
Neem oil vs systemic pesticides Illustration
Neem oil offers a natural, eco-friendly alternative to systemic pesticides by targeting pests without harming beneficial insects or contaminating the soil. Unlike systemic pesticides that penetrate plant tissues and can accumulate in the environment, neem oil acts as a bio-pesticide with a low toxicity profile and biodegradable properties. Its use promotes sustainable agriculture and reduces the risk of resistance development in pests.
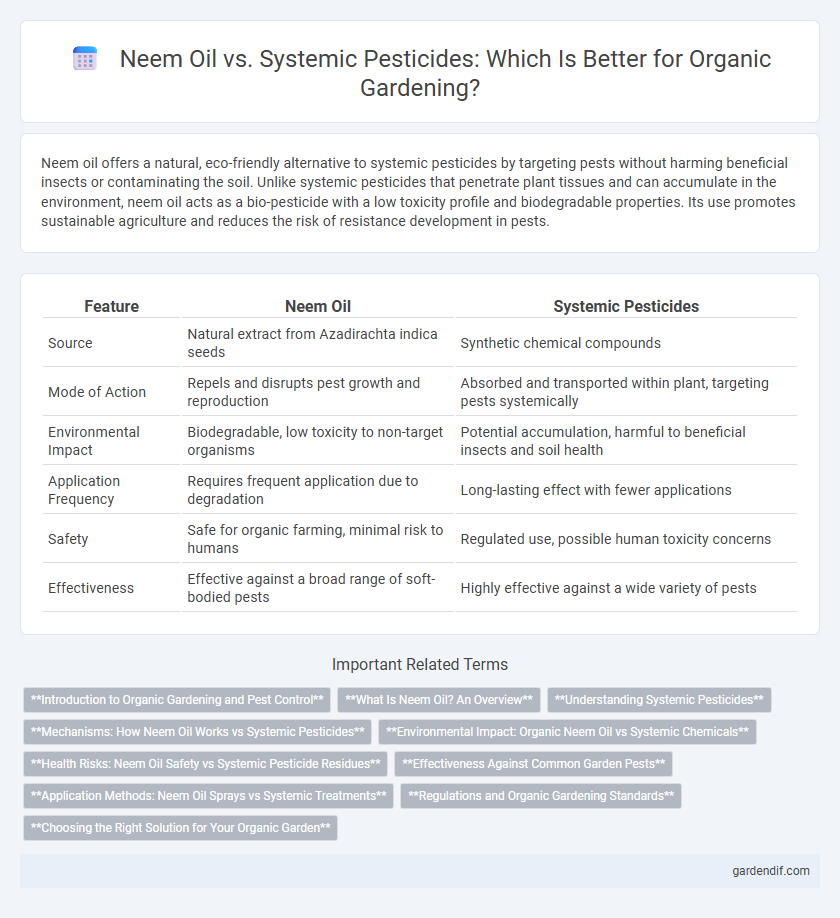
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Neem Oil | Systemic Pesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural extract from Azadirachta indica seeds | Synthetic chemical compounds |
| Mode of Action | Repels and disrupts pest growth and reproduction | Absorbed and transported within plant, targeting pests systemically |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low toxicity to non-target organisms | Potential accumulation, harmful to beneficial insects and soil health |
| Application Frequency | Requires frequent application due to degradation | Long-lasting effect with fewer applications |
| Safety | Safe for organic farming, minimal risk to humans | Regulated use, possible human toxicity concerns |
| Effectiveness | Effective against a broad range of soft-bodied pests | Highly effective against a wide variety of pests |
Introduction to Organic Gardening and Pest Control
Neem oil, derived from the seeds of the Azadirachta indica tree, offers a natural, biodegradable alternative to systemic pesticides in organic gardening. It controls a broad spectrum of pests by disrupting insect growth and feeding patterns without harming beneficial insects or the environment. Unlike synthetic systemic pesticides, neem oil promotes sustainable pest control by maintaining soil health and supporting biodiversity in organic ecosystems.
What Is Neem Oil? An Overview
Neem oil is a natural extract derived from the seeds of the Neem tree (Azadirachta indica), widely recognized for its organic pest control properties. It contains azadirachtin, a bioactive compound that disrupts insect growth and reproduction without harming beneficial organisms or pollinators. Unlike systemic pesticides, neem oil acts as a topical insect repellent and biopesticide, breaking down quickly in the environment and posing minimal risk to soil and water health.
