
Topiary pruning vs natural form pruning Illustration
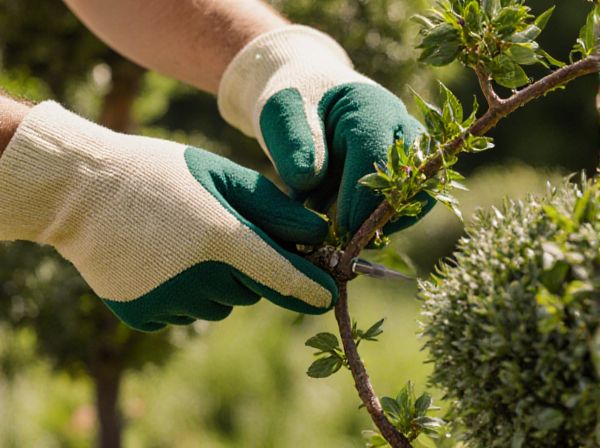
Topiary pruning involves shaping plants into defined, often geometric or ornamental forms, requiring regular trimming to maintain precise edges and symmetry. Natural form pruning promotes the plant's inherent growth patterns, enhancing health and structure without rigid shaping, resulting in a more organic appearance. Choosing between topiary and natural form pruning depends on aesthetic goals and maintenance preferences, balancing artistic design with plant longevity.
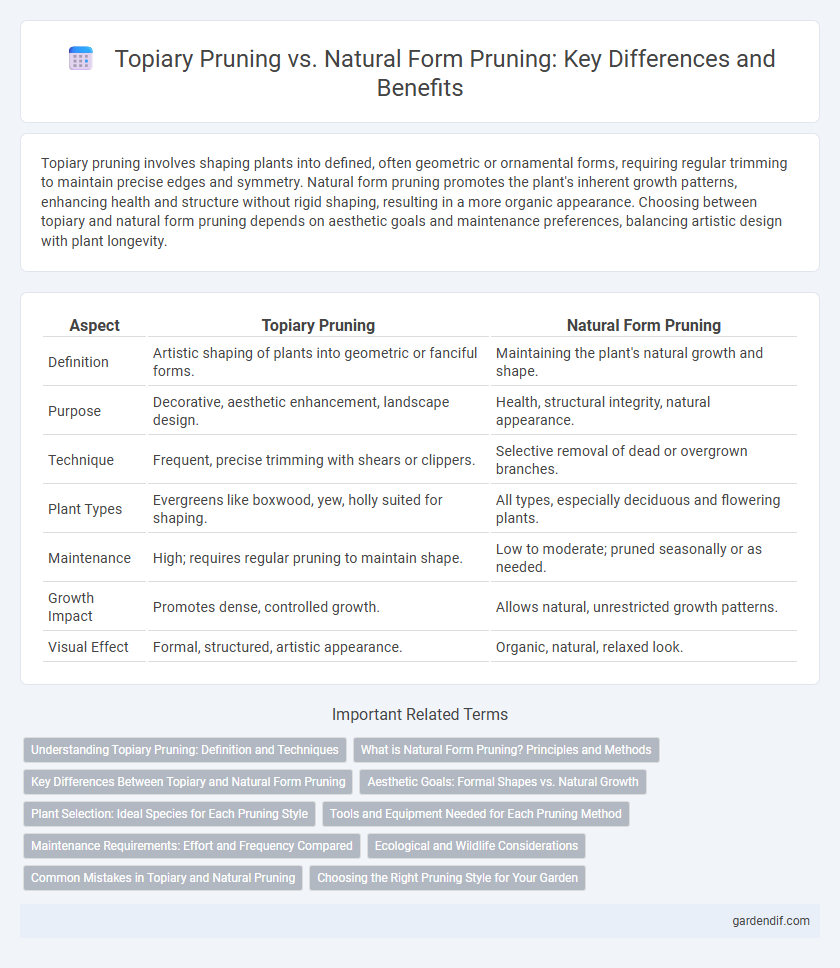
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Topiary Pruning | Natural Form Pruning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic shaping of plants into geometric or fanciful forms. | Maintaining the plant's natural growth and shape. |
| Purpose | Decorative, aesthetic enhancement, landscape design. | Health, structural integrity, natural appearance. |
| Technique | Frequent, precise trimming with shears or clippers. | Selective removal of dead or overgrown branches. |
| Plant Types | Evergreens like boxwood, yew, holly suited for shaping. | All types, especially deciduous and flowering plants. |
| Maintenance | High; requires regular pruning to maintain shape. | Low to moderate; pruned seasonally or as needed. |
| Growth Impact | Promotes dense, controlled growth. | Allows natural, unrestricted growth patterns. |
| Visual Effect | Formal, structured, artistic appearance. | Organic, natural, relaxed look. |
Understanding Topiary Pruning: Definition and Techniques
Topiary pruning involves shaping plants into clearly defined geometric or fanciful forms by carefully trimming leaves and branches, requiring precision and regular maintenance to maintain the design. This technique contrasts with natural form pruning, which allows plants to grow according to their inherent shapes, focusing on health and structural integrity rather than aesthetics. Mastering topiary pruning techniques, such as shearing, pinching, and framework guiding, enables gardeners to create intricate living sculptures from species like boxwood, yew, and privet.
