
Organic soil mix vs Commercial soil mix Illustration
Organic soil mix enhances raised bed gardening by providing a nutrient-rich, environmentally friendly foundation that improves soil structure and supports beneficial microorganisms. Commercial soil mixes offer convenience and consistency but may contain synthetic fertilizers and lack the diverse microbial life found in organic blends. Choosing organic soil promotes healthier plant growth and sustainable gardening practices in raised beds.
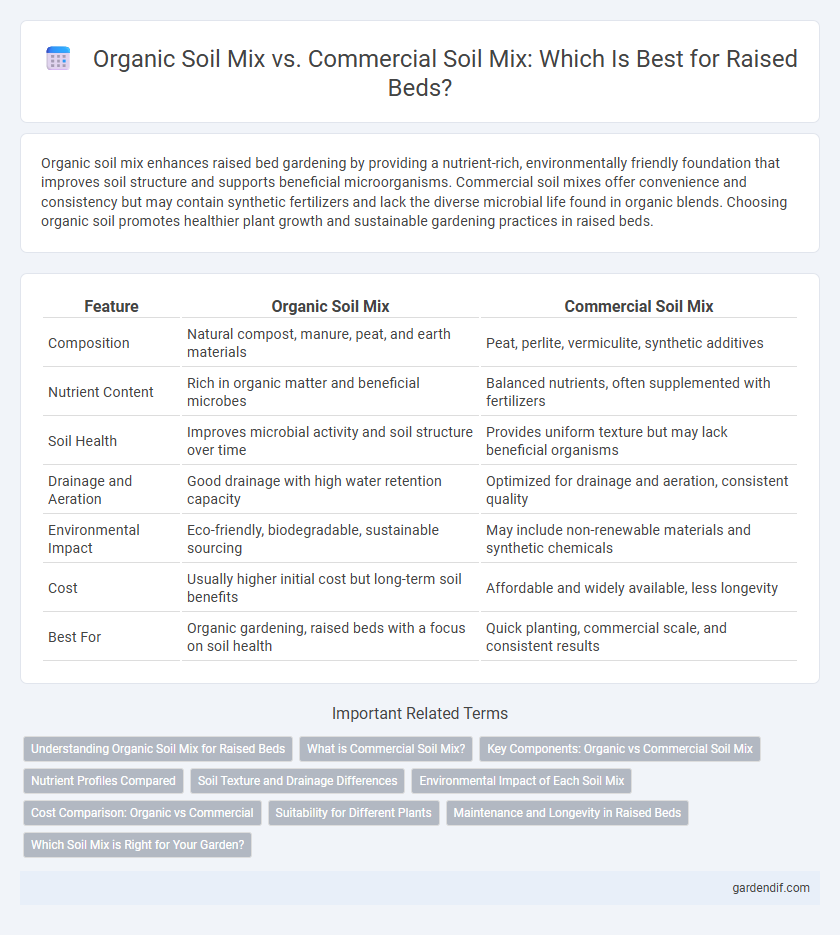
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Organic Soil Mix | Commercial Soil Mix |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural compost, manure, peat, and earth materials | Peat, perlite, vermiculite, synthetic additives |
| Nutrient Content | Rich in organic matter and beneficial microbes | Balanced nutrients, often supplemented with fertilizers |
| Soil Health | Improves microbial activity and soil structure over time | Provides uniform texture but may lack beneficial organisms |
| Drainage and Aeration | Good drainage with high water retention capacity | Optimized for drainage and aeration, consistent quality |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, sustainable sourcing | May include non-renewable materials and synthetic chemicals |
| Cost | Usually higher initial cost but long-term soil benefits | Affordable and widely available, less longevity |
| Best For | Organic gardening, raised beds with a focus on soil health | Quick planting, commercial scale, and consistent results |
Understanding Organic Soil Mix for Raised Beds
Organic soil mix for raised beds consists of compost, aged manure, peat moss, and vermiculite, providing rich nutrients and excellent water retention. This natural blend promotes beneficial microbial activity and improves soil structure, enhancing plant growth and root health. Choosing organic soil mix supports sustainable gardening practices by reducing chemical inputs and fostering a balanced ecosystem within raised beds.
