
Leaf cuttings vs cane cuttings Illustration
Leaf cuttings allow for propagation of plants that can regenerate entire new plants from leaf tissue, ideal for species like succulents and begonias, while cane cuttings involve sections of mature stems or canes, suitable for plants such as blackberries and raspberries. Leaf cuttings generally require a longer rooting period and more humidity control, whereas cane cuttings tend to root faster due to the presence of woody tissue and stored nutrients. Choosing between leaf and cane cuttings depends on the plant type and desired propagation speed.
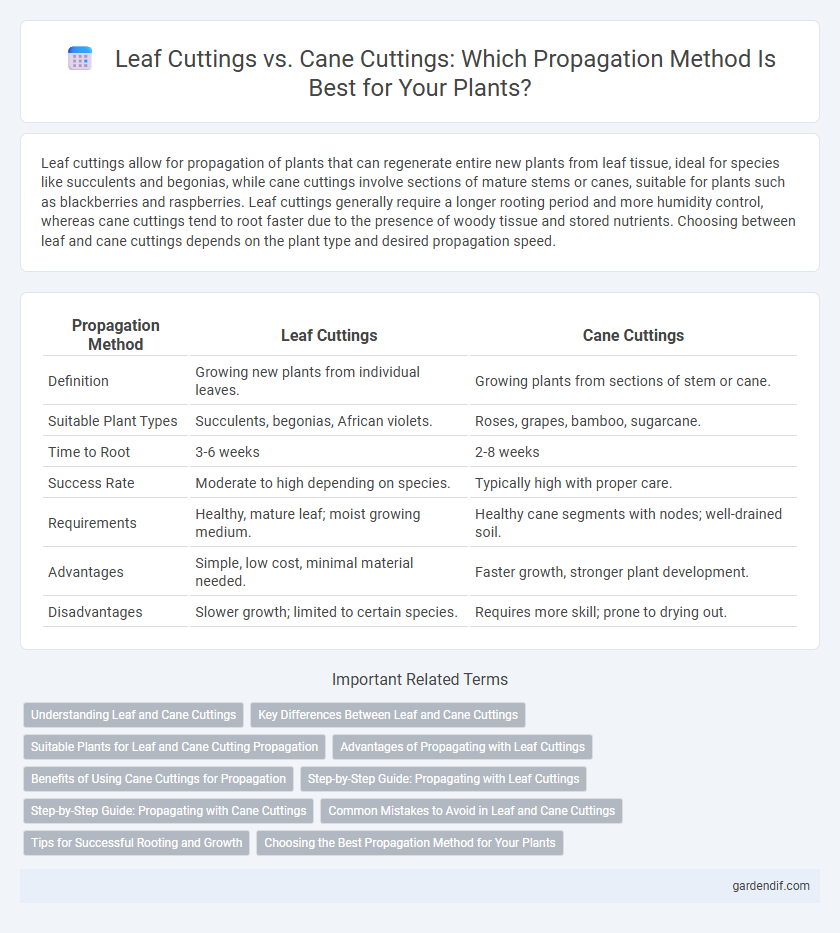
Table of Comparison
| Propagation Method | Leaf Cuttings | Cane Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing new plants from individual leaves. | Growing plants from sections of stem or cane. |
| Suitable Plant Types | Succulents, begonias, African violets. | Roses, grapes, bamboo, sugarcane. |
| Time to Root | 3-6 weeks | 2-8 weeks |
| Success Rate | Moderate to high depending on species. | Typically high with proper care. |
| Requirements | Healthy, mature leaf; moist growing medium. | Healthy cane segments with nodes; well-drained soil. |
| Advantages | Simple, low cost, minimal material needed. | Faster growth, stronger plant development. |
| Disadvantages | Slower growth; limited to certain species. | Requires more skill; prone to drying out. |
Understanding Leaf and Cane Cuttings
Leaf cuttings involve propagating plants by using a whole leaf or a section of a leaf to generate new roots and shoots, commonly applied in species like African violets and begonias. Cane cuttings utilize segments of a plant's stem, also known as canes, which contain nodes capable of developing roots and buds, making this method effective for plants such as raspberries and hydrangeas. Understanding the differences in cellular structure and rooting behavior between leaf and cane cuttings is crucial for selecting the appropriate propagation technique for specific plant species.
