
Directional Pruning vs Tip Pruning Illustration
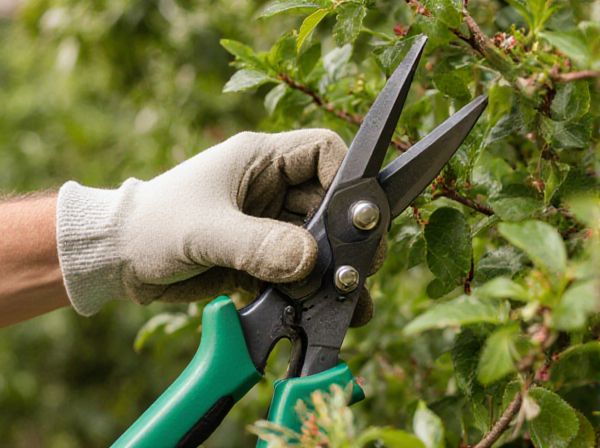
Directional pruning targets specific branches to shape the plant's growth and improve air circulation, while tip pruning involves removing only the growing tips to encourage bushier growth. Directional pruning is more precise and strategic, ideal for controlling size and form, whereas tip pruning promotes denser foliage without significantly altering the plant's overall structure. Both techniques enhance plant health but serve different horticultural purposes depending on growth goals.
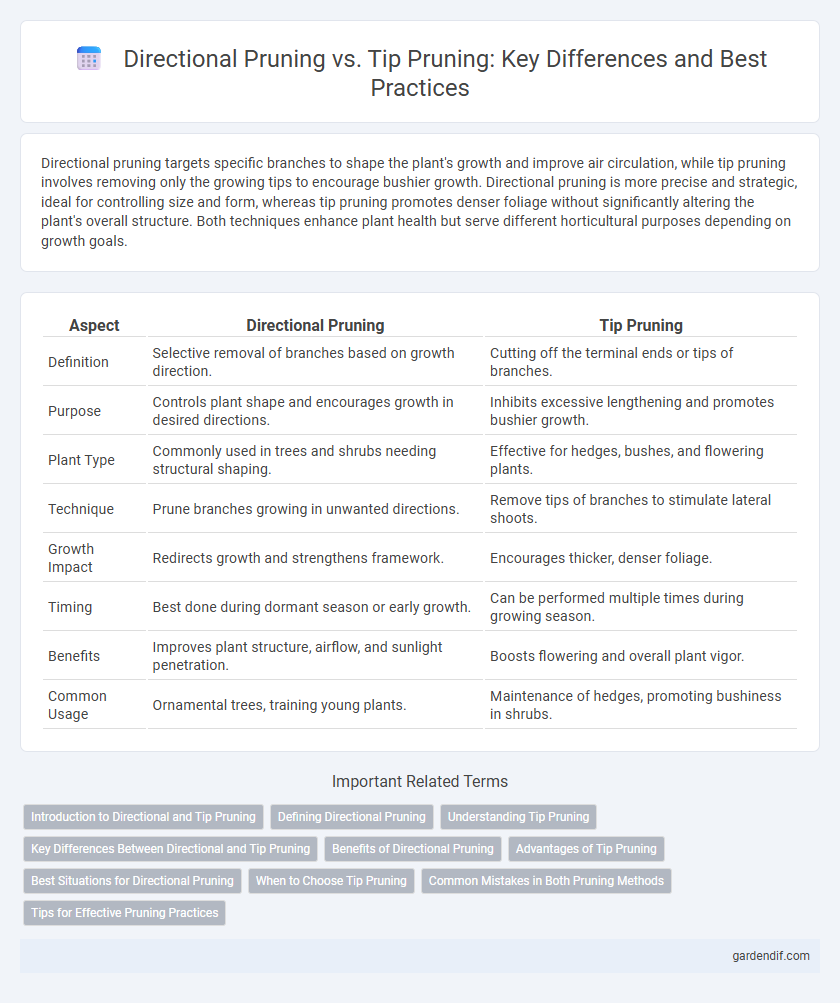
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Directional Pruning | Tip Pruning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Selective removal of branches based on growth direction. | Cutting off the terminal ends or tips of branches. |
| Purpose | Controls plant shape and encourages growth in desired directions. | Inhibits excessive lengthening and promotes bushier growth. |
| Plant Type | Commonly used in trees and shrubs needing structural shaping. | Effective for hedges, bushes, and flowering plants. |
| Technique | Prune branches growing in unwanted directions. | Remove tips of branches to stimulate lateral shoots. |
| Growth Impact | Redirects growth and strengthens framework. | Encourages thicker, denser foliage. |
| Timing | Best done during dormant season or early growth. | Can be performed multiple times during growing season. |
| Benefits | Improves plant structure, airflow, and sunlight penetration. | Boosts flowering and overall plant vigor. |
| Common Usage | Ornamental trees, training young plants. | Maintenance of hedges, promoting bushiness in shrubs. |
Introduction to Directional and Tip Pruning
Directional pruning involves selective removal of branches to shape a plant's growth in a specific direction, enhancing airflow and light penetration within the canopy. Tip pruning focuses on cutting the terminal ends of branches to control overall size, encourage bushier growth, and stimulate new shoot development. Both techniques are essential for maintaining plant health and optimizing structural form in gardening and horticulture.
