
Tissue culture vs traditional cuttings Illustration
Tissue culture offers a faster and more reliable method of propagation compared to traditional cuttings by producing disease-free and genetically uniform plants in controlled environments. This technique enables large-scale multiplication regardless of seasonal constraints, ensuring consistent quality and higher success rates. Traditional cuttings depend heavily on suitable environmental conditions and often result in variable growth outcomes and increased risk of pathogen transmission.
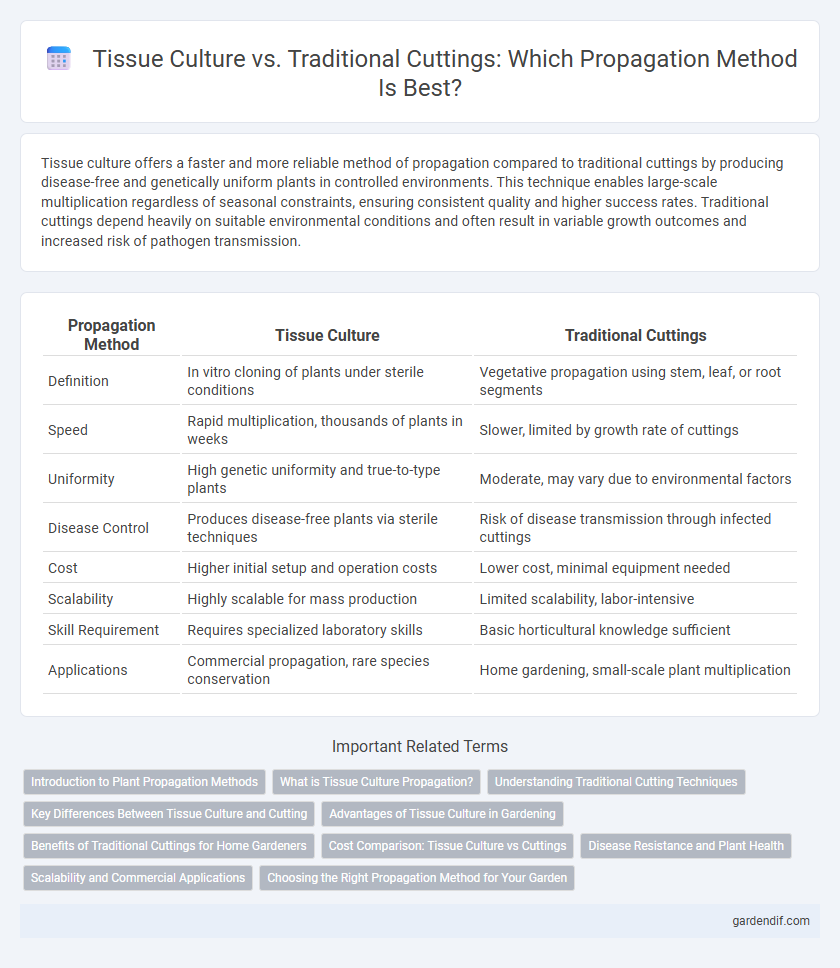
Table of Comparison
| Propagation Method | Tissue Culture | Traditional Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | In vitro cloning of plants under sterile conditions | Vegetative propagation using stem, leaf, or root segments |
| Speed | Rapid multiplication, thousands of plants in weeks | Slower, limited by growth rate of cuttings |
| Uniformity | High genetic uniformity and true-to-type plants | Moderate, may vary due to environmental factors |
| Disease Control | Produces disease-free plants via sterile techniques | Risk of disease transmission through infected cuttings |
| Cost | Higher initial setup and operation costs | Lower cost, minimal equipment needed |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for mass production | Limited scalability, labor-intensive |
| Skill Requirement | Requires specialized laboratory skills | Basic horticultural knowledge sufficient |
| Applications | Commercial propagation, rare species conservation | Home gardening, small-scale plant multiplication |
Introduction to Plant Propagation Methods
Plant propagation encompasses various techniques, with tissue culture and traditional cuttings as key methods. Tissue culture offers rapid, disease-free multiplication by growing plants from small tissue samples in sterile environments. Traditional cuttings involve rooting stem or leaf segments, providing an accessible and cost-effective approach for many species.
