
Hardwood Cuttings vs Softwood Cuttings Illustration
Hardwood cuttings, taken from mature, dormant stems, offer greater durability and a higher success rate for woody plants due to their established structure and nutrient reserves. Softwood cuttings, sourced from young, flexible growth, root faster and are ideal for plants with tender stems but require more careful handling to prevent drying out. Choosing between hardwood and softwood cuttings depends on plant species, season, and propagation goals to optimize rooting success.
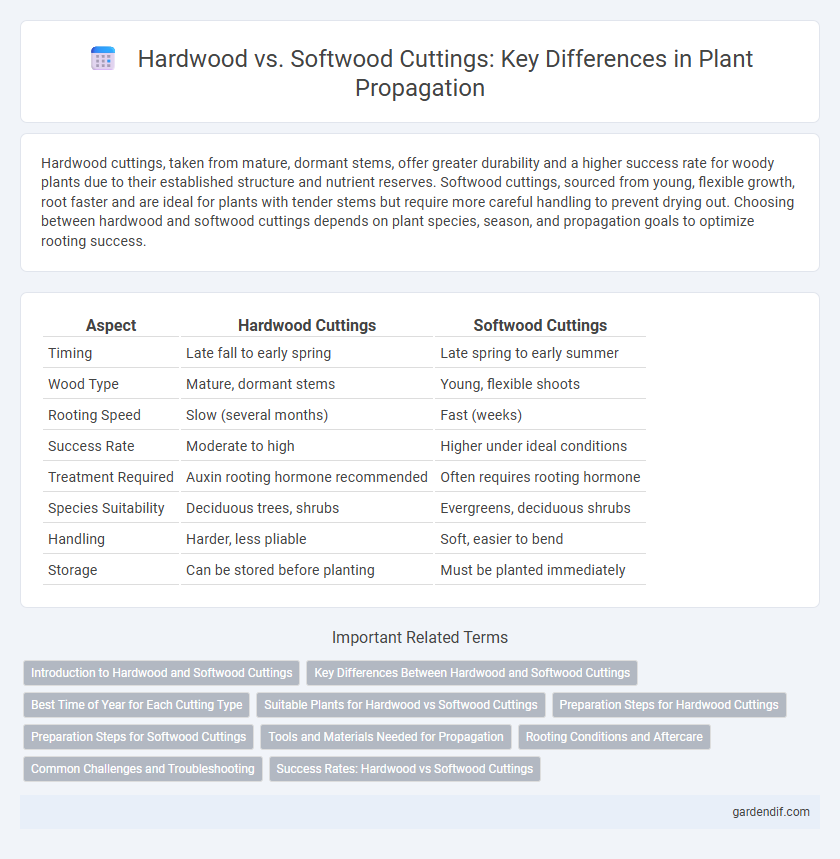
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hardwood Cuttings | Softwood Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Late fall to early spring | Late spring to early summer |
| Wood Type | Mature, dormant stems | Young, flexible shoots |
| Rooting Speed | Slow (several months) | Fast (weeks) |
| Success Rate | Moderate to high | Higher under ideal conditions |
| Treatment Required | Auxin rooting hormone recommended | Often requires rooting hormone |
| Species Suitability | Deciduous trees, shrubs | Evergreens, deciduous shrubs |
| Handling | Harder, less pliable | Soft, easier to bend |
| Storage | Can be stored before planting | Must be planted immediately |
Introduction to Hardwood and Softwood Cuttings
Hardwood cuttings involve mature, dormant stems taken from deciduous or evergreen plants during late autumn to winter, providing durability and higher success rates in rooting. Softwood cuttings, derived from new, flexible shoots in spring to early summer, have higher moisture content and root rapidly but require controlled humidity and temperature. Understanding the differences in timing, tissue type, and environmental needs is essential for optimizing propagation success in various plant species.
