
Rejuvenation pruning vs corrective pruning Illustration
Rejuvenation pruning involves cutting back old or overgrown plants to stimulate new growth and restore vitality, often used for shrubs and perennials. Corrective pruning targets specific issues such as dead, diseased, or damaged branches to improve plant health and structure. While rejuvenation promotes overall renewal, corrective pruning focuses on maintaining plant integrity and preventing further problems.
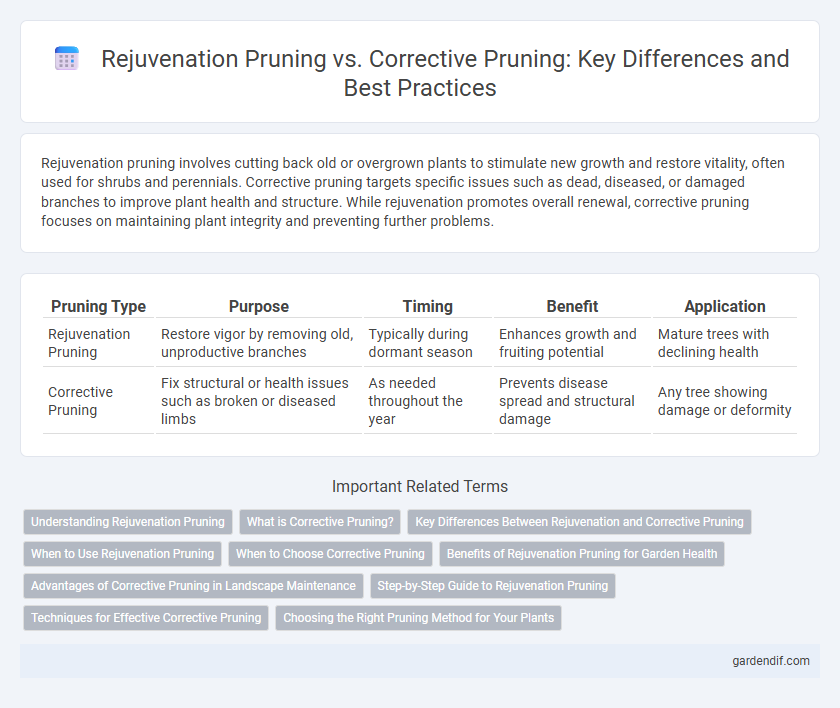
Table of Comparison
| Pruning Type | Purpose | Timing | Benefit | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rejuvenation Pruning | Restore vigor by removing old, unproductive branches | Typically during dormant season | Enhances growth and fruiting potential | Mature trees with declining health |
| Corrective Pruning | Fix structural or health issues such as broken or diseased limbs | As needed throughout the year | Prevents disease spread and structural damage | Any tree showing damage or deformity |
Understanding Rejuvenation Pruning
Rejuvenation pruning involves selectively removing older or overgrown branches to stimulate new growth, enhancing the plant's vitality and productivity. This method focuses on revitalizing declining plants by encouraging the development of fresh shoots and improving overall structure. By contrast, corrective pruning addresses structural issues or damage without necessarily aiming to renew the plant's growth potential.
What is Corrective Pruning?
Corrective pruning involves removing damaged, diseased, or structurally unsound branches to improve a plant's overall health and safety. This method targets issues that have already compromised the plant, aiming to prevent further decline and reduce hazards like falling limbs. Unlike rejuvenation pruning, which stimulates new growth, corrective pruning focuses on maintaining the current structure and addressing existing problems.
Key Differences Between Rejuvenation and Corrective Pruning
Rejuvenation pruning involves removing older, overgrown, or unproductive branches to stimulate new growth and enhance overall plant vitality, whereas corrective pruning targets damaged, diseased, or structurally unsound limbs to improve plant health and safety. Rejuvenation pruning promotes long-term plant renewal by encouraging fresh shoots and increased foliage density, while corrective pruning focuses on immediate restoration and repair. The timing and objectives differ, with rejuvenation pruning typically done during dormancy for sustained vigor and corrective pruning performed as needed to address specific issues.
When to Use Rejuvenation Pruning
Rejuvenation pruning is best used when plants exhibit overgrowth, decline in vigor, or have become leggy and unproductive, typically after several seasons without major pruning. This method stimulates new, healthy growth and restores structural balance by removing old, unproductive wood. Rejuvenation pruning is ideal during the dormant season to minimize stress and encourage robust regrowth in the next growing cycle.
When to Choose Corrective Pruning
Corrective pruning is essential when addressing damage from pests, diseases, or structural issues that compromise plant health and safety. Select corrective pruning to remove dead, diseased, or broken branches promptly to prevent further decay and maintain plant stability. This method is best applied during the growing season or immediately after detecting problems to encourage healthy new growth and reduce risks.
Benefits of Rejuvenation Pruning for Garden Health
Rejuvenation pruning stimulates vigorous new growth by removing old, unproductive branches, enhancing overall plant vitality and increasing flowering potential. This method improves air circulation and sunlight penetration, reducing the risk of fungal diseases and pest infestations in the garden. Rejuvenation pruning also promotes a balanced structure, leading to stronger plants that are more resilient to environmental stresses.
Advantages of Corrective Pruning in Landscape Maintenance
Corrective pruning enhances landscape maintenance by removing damaged, diseased, or structurally unsound branches, promoting plant health and safety. This method helps prevent potential hazards and reduces the risk of pest infestations, leading to a more resilient and aesthetically pleasing landscape. Corrective pruning also supports long-term growth by directing energy to healthier parts of the plant, improving overall vitality and appearance.
Step-by-Step Guide to Rejuvenation Pruning
Rejuvenation pruning involves systematically removing older, overgrown branches to stimulate new growth and restore plant vitality, unlike corrective pruning which targets damaged or diseased parts. Begin by assessing the plant's structure to identify aged, unproductive wood, then carefully cut back up to one-third of the plant to encourage fresh shoots. Regularly monitor progress and adjust pruning intensity to balance plant health with desired shape and growth renewal.
Techniques for Effective Corrective Pruning
Effective corrective pruning involves selectively removing diseased, damaged, or structurally unsound branches to improve tree health and safety. Techniques such as precise cutting at the branch collar, using sharp tools to minimize injury, and disinfecting tools to prevent pathogen spread are crucial for successful outcomes. Regular assessment and timely intervention enhance the tree's natural healing process and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Pruning Method for Your Plants
Rejuvenation pruning involves removing old, overgrown branches to stimulate new growth and restore plant vitality, making it ideal for neglected or mature plants. Corrective pruning targets specific issues like dead, diseased, or crossing branches to maintain plant health and structure. Selecting the appropriate pruning method depends on your plant's condition and growth goals, ensuring optimal health and aesthetic appeal.
Rejuvenation pruning vs corrective pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com