What is Tissue Culture Propagation?
Tissue culture propagation is a method of cloning plants by growing small tissue samples in sterile, nutrient-rich media under controlled environmental conditions. This technique enables rapid multiplication of genetically identical plants with disease-free status and uniform quality. Unlike traditional cuttings, tissue culture allows mass production of plants regardless of seasonal constraints and space limitations.
Understanding Traditional Cutting Techniques
Traditional cutting techniques involve selecting healthy parent plants and using portions such as stems, leaves, or roots to propagate new plants. This method relies on the natural ability of plant tissues to regenerate roots and shoots when placed in suitable environmental conditions, often requiring careful management of humidity, temperature, and light. Although slower and more variable than tissue culture, traditional cuttings are cost-effective and accessible for many growers aiming to replicate specific plant varieties.
Key Differences Between Tissue Culture and Cutting
Tissue culture involves the in vitro cultivation of plant cells or tissues under sterile conditions to produce genetically uniform and disease-free plants, while traditional cuttings rely on the natural rooting of plant segments in soil or water. Tissue culture offers rapid multiplication rates and mass production of clones from a small sample, whereas cuttings result in slower propagation with variable success depending on environmental factors. The precise control over growth conditions in tissue culture reduces contamination risks and enhances plant quality, contrasting with the inconsistent outcomes often seen in conventional cutting methods.
Advantages of Tissue Culture in Gardening
Tissue culture offers rapid multiplication of disease-free plants, ensuring uniformity and higher survival rates compared to traditional cuttings. This method enables large-scale propagation of rare or genetically identical plants under controlled conditions, reducing contamination risks. Enhanced efficiency and consistency make tissue culture a preferred technique for commercial and hobbyist gardeners aiming for sustainable plant production.
Benefits of Traditional Cuttings for Home Gardeners
Traditional cuttings offer home gardeners an affordable and straightforward method for plant propagation, requiring minimal specialized equipment or materials. This technique ensures genetic consistency, producing clones identical to the parent plant, which is crucial for preserving desirable traits. Furthermore, traditional cuttings often result in faster rooting and establishment in home garden conditions compared to tissue culture methods.
Cost Comparison: Tissue Culture vs Cuttings
Tissue culture offers higher initial setup costs due to lab equipment and skilled labor, but reduces long-term expenses by producing disease-free and uniform plants rapidly. Traditional cuttings have lower upfront costs, relying mainly on manual labor and simple tools, yet risk higher losses from pests and diseases, increasing overall expense. Over multiple propagation cycles, tissue culture proves more cost-effective by ensuring consistent quality and faster multiplication rates compared to traditional cuttings.
Disease Resistance and Plant Health
Tissue culture offers enhanced disease resistance by producing disease-free, sterile plantlets, reducing the risk of pathogen transmission common in traditional cuttings. This method ensures uniform plant health and vigor through controlled micropropagation environments, unlike cuttings that may carry latent infections. Implementing tissue culture significantly improves crop reliability and sustainability in commercial propagation.
Scalability and Commercial Applications
Tissue culture enables large-scale propagation with high uniformity and disease-free plants, making it ideal for commercial applications requiring mass production of genetically identical crops. Traditional cuttings, while simple and cost-effective for small-scale growers, face limitations in scalability due to slower multiplication rates and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. Commercial operations prioritize tissue culture for its efficiency in producing large quantities of high-quality planting material within shorter timeframes.
Choosing the Right Propagation Method for Your Garden
Tissue culture offers rapid multiplication of disease-free plants with uniform traits, making it ideal for large-scale propagation and rare species preservation. Traditional cuttings provide a cost-effective, simple method suitable for home gardeners and plants that root easily, ensuring genetic consistency with the parent. Selecting the right method depends on plant type, available resources, and desired scale of propagation for optimal garden success.
Tissue culture vs traditional cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com