Understanding Systemic Pesticides
Systemic pesticides are absorbed by plants and transported through their vascular system to protect against pests from within, offering long-lasting protection compared to surface-applied treatments like neem oil. Unlike neem oil, which acts primarily as a contact insecticide and repellent derived from Azadirachta indica seeds, systemic pesticides penetrate plant tissues to target sap-feeding insects and larvae effectively. The extensive persistence and internalized mode of action of systemic pesticides raise concerns about environmental impact and non-target organism safety, making neem oil a preferred choice for organic and sustainable pest management.
Mechanisms: How Neem Oil Works vs Systemic Pesticides
Neem oil acts as a natural insect repellent and growth regulator by disrupting the hormonal system of pests, particularly through its active compound azadirachtin that inhibits feeding and reproduction. Systemic pesticides are absorbed by plant tissues and transported throughout, targeting pests internally by interfering with their nervous system or metabolic processes. While neem oil offers a broad-spectrum, eco-friendly mode of action with minimal resistance buildup, systemic pesticides provide stronger, targeted pest control but pose higher risks to beneficial organisms and environmental health.
Environmental Impact: Organic Neem Oil vs Systemic Chemicals
Neem oil, derived from the neem tree, offers a biodegradable, eco-friendly alternative to systemic pesticides that often persist in soil and water, causing long-term environmental harm. Unlike synthetic systemic chemicals, neem oil targets pests with minimal impact on beneficial insects, pollinators, and soil microbiota, preserving biodiversity and ecosystem balance. The use of neem oil in organic agriculture reduces chemical residues and mitigates contamination risks to wildlife and groundwater, supporting sustainable pest management practices.
Health Risks: Neem Oil Safety vs Systemic Pesticide Residues
Neem oil is widely regarded for its low toxicity and biodegradability, posing minimal health risks to humans and beneficial insects compared to systemic pesticides, which often leave harmful residues in crops and soil. Systemic pesticides, absorbed by plants and distributed internally, can accumulate in edible plant parts, increasing exposure risks to consumers and potentially causing long-term health issues such as neurotoxicity and hormone disruption. Neem oil's natural insecticidal properties offer a safer alternative by effectively managing pests without the persistent chemical residues associated with synthetic systemic pesticides.
Effectiveness Against Common Garden Pests
Neem oil effectively targets a wide range of common garden pests such as aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, and caterpillars by disrupting their hormonal balance and inhibiting feeding. Systemic pesticides penetrate plant tissues to provide long-lasting protection by killing pests on contact or ingestion, but they may also impact beneficial insects and soil health. Organic gardeners prefer neem oil for its biodegradability and lower toxicity, balancing pest control with environmental safety.
Application Methods: Neem Oil Sprays vs Systemic Treatments
Neem oil sprays are applied topically, targeting pests directly on plant surfaces and disrupting insect feeding and reproduction through contact and ingestion. Systemic pesticides are absorbed by plants and distributed internally via vascular tissues, offering protection from pests that feed beneath the surface or are difficult to reach with sprays. Neem oil's surface application minimizes environmental impact and reduces chemical residues, while systemic treatments provide longer-lasting pest control but carry higher risks of toxicity and resistance development.
Regulations and Organic Gardening Standards
Neem oil complies with organic gardening standards and is approved by major certification bodies such as OMRI and EPA for organic use due to its natural, biodegradable properties. In contrast, systemic pesticides often contain synthetic chemicals that are restricted or banned under organic regulations because they can persist in soil and harm non-target organisms. Organic gardening standards emphasize the use of neem oil to maintain ecosystem balance and promote sustainable pest management without compromising soil and plant health.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Organic Garden
Neem oil offers a natural, biodegradable alternative to systemic pesticides, effectively controlling pests while preserving beneficial insects and soil health in organic gardens. Systemic pesticides, though potent, often leave harmful residues that can disrupt the delicate balance of an organic ecosystem. Selecting neem oil aligns with sustainable gardening practices by ensuring pest control without compromising the principles of organic cultivation.
Neem oil vs systemic pesticides Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com