What is Commercial Soil Mix?
Commercial soil mix is a pre-formulated growing medium composed of peat moss, perlite, vermiculite, and balanced nutrients designed for optimal drainage and aeration in raised beds. It often contains added fertilizers and pH adjusters to support consistent plant growth and reduce soil-borne diseases. Unlike organic soil mixes, commercial blends provide a standardized environment that enhances seed germination and crop yield in controlled gardening setups.
Key Components: Organic vs Commercial Soil Mix
Organic soil mix contains natural materials such as compost, peat moss, coconut coir, and aged manure, enhancing microbial activity and nutrient availability essential for plant health in raised beds. Commercial soil mixes often include peat-based substrates, synthetic fertilizers, and perlite or vermiculite, designed for consistent texture and drainage but may lack long-term nutrient sustainability. The organic mix promotes soil biodiversity and improves water retention, whereas commercial mixes offer immediate nutrient delivery and standardized growing conditions.
Nutrient Profiles Compared
Organic soil mix in raised beds offers a richer nutrient profile, including higher levels of essential macro and micronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium due to natural compost and organic matter. Commercial soil mixes often contain synthetic fertilizers that provide immediate nutrient availability but may lack the diversity of trace elements and beneficial microbes found in organic blends. Long-term plant health and soil fertility generally improve with organic soil mixes, supporting sustainable growth and stronger root systems.
Soil Texture and Drainage Differences
Organic soil mix for raised beds typically contains a balanced blend of compost, peat moss, and vermiculite, promoting a light, crumbly texture that enhances aeration and water retention. Commercial soil mixes often include synthetic components and fillers, resulting in a denser texture with variable drainage efficiency. The superior drainage of organic mixes helps prevent waterlogging, supporting healthier root development compared to some commercial alternatives.
Environmental Impact of Each Soil Mix
Organic soil mix significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing natural, renewable materials like compost, peat moss, and coconut coir, which enhance soil biodiversity and minimize chemical runoff. Commercial soil mixes often contain synthetic fertilizers and peat-based components that contribute to habitat destruction and increased carbon emissions. Choosing organic soil mix supports sustainable gardening practices by improving soil health and reducing pollution in raised bed cultivation.
Cost Comparison: Organic vs Commercial
Organic soil mix typically costs more upfront due to the inclusion of high-quality compost, manure, and natural amendments that improve soil health and nutrient retention. Commercial soil mixes often contain synthetic fertilizers and fillers, offering a lower initial price but potentially requiring more frequent replenishment and supplementation. Considering long-term productivity and sustainability, organic soil mixes can be more cost-effective despite higher initial expenses.
Suitability for Different Plants
Organic soil mix offers superior nutrient retention and microbial activity, making it highly suitable for vegetables, herbs, and fruit-bearing plants that require rich, well-drained soil conditions. Commercial soil mixes often contain synthetic nutrients and fillers, which may support flowering plants and container plants with moderate nutrient demands but can lack the complexity needed for root vegetables or leafy greens. Selecting soil based on plant type ensures optimal growth, with organic mixes favoring nutrient-intensive crops and commercial mixes catering to plants with less specific soil nutrient requirements.
Maintenance and Longevity in Raised Beds
Organic soil mix in raised beds requires more frequent maintenance due to its higher nutrient cycling and microbial activity, promoting healthier plant growth but necessitating regular amendments like compost to sustain fertility. Commercial soil mixes offer longer initial nutrient availability and structure stability, reducing the need for frequent replenishment, but may lack the biological benefits essential for long-term soil health. Choosing between the two depends on balancing ease of maintenance with the desire for sustainable soil enrichment and extended bed productivity.
Which Soil Mix is Right for Your Garden?
Organic soil mix offers enhanced nutrient retention, improved microbial activity, and better moisture regulation, making it ideal for gardeners seeking sustainable growth with natural inputs. Commercial soil mixes provide consistent texture, pH balance, and added fertilizers, suited for quick establishment and maintenance with minimal effort. Choosing the right soil mix depends on your gardening goals, plant types, and commitment to organic practices or convenience.
Organic soil mix vs Commercial soil mix Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com