
Biodynamic gardening vs conventional gardening Illustration
Biodynamic gardening emphasizes holistic soil health and cosmic rhythms, using natural composts and herbal preparations to enhance plant vitality. Conventional gardening often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, prioritizing immediate yield over long-term ecosystem balance. Biodynamic methods foster resilient, sustainable growth by integrating ecological and spiritual principles beyond standard organic practices.
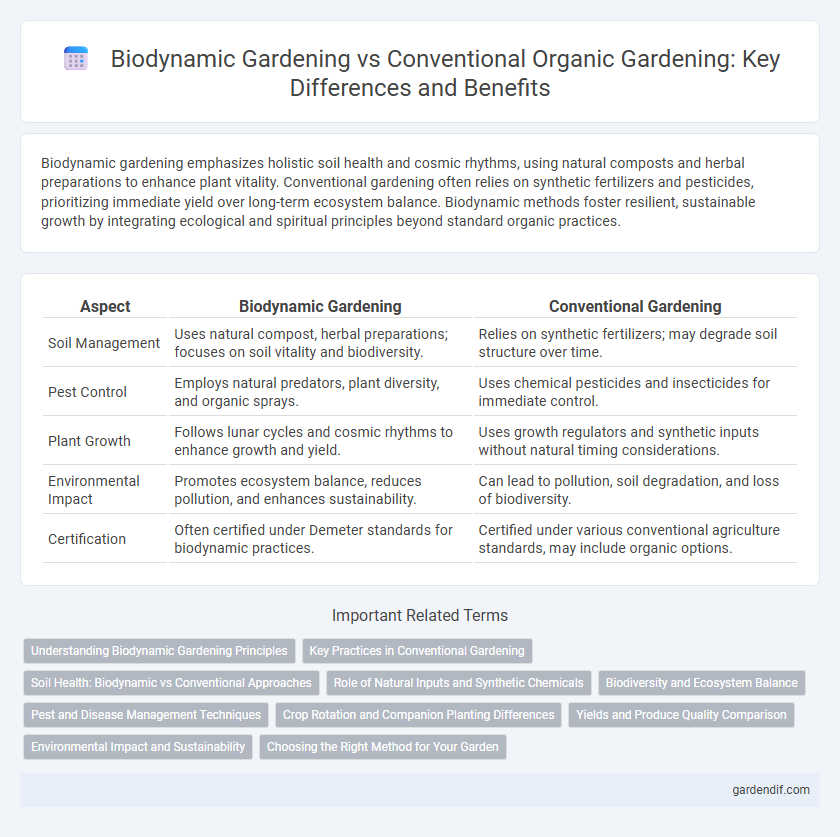
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Biodynamic Gardening | Conventional Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Management | Uses natural compost, herbal preparations; focuses on soil vitality and biodiversity. | Relies on synthetic fertilizers; may degrade soil structure over time. |
| Pest Control | Employs natural predators, plant diversity, and organic sprays. | Uses chemical pesticides and insecticides for immediate control. |
| Plant Growth | Follows lunar cycles and cosmic rhythms to enhance growth and yield. | Uses growth regulators and synthetic inputs without natural timing considerations. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes ecosystem balance, reduces pollution, and enhances sustainability. | Can lead to pollution, soil degradation, and loss of biodiversity. |
| Certification | Often certified under Demeter standards for biodynamic practices. | Certified under various conventional agriculture standards, may include organic options. |
Understanding Biodynamic Gardening Principles
Biodynamic gardening integrates holistic principles based on Rudolf Steiner's philosophy, emphasizing soil fertility, plant health, and cosmic rhythms to create a self-sustaining ecosystem. This method uses herbal preparations, composting techniques, and lunar planting calendars to enhance soil vitality and promote plant resilience, contrasting with conventional gardening that often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Emphasizing biodiversity and natural cycles, biodynamic gardening fosters ecological balance and long-term sustainability in organic agriculture.
