
Summer pruning vs winter pruning Illustration
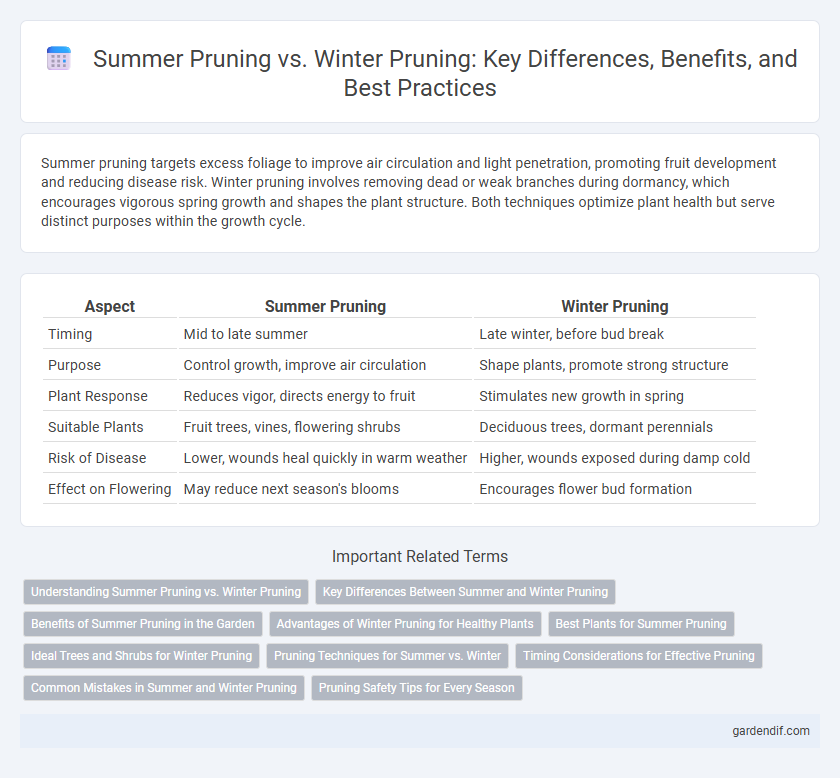
Summer pruning targets excess foliage to improve air circulation and light penetration, promoting fruit development and reducing disease risk. Winter pruning involves removing dead or weak branches during dormancy, which encourages vigorous spring growth and shapes the plant structure. Both techniques optimize plant health but serve distinct purposes within the growth cycle.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Summer Pruning | Winter Pruning |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Mid to late summer | Late winter, before bud break |
| Purpose | Control growth, improve air circulation | Shape plants, promote strong structure |
| Plant Response | Reduces vigor, directs energy to fruit | Stimulates new growth in spring |
| Suitable Plants | Fruit trees, vines, flowering shrubs | Deciduous trees, dormant perennials |
| Risk of Disease | Lower, wounds heal quickly in warm weather | Higher, wounds exposed during damp cold |
| Effect on Flowering | May reduce next season's blooms | Encourages flower bud formation |
Understanding Summer Pruning vs. Winter Pruning
Summer pruning primarily targets controlling growth and improving fruit quality by removing excess shoots and water sprouts, while winter pruning focuses on shaping the plant structure and promoting vigorous growth in the next season. Timing is crucial; summer pruning occurs during active growth to limit vigor and enhance sunlight penetration, whereas winter pruning happens during dormancy to prepare the plant for optimal development. Each method influences plant health and productivity differently, making it essential to choose the appropriate technique based on specific horticultural goals.
Key Differences Between Summer and Winter Pruning
Summer pruning involves trimming plants during active growth to control size and improve sunlight penetration, while winter pruning is done during dormancy to shape the plant and promote vigorous growth in spring. Summer pruning targets removing excess foliage and water sprouts, whereas winter pruning focuses on cutting back old wood and dead branches. The timing and methods differ significantly to optimize plant health and productivity based on seasonal growth patterns.
Benefits of Summer Pruning in the Garden
Summer pruning helps control plant growth by removing excess foliage, improving air circulation and sunlight penetration. It reduces the risk of disease and pest infestations while encouraging better fruit and flower production. This method also allows gardeners to shape plants precisely during active growth periods, resulting in healthier, more manageable gardens.
Advantages of Winter Pruning for Healthy Plants
Winter pruning promotes robust plant health by encouraging vigorous spring growth through the removal of dead or diseased wood during dormancy. This practice enhances air circulation and sunlight penetration, reducing the risk of fungal infections and pest infestations. Furthermore, cutting back branches in winter minimizes sap loss and stress on the plant, leading to stronger structural development.
Best Plants for Summer Pruning
Summer pruning is ideal for plants that benefit from controlled growth and improved air circulation during the active growing season. Best plants for summer pruning include fruit trees like apples and pears, as well as flowering shrubs such as hydrangeas and roses, which respond well to selective cutting. This method helps enhance fruit quality and encourages more blooms by removing excess foliage and directing energy to key growth areas.
Ideal Trees and Shrubs for Winter Pruning
Winter pruning is ideal for deciduous trees and shrubs such as maples, oaks, and roses, as it promotes strong spring growth by removing dead or diseased wood during dormancy. Hardy evergreens like junipers and pines also benefit from winter pruning to maintain shape and health without stimulating new growth too early. Summer pruning suits fruiting trees like apples and pears for controlling size and improving sunlight exposure, but winter pruning remains preferable for maintenance on many woody perennials.
Pruning Techniques for Summer vs. Winter
Summer pruning involves selective removal of new growth to improve sunlight penetration and air circulation, promoting fruit ripening and reducing disease risk. Winter pruning targets dormant wood, focusing on structural shaping and removal of dead or weak branches to encourage vigorous spring growth. Techniques like heading cuts dominate summer pruning, while thinning cuts are preferred in winter to maintain framework and balance.
Timing Considerations for Effective Pruning
Summer pruning targets active growth phases, helping to control size and improve sunlight penetration, typically done in late June to August. Winter pruning occurs during dormancy, from late December to early March, focusing on structural shaping and encouraging vigorous spring growth. Choosing the right timing depends on plant species and desired outcomes like controlling growth or enhancing fruit production.
Common Mistakes in Summer and Winter Pruning
Common mistakes in summer pruning include removing too much foliage, which can reduce photosynthesis and weaken the plant. In winter pruning, errors such as pruning too early or too late can expose vines to cold damage or disrupt the plant's growth cycle. Failing to use proper sanitation tools during both summer and winter pruning can lead to disease transmission and poor plant health.
Pruning Safety Tips for Every Season
Summer pruning involves removing excess growth and shaping plants during active growth periods, reducing the risk of disease by allowing wounds to dry quickly in warm weather. Winter pruning is typically done during dormancy, promoting vigorous spring growth and minimizing sap loss, but requires extra caution to avoid cold damage and ensure tools are properly sanitized to prevent pathogen spread. Always use sharp, clean tools and wear protective gloves regardless of the season to maintain plant health and personal safety.
Summer pruning vs winter pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com