Key Differences Between Leaf and Cane Cuttings
Leaf cuttings involve using a single leaf or a portion of it to generate new plants, relying on the leaf's ability to produce roots and shoots, while cane cuttings utilize mature, woody stems with nodes that can develop into independent plants. Leaf cuttings are typically faster in producing new growth for plants like succulents and begonias, whereas cane cuttings are preferred for woody plants such as roses and raspberries due to their structural robustness. The success rate of propagation varies, with cane cuttings often having a higher rooting percentage given the presence of established vascular tissue compared to the more delicate leaf cuttings.
Suitable Plants for Leaf and Cane Cutting Propagation
Leaf cuttings are ideal for propagating plants like African violets, begonias, and succulents, which have large, fleshy leaves capable of generating new roots and shoots. Cane cuttings work best with woody-stemmed species such as grapes, raspberries, and crotons, where sections of the stem, or canes, are used to root and grow new plants. Choosing the right propagation method based on plant type ensures higher success rates and healthier offspring.
Advantages of Propagating with Leaf Cuttings
Propagating with leaf cuttings offers advantages such as faster root development and higher success rates compared to cane cuttings. Leaf cuttings typically require less space and fewer resources, making them ideal for mass propagation of plants like African violets and begonias. This method also allows for the production of numerous new plants from a single leaf, enhancing efficiency in nursery operations.
Benefits of Using Cane Cuttings for Propagation
Cane cuttings offer higher success rates due to their mature woody structure, which provides better moisture retention and enhanced nutrient transport compared to leaf cuttings. This method promotes faster rooting and stronger plant development, making it ideal for propagating woody plants like raspberries, blackberries, and certain ornamental shrubs. Cane cuttings also reduce vulnerability to rot and fungal infections, resulting in more robust and sustainable propagation outcomes.
Step-by-Step Guide: Propagating with Leaf Cuttings
Propagating with leaf cuttings involves selecting a healthy, mature leaf, cutting it with a clean, sharp blade, and placing the leaf base in a well-draining propagation medium. Maintaining consistent moisture and indirect sunlight accelerates root development within 2 to 4 weeks, while using rooting hormone can further enhance successful propagation rates. Monitoring for new shoots and ensuring proper humidity levels supports robust plant growth during the initial rooting phase.
Step-by-Step Guide: Propagating with Cane Cuttings
Propagating with cane cuttings involves selecting healthy, mature cane sections typically 8-12 inches long, ensuring each has multiple nodes where roots and shoots will develop. After trimming the cane into individual cuttings, remove lower leaves and dip the cut ends in rooting hormone to enhance root growth before planting in a well-draining propagation medium. Maintain consistent moisture and warm temperatures around 70-75degF for 4-6 weeks to ensure successful root establishment and new shoot development.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Leaf and Cane Cuttings
Common mistakes in leaf cuttings include using damaged or overly mature leaves, which reduces rooting success and increases the risk of rot. For cane cuttings, planting sections with insufficient nodes or failing to maintain proper humidity causes poor root development and desiccation. Avoiding these errors enhances propagation efficiency and ensures healthier plant growth.
Tips for Successful Rooting and Growth
Leaf cuttings require consistent moisture and indirect light to promote root initiation, while cane cuttings benefit from a brief drying period before planting to prevent rot. Using rooting hormones enhances root development in both methods, and maintaining a warm, humid environment accelerates growth. Proper sanitation of tools and planting medium reduces the risk of infection, ensuring healthier propagation outcomes.
Choosing the Best Propagation Method for Your Plants
Leaf cuttings work best for plants like begonias and succulents that readily regenerate from leaf tissue, ensuring fast and efficient propagation. Cane cuttings suit woody plants such as raspberries and grapes, providing sturdy stems that develop into mature plants with robust root systems. Selecting the ideal method depends on the plant species' growth habits and propagation success rates recorded in horticultural studies.
Leaf cuttings vs cane cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com