
Lasagna bed vs Mounded bed Illustration
Lasagna beds use layers of organic materials such as compost, leaves, and grass clippings to create nutrient-rich soil that retains moisture and improves fertility. Mounded beds involve piling soil into raised hills, enhancing drainage and soil warmth, which is ideal for root vegetables and plants requiring well-drained soil. Choosing between lasagna and mounded beds depends on soil quality, crop type, and water management preferences.
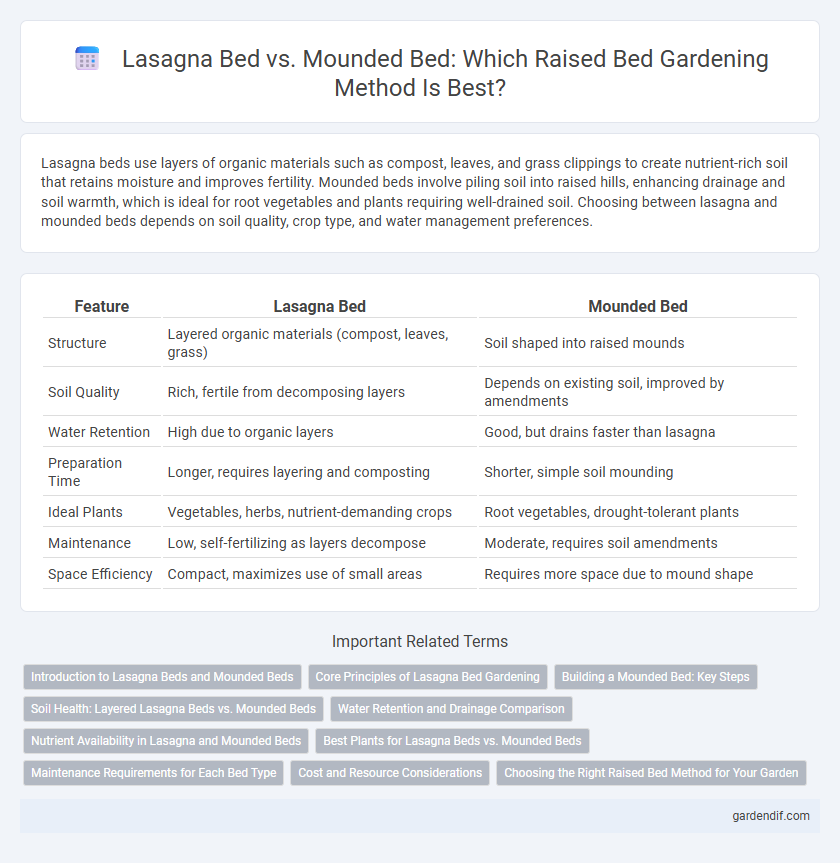
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lasagna Bed | Mounded Bed |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Layered organic materials (compost, leaves, grass) | Soil shaped into raised mounds |
| Soil Quality | Rich, fertile from decomposing layers | Depends on existing soil, improved by amendments |
| Water Retention | High due to organic layers | Good, but drains faster than lasagna |
| Preparation Time | Longer, requires layering and composting | Shorter, simple soil mounding |
| Ideal Plants | Vegetables, herbs, nutrient-demanding crops | Root vegetables, drought-tolerant plants |
| Maintenance | Low, self-fertilizing as layers decompose | Moderate, requires soil amendments |
| Space Efficiency | Compact, maximizes use of small areas | Requires more space due to mound shape |
Introduction to Lasagna Beds and Mounded Beds
Lasagna beds are layered garden beds built by alternating organic materials like compost, straw, and kitchen scraps, creating nutrient-rich soil through decomposition. Mounded beds are formed by piling existing soil into raised, rounded structures that improve drainage and root aeration. Both methods enhance plant health but differ in soil-building approach and maintenance requirements.
Core Principles of Lasagna Bed Gardening
Lasagna bed gardening relies on layering organic materials such as compost, leaves, and straw to create nutrient-rich, moisture-retentive soil that promotes healthy plant growth. Unlike mounded beds that primarily focus on soil elevation for drainage and root expansion, lasagna beds emphasize decomposition and soil amendment through stratified layers. This core principle enhances soil fertility naturally, reduces the need for tilling, and supports sustainable gardening practices.
Building a Mounded Bed: Key Steps
Building a mounded bed involves layering soil and organic matter into a raised, rounded shape to enhance drainage and root development. Start by clearing the area, then pile compost, soil, and mulch into a mound, ensuring each layer is firm but loose enough for aeration. Regularly water and maintain the bed to promote nutrient-rich, well-drained growing conditions ideal for vegetables and flowers.
Soil Health: Layered Lasagna Beds vs. Mounded Beds
Lasagna beds improve soil health through layered organic materials that promote microbial activity, nutrient retention, and moisture balance. In contrast, mounded beds rely on soil elevation and compaction, which may limit organic matter integration and microbial diversity. The layered structure of lasagna beds accelerates decomposition and enriches soil fertility more effectively than the simpler buildup of mounded beds.
Water Retention and Drainage Comparison
Lasagna beds enhance water retention through layered organic materials that slowly decompose, promoting moisture retention and nutrient availability. Mounded beds offer superior drainage due to their elevated structure, preventing waterlogging in heavy or clay soils. Gardeners seeking balanced moisture often prefer lasagna beds for their water-holding capacity, while those in wetter climates benefit from mounded beds to avoid root rot.
Nutrient Availability in Lasagna and Mounded Beds
Lasagna beds enhance nutrient availability through layered organic matter that decomposes slowly, providing a steady release of nutrients and improving soil structure. Mounded beds offer rapid drainage and warmer soil temperatures, which can accelerate nutrient uptake but may require more frequent fertilization. The high carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in lasagna layers promotes microbial activity, whereas mounded beds depend more on external nutrient inputs for sustained fertility.
Best Plants for Lasagna Beds vs. Mounded Beds
Lasagna beds thrive with nutrient-loving plants such as tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens due to their rich, layered organic matter that retains moisture and nutrients effectively. Mounded beds excel with root vegetables like carrots, potatoes, and onions, which benefit from the loose, well-aerated soil structure that promotes deep root growth. Both bed types support herbs like basil and thyme, but lasagna beds provide enhanced fertility, making them ideal for heavy feeders compared to the faster-draining nature of mounded beds.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Bed Type
Lasagna beds require regular layering of organic materials like compost, leaves, and grass clippings, demanding consistent monitoring to maintain nutrient balance and moisture levels. Mounded beds, formed by piling soil and organic matter into raised hills, generally need less frequent replenishing but require careful erosion control and occasional soil aeration. Both bed types benefit from mulching, yet lasagna beds typically demand higher ongoing attention to layering and decomposition processes for optimal plant growth.
Cost and Resource Considerations
Lasagna beds require more organic materials such as compost, leaves, and kitchen scraps, which can increase initial costs but reduce the need for soil amendments over time. Mounded beds typically use native soil piled into raised shapes, making them more cost-effective with fewer external resources needed. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and the availability of organic matter for sustainable soil enrichment.
Choosing the Right Raised Bed Method for Your Garden
Lasagna beds use layered organic materials like compost and mulch to create nutrient-rich soil, ideal for sustainable gardening with minimal soil disturbance. Mounded beds shape soil into elevated rows or hills, improving drainage and warming the soil faster, which benefits early planting and root development. Choosing between lasagna and mounded beds depends on your soil quality, available materials, and crop requirements, ensuring optimal growth and garden productivity.
Lasagna bed vs Mounded bed Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com