
Node cuttings vs heel cuttings Illustration
Node cuttings involve using sections of a stem with at least one node to promote root development, ensuring faster and more reliable propagation. Heel cuttings include a small piece of older wood attached to the base of the cutting, which can enhance rooting success by providing additional stored nutrients. Both methods are effective, but node cuttings generally root quicker while heel cuttings offer greater resilience in tougher propagation conditions.
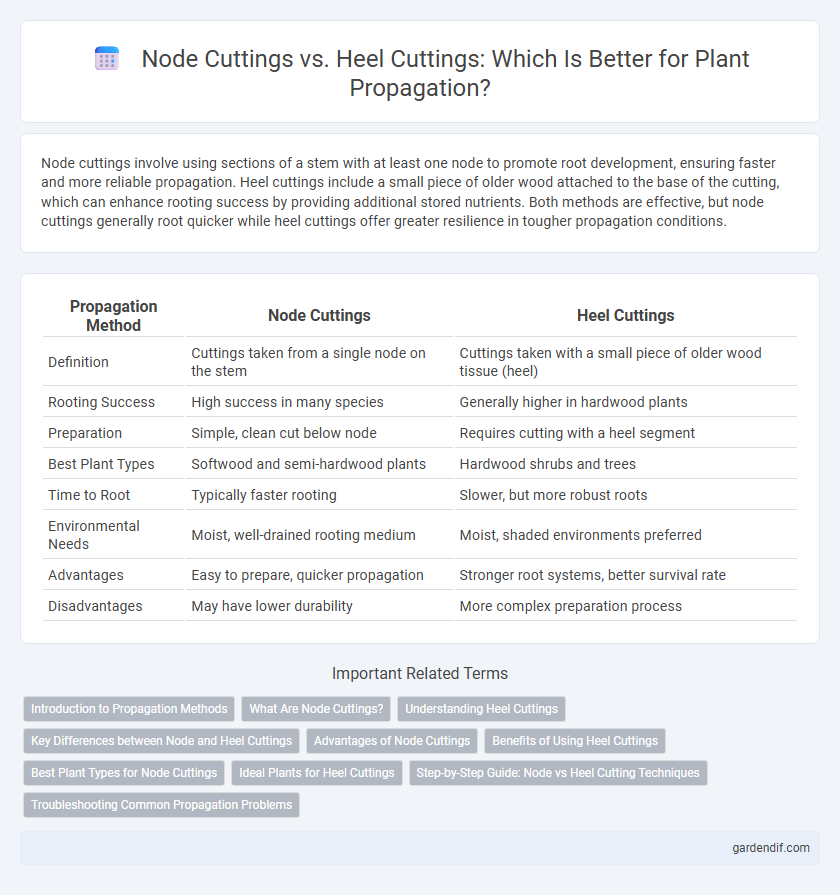
Table of Comparison
| Propagation Method | Node Cuttings | Heel Cuttings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cuttings taken from a single node on the stem | Cuttings taken with a small piece of older wood tissue (heel) |
| Rooting Success | High success in many species | Generally higher in hardwood plants |
| Preparation | Simple, clean cut below node | Requires cutting with a heel segment |
| Best Plant Types | Softwood and semi-hardwood plants | Hardwood shrubs and trees |
| Time to Root | Typically faster rooting | Slower, but more robust roots |
| Environmental Needs | Moist, well-drained rooting medium | Moist, shaded environments preferred |
| Advantages | Easy to prepare, quicker propagation | Stronger root systems, better survival rate |
| Disadvantages | May have lower durability | More complex preparation process |
Introduction to Propagation Methods
Node cuttings involve using a segment of a stem with nodes to encourage root development, making them ideal for plants with strong stem tissues. Heel cuttings include a small portion of older wood from the previous season's growth, which provides increased rooting hormones and improves success rates in woody plants. Both methods are fundamental in vegetative propagation, allowing growers to produce clones with specific desired traits efficiently.
What Are Node Cuttings?
Node cuttings involve propagating plants by cutting sections of stems that contain nodes, which are critical growth points where leaves, roots, and buds develop. These cuttings capitalize on the nodes' ability to generate roots and shoots, making them highly effective for producing new plants. Node cuttings are commonly used in propagation of species like coleus, pothos, and philodendrons due to their rapid root initiation from nodes.
Understanding Heel Cuttings
Heel cuttings involve taking a portion of the stem with a small piece of the previous season's wood attached, enhancing rooting success compared to simple node cuttings. This method provides greater carbohydrate reserves and hormonal balance, critical for root initiation and early growth development. Understanding heel cuttings enables propagators to improve plant viability and establish stronger, more resilient root systems.
Key Differences between Node and Heel Cuttings
Node cuttings contain a section of stem with one or more nodes, where buds can develop into new shoots, making them effective for propagating many woody and herbaceous plants. Heel cuttings include a small portion of the older stem tissue attached below the node, which helps improve rooting success by providing additional cambium tissue for nutrient transport. The key difference lies in the presence of this older stem segment in heel cuttings, which enhances root initiation and plant vigor compared to node cuttings.
Advantages of Node Cuttings
Node cuttings offer enhanced rooting potential due to the presence of active meristematic tissues at the nodes, which accelerates new root development compared to heel cuttings. They typically result in higher propagation success rates and more vigorous plant growth because nodes contain essential nutrients and growth hormones. This method also reduces the likelihood of disease transmission, ensuring healthier plant propagation overall.
Benefits of Using Heel Cuttings
Heel cuttings preserve a small portion of the original stem tissue, enhancing root formation by maintaining hormone-rich cambium and vascular connections. This method results in higher rooting success rates and faster establishment compared to standard node cuttings. Utilizing heel cuttings also improves plant vigor and reduces the risk of cutting desiccation, promoting healthier propagation outcomes.
Best Plant Types for Node Cuttings
Node cuttings are ideal for plants with pronounced nodes such as coleus, jasmine, and hydrangeas, where new roots readily develop from these specialized regions. These cuttings ensure faster rooting and higher success rates due to the presence of dormant buds and vascular tissues at the nodes. Plants with woody or semi-woody stems, including blackberries and grapevines, especially benefit from node cuttings for effective propagation.
Ideal Plants for Heel Cuttings
Heel cuttings are ideal for semi-hardwood plants with established root systems, such as camellias, azaleas, and gardenias, which root more successfully when a portion of older wood is retained. These plants benefit from the heel's attached tissue, providing hormones and nutrients that enhance root formation compared to simple nodal cuttings. Using heel cuttings increases propagation success in woody shrubs and ornamental plants requiring stable, durable growth.
Step-by-Step Guide: Node vs Heel Cutting Techniques
Node cuttings involve selecting stem sections containing one or more nodes, cutting just below a node, and planting horizontally or vertically to encourage root formation at the nodes. Heel cuttings are taken by removing shoots with a small wedge of mature wood, maintaining a piece of older stem tissue to improve rooting success. Both techniques require preparing cuttings with clean tools, applying rooting hormone for better establishment, and ensuring consistent moisture and humidity for optimal propagation results.
Troubleshooting Common Propagation Problems
Node cuttings often root faster due to the presence of natural growth nodes, but they can suffer from fungal infections if kept too moist, requiring careful moisture control to prevent rot. Heel cuttings, taken with a small section of mature stem, offer increased rooting success for woody plants but can experience delayed root development if cuttings are too old or taken incorrectly. Managing humidity levels, using sterilized tools, and selecting healthy plant material are essential troubleshooting steps to overcome common propagation challenges with both methods.
Node cuttings vs heel cuttings Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com