
Perennial crops vs Annual crops Illustration
Perennial crops in raised beds provide long-term soil stability and reduce the need for frequent replanting, making them ideal for sustainable gardening. Annual crops, however, offer the flexibility to rotate varieties each season, optimizing nutrient use and controlling pests. Choosing between perennials and annuals depends on garden goals, space, and maintenance preferences.
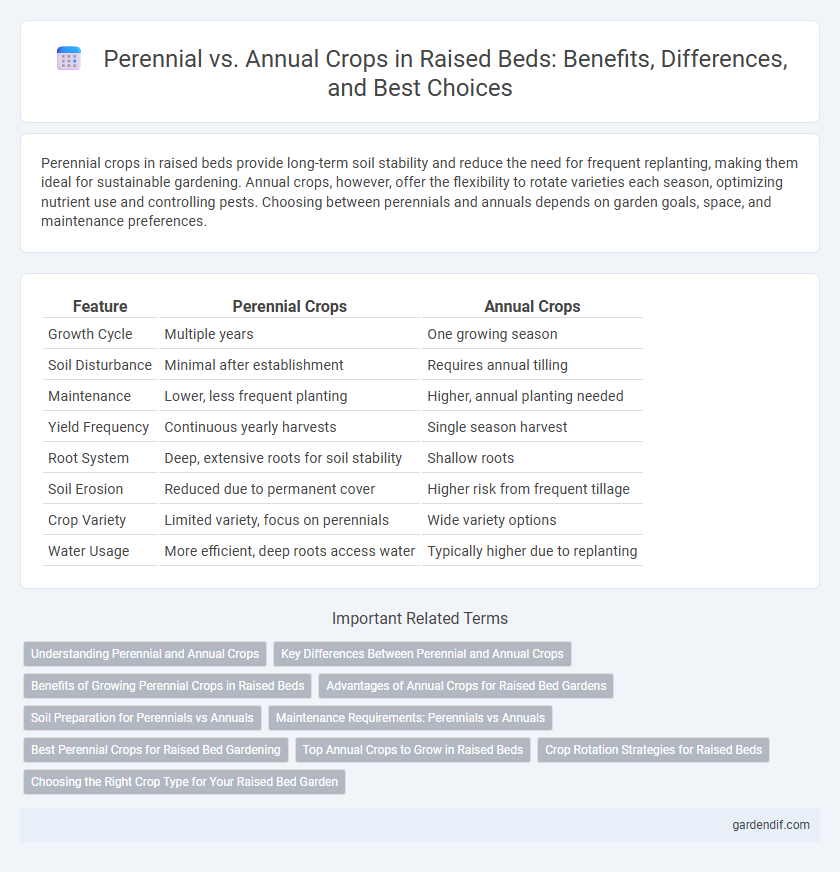
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Perennial Crops | Annual Crops |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Cycle | Multiple years | One growing season |
| Soil Disturbance | Minimal after establishment | Requires annual tilling |
| Maintenance | Lower, less frequent planting | Higher, annual planting needed |
| Yield Frequency | Continuous yearly harvests | Single season harvest |
| Root System | Deep, extensive roots for soil stability | Shallow roots |
| Soil Erosion | Reduced due to permanent cover | Higher risk from frequent tillage |
| Crop Variety | Limited variety, focus on perennials | Wide variety options |
| Water Usage | More efficient, deep roots access water | Typically higher due to replanting |
Understanding Perennial and Annual Crops
Perennial crops, such as asparagus and rhubarb, grow back year after year from the same root system, reducing the need for replanting and providing long-term soil stability in raised beds. Annual crops like tomatoes and lettuce complete their life cycle within a single growing season, requiring replanting each year but allowing for crop rotation to manage soil fertility and pests. Understanding the growth habits and maintenance needs of perennial versus annual crops helps optimize raised bed productivity and sustainability.
Key Differences Between Perennial and Annual Crops
Perennial crops grow and produce yields for multiple years without replanting, reducing soil disturbance and improving long-term soil health in raised beds. Annual crops complete their life cycle within a single season, requiring replanting each year but allowing for crop rotation to manage pests and optimize nutrient use. The choice between perennial and annual crops in raised beds impacts maintenance frequency, soil sustainability, and overall garden productivity.
Benefits of Growing Perennial Crops in Raised Beds
Growing perennial crops in raised beds offers long-term soil stability and reduced erosion due to their deep, extensive root systems. These crops improve soil organic matter and nutrient cycling, enhancing fertility and moisture retention without frequent replanting. Raised beds also facilitate better drainage and root aeration, which supports the vigorous growth of perennial plants over multiple growing seasons.
Advantages of Annual Crops for Raised Bed Gardens
Annual crops in raised bed gardens offer faster harvest cycles, allowing gardeners to maximize space efficiency and achieve multiple yields within a single growing season. These crops typically require less maintenance and are easier to rotate, reducing soil-borne diseases and nutrient depletion. Their adaptability to different soil conditions and the ability to select varieties tailored for raised beds enhance productivity and garden vibrancy.
Soil Preparation for Perennials vs Annuals
Soil preparation for perennial crops in raised beds requires deep soil cultivation and rich organic matter to support long-term root systems and nutrient uptake. Annual crops demand well-tilled, loose soil with balanced nutrient levels to promote rapid growth and frequent replanting each season. Incorporating compost and mulch enhances soil structure and moisture retention essential for both crop types but differs in intensity based on crop lifespan and root depth.
Maintenance Requirements: Perennials vs Annuals
Perennial crops in raised beds require lower maintenance as they grow back year after year, reducing the need for replanting and soil disturbance. Annual crops demand more frequent upkeep, including soil preparation, planting, and harvesting within a single growing season. This difference significantly impacts labor and resource allocation in garden management.
Best Perennial Crops for Raised Bed Gardening
Perennial crops such as asparagus, rhubarb, and artichokes thrive in raised bed gardens by providing multiple harvests over several years with minimal replanting. These deep-rooted plants benefit from the improved soil drainage and aeration typical of raised beds, promoting healthier growth and increased yield. Choosing perennial crops for raised beds enhances long-term productivity while reducing maintenance compared to annuals like tomatoes or lettuce.
Top Annual Crops to Grow in Raised Beds
Top annual crops for raised beds include tomatoes, lettuce, and radishes, which thrive due to the improved soil drainage and controlled environment. These crops benefit from raised beds' ability to warm up faster in spring, leading to earlier harvests. Incorporating fast-growing annuals maximizes productivity and allows for multiple planting cycles within a growing season.
Crop Rotation Strategies for Raised Beds
Perennial crops in raised beds offer long-term soil stability and reduced disturbance, enhancing microbial diversity, while annual crops require frequent replanting, making crop rotation essential to prevent nutrient depletion and disease buildup. Implementing crop rotation strategies with varied plant families in raised beds maximizes soil health by balancing nutrient use and interrupting pest cycles, promoting sustainable yields. Integrating deep-rooted perennials with shallow-rooted annuals optimizes nutrient cycling and soil structure, ensuring resilient and productive raised bed systems.
Choosing the Right Crop Type for Your Raised Bed Garden
Perennial crops, such as asparagus and rhubarb, provide long-term yield with minimal replanting, making them ideal for raised beds designed for sustainability and soil stability. Annual crops like tomatoes and lettuce offer diverse seasonal harvesting but require yearly planting and soil renewal to maintain productivity. Selecting the right crop type depends on your garden's size, maintenance commitment, and desired harvesting frequency, ensuring optimal use of raised bed space and nutrient management.
Perennial crops vs Annual crops Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com