Key Differences Between Hardwood and Softwood Cuttings
Hardwood cuttings are taken from mature, dormant stems of deciduous or woody plants during late autumn to early spring, offering higher success rates due to their sturdier structure and lower moisture content. Softwood cuttings come from young, actively growing shoots in spring or early summer, containing higher moisture and less lignified tissue, which promotes faster rooting but requires more humidity control. Key differences include timing, tissue maturity, moisture levels, and rooting speed, influencing propagation techniques and plant species suitability.
Best Time of Year for Each Cutting Type
Hardwood cuttings are best taken during late autumn to early winter when the plant is dormant, ensuring higher rooting success due to reduced sap flow. Softwood cuttings perform optimally in late spring to early summer when new growth is pliable and actively growing, which promotes faster root development. Timing the collection according to these seasonal phases enhances propagation efficiency for hardwood and softwood species.
Suitable Plants for Hardwood vs Softwood Cuttings
Hardwood cuttings are ideal for deciduous shrubs and trees such as roses, blackberries, and grapevines, thriving in dormant seasons for robust root development. Softwood cuttings suit fast-growing, herbaceous plants like coleus, azaleas, and hydrangeas, harvested from actively growing shoots in spring or early summer. Selecting the appropriate cutting type aligns with plant species and growth stage, optimizing propagation success and plant vigor.
Preparation Steps for Hardwood Cuttings
Hardwood cuttings require careful preparation, including selecting mature, disease-free stems from the previous season's growth and cutting them into 6-12 inch sections with several nodes. Removing leaves and trimming the cutting at a 45-degree angle enhances water absorption, while applying rooting hormone to the base promotes faster root development. Finally, inserting the cuttings into well-draining media at the proper depth ensures optimal moisture retention and reduces the risk of rot during propagation.
Preparation Steps for Softwood Cuttings
Softwood cuttings require selecting healthy, non-flowering shoots from the current season's growth, typically 4-6 inches long with several leaf nodes. The lower leaves are carefully removed to reduce moisture loss, while the base is often dipped in rooting hormone to enhance root development. Maintaining high humidity and placing cuttings in well-draining propagation media such as perlite or a peat-perlite mix ensures optimal conditions for root initiation.
Tools and Materials Needed for Propagation
Hardwood cuttings require clean, sharp pruning shears or a knife, rooting hormone, and well-draining potting mix, while softwood cuttings also need a misting spray bottle and a humidity dome or plastic cover to maintain moisture levels. Both methods benefit from using sterilized tools to prevent disease and containers that provide adequate drainage to encourage root development. Selecting appropriate tools and materials tailored to the wood type ensures higher success rates in plant propagation.
Rooting Conditions and Aftercare
Hardwood cuttings require a dormant period with cooler temperatures around 10-15degC and well-drained, moist soil to promote root development, while softwood cuttings thrive in warmer, humid environments of about 20-25degC with consistent moisture and indirect sunlight. Rooting hormones like auxins enhance root formation in both types, but hardwood cuttings generally take longer to root compared to the faster-rooting softwood cuttings. Aftercare involves maintaining stable humidity levels, avoiding waterlogging for hardwood cuttings, and providing gentle shading for softwood cuttings to prevent desiccation and support healthy root establishment.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Hardwood cuttings often face challenges like slow rooting and desiccation due to their dormant state, requiring careful moisture control and hormone treatments to improve success rates. Softwood cuttings are prone to wilt and fungal infections because of their tender tissue, demanding high humidity environments and sterilized tools to prevent disease. Both cutting types benefit from consistent temperature management and monitoring for pests to troubleshoot propagation issues effectively.
Success Rates: Hardwood vs Softwood Cuttings
Hardwood cuttings generally exhibit higher success rates than softwood cuttings due to their mature, lignified stems that resist desiccation and disease, promoting better root development. Softwood cuttings, derived from new, tender growth, often require precise environmental controls such as high humidity and misting to improve survival and rooting percentage. Environmental factors, species variability, and timing significantly influence propagation success in both hardwood and softwood cuttings.
Hardwood Cuttings vs Softwood Cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com