What is Natural Form Pruning? Principles and Methods
Natural form pruning emphasizes shaping plants to enhance their inherent growth patterns, promoting health and structural integrity without forcing unnatural shapes. This method relies on selective trimming that respects a plant's natural habit, encouraging airflow, light penetration, and balanced growth. Techniques include thinning, crown raising, and crown reduction performed to maintain the tree's original silhouette while removing dead or overcrowded branches.
Key Differences Between Topiary and Natural Form Pruning
Topiary pruning involves meticulously shaping plants into defined, often geometric or ornamental forms, requiring regular trimming to maintain precise contours, whereas natural form pruning emphasizes preserving and enhancing the plant's inherent shape and growth habits. Topiary demands detailed attention to symmetry and design, typically utilizing tools like shears for fine adjustments, while natural form pruning prioritizes plant health and structural balance, encouraging natural branching and airflow. The key differences lie in the aesthetic goals: topiary aims for artistic expression and controlled shapes, whereas natural form pruning promotes organic growth and ecological function.
Aesthetic Goals: Formal Shapes vs. Natural Growth
Topiary pruning emphasizes creating formal, geometric shapes such as spirals and spheres, enhancing garden aesthetics through structured and artistic designs. Natural form pruning prioritizes maintaining the plant's inherent growth habit, promoting a more organic and free-flowing appearance that blends harmoniously with the landscape. Each method targets distinct aesthetic goals, with topiary offering precision and control, while natural form pruning preserves the authentic beauty of the plant species.
Plant Selection: Ideal Species for Each Pruning Style
Topiary pruning suits species with dense, small leaves and slow, compact growth such as boxwood (Buxus), yew (Taxus), and holly (Ilex), allowing precise shaping and repeated trimming. Natural form pruning favors trees and shrubs with strong natural structure and seasonal interest like oak (Quercus), dogwood (Cornus), and Japanese maple (Acer palmatum), emphasizing health and organic shape development. Selecting the appropriate plant species is critical for achieving the desired aesthetic and maintenance level in either pruning style.
Tools and Equipment Needed for Each Pruning Method
Topiary pruning requires precision tools such as hand shears, topiary scissors, and electric trimmers to achieve detailed shapes and clean lines. Natural form pruning relies on more general equipment like bypass pruners, loppers, and pruning saws to maintain the plant's organic structure. Both methods benefit from gloves and disinfectants to ensure plant health and safety during the pruning process.
Maintenance Requirements: Effort and Frequency Compared
Topiary pruning demands high maintenance with frequent, meticulous trimming to maintain precise shapes, often requiring weekly attention during the growing season. In contrast, natural form pruning involves less frequent, moderate effort focused on removing dead or overgrown branches, typically performed once or twice a year. Gardeners choosing topiary must commit to intensive upkeep, while those opting for natural form pruning benefit from reduced labor and a more relaxed schedule.
Ecological and Wildlife Considerations
Topiary pruning shapes plants into ornamental forms, often reducing habitat complexity and limiting shelter and food sources for wildlife. Natural form pruning maintains a plant's inherent structure, supporting biodiversity by preserving nesting sites, insect habitats, and foraging opportunities. Choosing natural form pruning promotes ecological balance and enhances urban wildlife habitats.
Common Mistakes in Topiary and Natural Pruning
Topiary pruning often suffers from over-shaping, causing plants to lose natural growth patterns and increasing stress on branches, while natural form pruning commonly involves under-pruning or neglecting structural cuts, leading to weak branch formation and poor airflow. Gardeners frequently make the mistake of trimming too frequently in topiary, resulting in unnatural shapes and stunted growth, whereas natural form pruning errors include leaving dead or diseased wood unremoved, which compromises plant health. Proper timing and understanding plant-specific growth habits are crucial to avoid these common mistakes and ensure healthy, aesthetically pleasing results.
Choosing the Right Pruning Style for Your Garden
Topiary pruning shapes plants into precise geometric or whimsical forms, ideal for formal gardens and creating visual focal points, while natural form pruning emphasizes maintaining a plant's inherent shape, promoting healthy growth and ecological balance. Selecting the appropriate pruning style depends on garden design preferences, plant species, and maintenance capacity; topiary requires frequent, skillful trimming, whereas natural form pruning suits gardeners aiming for low-maintenance and biodiversity support. Consider factors such as plant growth habits, aesthetic goals, and long-term care when choosing between topiary and natural form pruning to achieve a harmonious and sustainable garden landscape.
Topiary pruning vs natural form pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com