, but sided beds offer more control over soil amendments and weed management.
Drainage and Moisture Control Comparison
Sided raised beds offer superior drainage control by preventing soil erosion and allowing excess water to escape through designated drainage holes, reducing waterlogging risks compared to open-bottom beds. Open-bottom beds enhance natural moisture retention by allowing water to permeate directly into the native soil beneath, promoting deeper root growth. Effective moisture management depends on garden soil type, with sided beds better suited for heavy clay soils and open-bottom designs preferred in sandy or well-draining environments.
Pest and Weed Management
Sided raised beds provide a physical barrier that helps reduce weed invasion and limits the entry of certain soil-dwelling pests, enhancing effective pest and weed management. Open-bottom beds allow better soil drainage and natural microbial exchange but may require more frequent manual weed removal and pest control interventions. Proper selection between sided and open-bottom designs depends on the specific pest pressures and weed prevalence in the gardening environment.
Plant Root Growth and Development
Sided raised beds provide a controlled environment that promotes healthier root growth by preventing soil compaction and enhancing aeration, which supports robust root development. Open-bottom beds allow roots to penetrate deeper into native soil, potentially accessing additional nutrients and moisture, but may face variable soil conditions that can hinder consistent root expansion. Optimal plant root development depends on balancing soil quality and drainage, with sided beds offering more control and open-bottom beds leveraging natural soil properties.
Installation and Material Considerations
Sided raised beds require sturdy materials like treated wood, composite, or metal to support soil weight and maintain shape, with installation involving securing panels together and anchoring to prevent shifting. Open-bottom beds offer easier installation since they sit directly on the ground, allowing natural soil drainage and root expansion without additional support structures. Material choice impacts durability and soil interaction, where rot-resistant woods or rust-proof metals extend lifespan, while cost and environmental factors influence selection.
Cost and Maintenance Differences
Sided raised beds, constructed with durable materials like wood or metal, typically incur higher initial costs but offer easier maintenance by preventing soil erosion and facilitating weed control. Open-bottom beds generally cost less due to minimal materials and allow natural soil organisms to thrive, yet they require more frequent soil amendments and weed management to maintain productivity. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and long-term maintenance preferences.
Which Raised Bed Option is Best for You?
Sided raised beds offer better soil control and temperature regulation, making them ideal for gardeners seeking enhanced root protection and easier maintenance. Open-bottom beds provide superior drainage and allow roots to access native soil, benefiting plants requiring extensive root expansion and natural soil microorganisms. Choosing the best raised bed depends on your soil quality, drainage needs, and plant types, with sided beds preferred for compact or nutrient-poor soils and open-bottom beds suited for well-drained, fertile ground.
Sided raised beds vs open-bottom beds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com