Key Practices in Conventional Gardening
Conventional gardening primarily relies on synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides to enhance plant growth and manage pests, often prioritizing high yield and uniform crop production. Soil is frequently tilled to prepare seedbeds, which can lead to soil erosion and nutrient depletion over time. Irrigation in conventional systems tends to use standard methods without emphasizing water conservation or soil health enhancement.
Soil Health: Biodynamic vs Conventional Approaches
Biodynamic gardening emphasizes soil vitality through the use of compost, biodynamic preparations, and crop rotation to enhance microbial diversity and soil structure. Conventional gardening often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides that may degrade soil organic matter and disrupt soil ecosystems over time. Studies show biodynamic methods increase soil nutrient availability and promote resilient soil health compared to conventional techniques.
Role of Natural Inputs and Synthetic Chemicals
Biodynamic gardening relies heavily on natural inputs such as compost, herbal preparations, and biodynamic compost teas to enhance soil health and plant vitality, avoiding synthetic chemicals entirely. In contrast, conventional gardening often uses synthetic fertilizers and pesticides to boost growth and manage pests, which can disrupt soil ecosystems and reduce biodiversity. The emphasis on natural inputs in biodynamic gardening supports sustainable nutrient cycles and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Balance
Biodynamic gardening enhances biodiversity by integrating crop diversity, livestock, and natural composting methods, fostering resilient ecosystems and robust soil health. Conventional gardening often relies on monocultures and synthetic inputs, which can disrupt ecological balance and reduce habitat variety for beneficial organisms. Emphasizing holistic ecosystem management, biodynamic practices promote symbiotic relationships that sustain long-term environmental stability and biodiversity richness.
Pest and Disease Management Techniques
Biodynamic gardening employs natural pest and disease management techniques such as herbal sprays, companion planting, and biodynamic preparations like horn manure to enhance soil vitality and plant resilience. Conventional gardening often relies on synthetic pesticides and fungicides to control pests and diseases, which can lead to chemical residues and resistance issues. The holistic approach in biodynamic methods promotes ecological balance and long-term soil health, reducing dependency on chemical interventions.
Crop Rotation and Companion Planting Differences
Biodynamic gardening emphasizes crop rotation and companion planting based on lunar cycles and cosmic rhythms to enhance soil vitality and plant health, unlike conventional gardening which follows fixed crop rotation schedules primarily to manage pests and nutrient depletion. In biodynamic practices, companion planting incorporates plants that promote energetic balance and biodiversity, while conventional methods focus on practical benefits like pest control and yield optimization. These distinctions result in biodynamic gardens fostering holistic ecosystem resilience compared to the more utilitarian approach in conventional gardening.
Yields and Produce Quality Comparison
Biodynamic gardening typically yields crops with higher nutrient density and enhanced flavor profiles compared to conventional gardening, which often relies on synthetic inputs that may boost volume but can compromise produce quality. Studies indicate biodynamic methods improve soil health and microbial activity, resulting in more resilient plants and superior harvests. Conventional gardening may produce higher immediate yields, but biodynamic practices emphasize sustainability and long-term soil fertility, leading to consistent, high-quality produce over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Biodynamic gardening promotes soil health and biodiversity by using natural composts and crop rotations, significantly reducing chemical runoff and soil erosion compared to conventional gardening. Conventional methods often rely on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, leading to pollution and long-term soil degradation. Sustainability in biodynamic gardening is enhanced through closed-loop systems and plant diversity, fostering resilient ecosystems and minimizing environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Garden
Biodynamic gardening emphasizes holistic soil health and cosmic rhythms, using natural preparations to enhance plant vitality, while conventional gardening often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides for immediate results. Selecting the right method depends on your garden's goals, sustainability priorities, and commitment to ecological balance. Integrating biodynamic practices can improve biodiversity and soil structure, making it ideal for gardeners focused on long-term environmental health.
Biodynamic gardening vs conventional gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com