
Rainwater irrigation vs Tap water irrigation Illustration
Rainwater irrigation conserves resources by utilizing natural precipitation, reducing dependency on treated tap water and minimizing environmental impact. Unlike tap water, rainwater is free from chemicals like chlorine and fluoride, promoting healthier soil and plant growth. Implementing rainwater irrigation also lowers water bills and supports sustainable gardening practices.
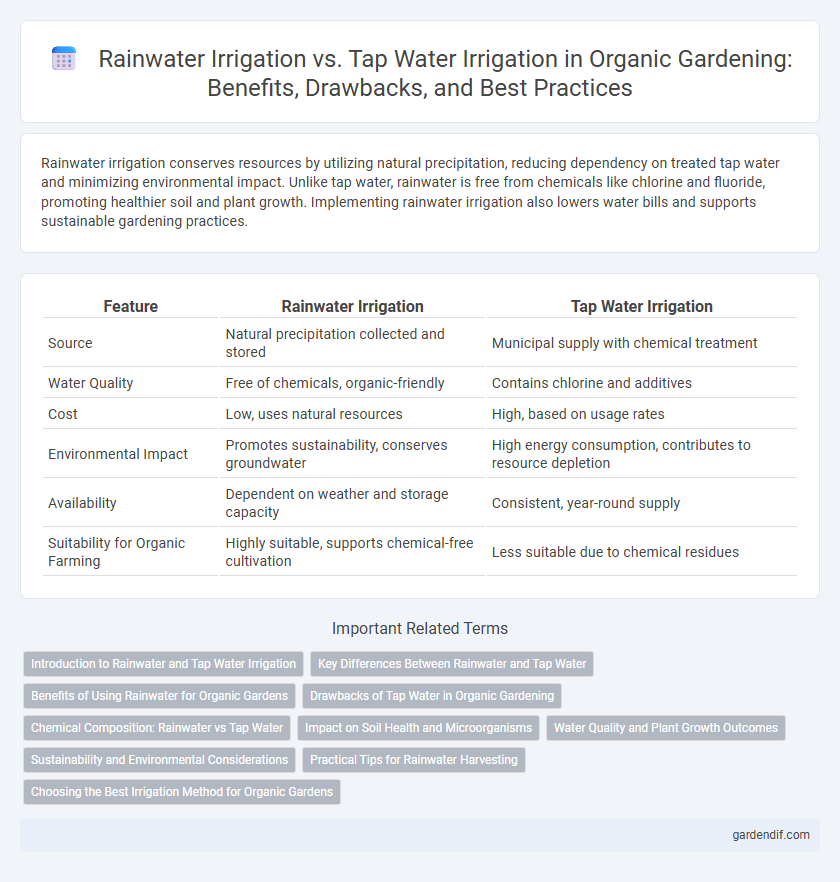
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rainwater Irrigation | Tap Water Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural precipitation collected and stored | Municipal supply with chemical treatment |
| Water Quality | Free of chemicals, organic-friendly | Contains chlorine and additives |
| Cost | Low, uses natural resources | High, based on usage rates |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability, conserves groundwater | High energy consumption, contributes to resource depletion |
| Availability | Dependent on weather and storage capacity | Consistent, year-round supply |
| Suitability for Organic Farming | Highly suitable, supports chemical-free cultivation | Less suitable due to chemical residues |
Introduction to Rainwater and Tap Water Irrigation
Rainwater irrigation utilizes naturally collected rainwater, reducing dependency on municipal sources and minimizing environmental impact through sustainable water management. Tap water irrigation relies on treated municipal water, which often involves higher energy consumption and chemical additives, potentially affecting soil health and crop quality. Choosing rainwater irrigation can enhance organic farming practices by preserving soil microbiomes and reducing exposure to chlorinated water.
Key Differences Between Rainwater and Tap Water
Rainwater irrigation utilizes naturally collected precipitation, offering a chemical-free and sustainably sourced water option that reduces dependency on municipal systems. Tap water irrigation relies on treated water from public supplies, often containing chlorine and other additives that can affect soil health and plant growth over time. Key differences include mineral content, availability, and environmental impact, with rainwater generally promoting healthier soil microbiomes and conserving potable water resources.
Benefits of Using Rainwater for Organic Gardens
Rainwater irrigation conserves energy and reduces reliance on treated tap water, promoting sustainability in organic gardens. It naturally contains fewer chemicals and salts, preserving soil health and enhancing microbial activity essential for plant growth. Using rainwater minimizes water bills and supports the organic garden's eco-friendly principles by harnessing a renewable, chemical-free water source.
Drawbacks of Tap Water in Organic Gardening
Tap water irrigation in organic gardening often contains chlorine and fluoride, which can disrupt soil microbial activity and harm beneficial organisms essential for nutrient cycling. The presence of dissolved salts and chemicals in tap water may lead to soil salinization, reducing soil fertility and inhibiting plant growth over time. In contrast, rainwater provides a natural, chemical-free alternative that supports a healthy soil ecosystem and promotes sustainable organic cultivation.
Chemical Composition: Rainwater vs Tap Water
Rainwater irrigation contains minimal chemical additives, primarily consisting of dissolved atmospheric gases and trace minerals, resulting in softer water with a neutral pH ideal for organic soil health. Tap water often contains chlorine, fluoride, and various salts added for disinfection and safety, which can accumulate in the soil and alter its chemical balance over time. The lower chemical load in rainwater supports beneficial microbial activity and reduces the risk of plant stress caused by accumulated chemicals in tap water irrigation.
Impact on Soil Health and Microorganisms
Rainwater irrigation supports soil health by maintaining natural pH levels and providing nutrient-rich water free of chlorine and fluoride, which can harm beneficial microorganisms. Tap water irrigation often contains chemicals and minerals that disrupt soil microbial communities, reducing microbial diversity and activity essential for nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition. Consistent use of rainwater promotes a balanced microbial ecosystem, enhancing soil structure and fertility for sustainable organic agriculture.
Water Quality and Plant Growth Outcomes
Rainwater irrigation typically contains fewer chemicals and salts compared to tap water, promoting healthier soil microbiota and improved nutrient absorption for organic plants. Tap water often includes chlorine and fluoride, which can accumulate in soil and potentially hinder plant growth over time. Studies show rainwater irrigation leads to more robust plant development and higher yields in organic gardening due to its superior water quality.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Rainwater irrigation significantly reduces dependence on municipal tap water, conserving valuable freshwater resources and decreasing strain on urban water supply systems. It minimizes chemical runoff and pollution by eliminating the need for treated water, promoting healthier soil and plant ecosystems. Using rainwater also lowers energy consumption associated with water treatment and distribution, enhancing overall sustainability in agricultural practices.
Practical Tips for Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater irrigation offers nutrient-rich water that enhances soil health and reduces dependence on chemical fertilizers compared to tap water irrigation. Installing gutters, downspouts, and storage tanks allows efficient collection and minimizes water waste while promoting sustainable gardening practices. Regular maintenance of filtration systems and monitoring water quality ensures optimal irrigation performance and plant growth.
Choosing the Best Irrigation Method for Organic Gardens
Rainwater irrigation preserves soil health by avoiding chemicals and chlorine found in tap water, enhancing microbial activity essential for organic gardens. Tap water often contains salts and additives that can accumulate in soil, potentially harming sensitive organic plants over time. Selecting rainwater irrigation supports sustainable gardening practices by conserving water and promoting nutrient-rich, natural growth environments.
Rainwater irrigation vs Tap water irrigation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com