Defining Directional Pruning
Directional pruning is a horticultural technique that selectively removes branches to encourage growth in a specific direction, enhancing plant structure and light exposure. Unlike tip pruning, which involves cutting the terminal buds to stimulate lateral growth, directional pruning focuses on guiding the overall shape and form by targeting specific branches. This method improves airflow, reduces disease risk, and maximizes fruit or flower production by optimizing canopy orientation.
Understanding Tip Pruning
Tip pruning targets the terminal growth points of plants, encouraging bushier development and increased branching by removing shoot tips. This method contrasts with directional pruning, which selectively trims lateral branches to shape overall plant structure and control growth direction. Understanding tip pruning is essential for gardeners aiming to enhance plant density and promote uniform foliage.
Key Differences Between Directional and Tip Pruning
Directional pruning targets specific branches to control plant shape and encourage growth in a desired direction, optimizing light exposure and airflow. Tip pruning involves cutting the end of branches to stimulate bushier growth and increase flower or fruit production. The key difference lies in directional pruning's focus on structure and growth orientation, while tip pruning primarily enhances density and vigor.
Benefits of Directional Pruning
Directional pruning enhances plant structure by selectively removing branches along a specific axis, promoting balanced growth and improved light penetration. This method directs energy to desired parts, increasing fruit yield and overall plant health compared to tip pruning. It also reduces branch overcrowding, minimizing disease risk and easing maintenance.
Advantages of Tip Pruning
Tip pruning promotes bushier plant growth by encouraging lateral branching and increasing overall foliage density, which can enhance photosynthesis and yield. It reduces vulnerability to diseases by improving air circulation around the plant's canopy. This method requires less skill and precision compared to directional pruning, making it more accessible for novice gardeners.
Best Situations for Directional Pruning
Directional pruning is best suited for shaping trees or shrubs to promote growth toward a specific direction, enhancing airflow and light penetration on one side of the plant. This technique is ideal when managing hedges along pathways, fences, or property lines where controlled growth is essential. It effectively prevents overgrowth in unwanted areas, maintaining a neat, structured appearance without compromising the plant's overall health.
When to Choose Tip Pruning
Tip pruning is ideal for young or densely branched plants requiring controlled growth and improved air circulation. It effectively encourages bushier development by removing shoot tips without altering the main branch direction. Choose tip pruning when the goal is to enhance overall plant shape and stimulate lateral branching rather than redirect growth.
Common Mistakes in Both Pruning Methods
Common mistakes in directional pruning include uneven branch removal, which can lead to imbalanced plant growth and reduced fruit yield. In tip pruning, overcutting terminal buds often stunts plant development and limits flowering potential. Both methods risk improper timing, weakening the plant's health and increasing susceptibility to diseases.
Tips for Effective Pruning Practices
Directional pruning enhances plant shape and structure by selectively removing branches that grow in undesired directions, promoting balanced growth and improved air circulation. Tip pruning involves cutting back the tips of branches to encourage bushier growth and denser foliage, which is essential for plants requiring compact forms. For effective pruning, consistently use sharp, clean tools, prune during the plant's dormant season to minimize stress, and always cut just above a bud facing the desired growth direction.
Directional Pruning vs Tip Pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com