
Organic Mulch vs Synthetic Mulch Illustration
Organic mulch, made from natural materials like wood chips, leaves, or straw, enriches soil fertility and supports beneficial microbial activity as it decomposes. Synthetic mulch, typically composed of plastic or rubber, offers longer-lasting weed suppression and moisture retention but lacks soil-enriching properties. Choosing between organic and synthetic mulch depends on balancing environmental benefits with durability and maintenance preferences.
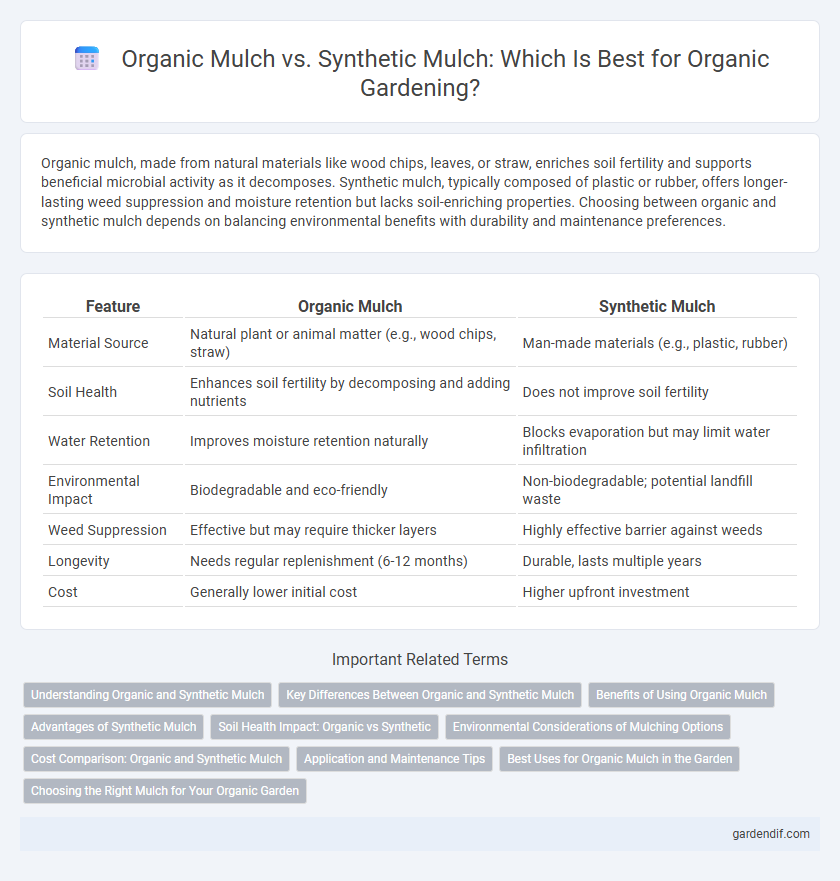
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Organic Mulch | Synthetic Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural plant or animal matter (e.g., wood chips, straw) | Man-made materials (e.g., plastic, rubber) |
| Soil Health | Enhances soil fertility by decomposing and adding nutrients | Does not improve soil fertility |
| Water Retention | Improves moisture retention naturally | Blocks evaporation but may limit water infiltration |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable; potential landfill waste |
| Weed Suppression | Effective but may require thicker layers | Highly effective barrier against weeds |
| Longevity | Needs regular replenishment (6-12 months) | Durable, lasts multiple years |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
Understanding Organic and Synthetic Mulch
Organic mulch, derived from natural materials like wood chips, leaves, and compost, improves soil fertility by decomposing and enriching the earth with essential nutrients. Synthetic mulch, made from plastic or rubber, provides long-lasting weed control and moisture retention but lacks nutrient contribution to the soil. Choosing between organic and synthetic mulch depends on factors such as soil health goals, environmental impact, and maintenance preferences.
Key Differences Between Organic and Synthetic Mulch
Organic mulch, derived from natural materials like wood chips, bark, and leaves, enhances soil fertility by decomposing and enriching the soil with nutrients. Synthetic mulch, made from plastic or rubber, provides longer-lasting weed control and moisture retention but lacks nutrient contribution and may impact soil health negatively. Key differences include biodegradability, nutrient addition, environmental impact, and long-term soil benefits, favoring organic mulch for sustainable gardening.
Benefits of Using Organic Mulch
Organic mulch improves soil health by adding essential nutrients and enhancing microbial activity, promoting sustainable plant growth. It effectively conserves moisture, reduces erosion, and regulates soil temperature, creating an ideal environment for roots. Organic mulch also suppresses weed growth naturally, minimizing the need for chemical herbicides and supporting eco-friendly gardening practices.
Advantages of Synthetic Mulch
Synthetic mulch offers superior durability and longevity compared to organic mulch, reducing the need for frequent replacement and maintenance. Its impermeable barrier effectively suppresses weeds and conserves soil moisture by minimizing evaporation. Additionally, synthetic mulch does not decompose, making it an ideal choice for long-term landscaping projects where consistent appearance and performance are desired.
Soil Health Impact: Organic vs Synthetic
Organic mulch improves soil health by enhancing microbial activity, increasing nutrient availability, and promoting moisture retention, leading to healthier plant growth. Synthetic mulch, while effective at weed control, can impede soil aeration and water infiltration, potentially disrupting natural soil ecosystems. Over time, organic mulch decomposes to enrich soil organic matter, whereas synthetic mulch may contribute to soil compaction and pollution.
Environmental Considerations of Mulching Options
Organic mulch, such as wood chips, straw, and compost, enhances soil health by improving water retention, promoting microbial activity, and gradually decomposing into nutrient-rich humus, which supports sustainable gardening practices. Synthetic mulch, typically made from plastics or rubber, can reduce water evaporation and weed growth but poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradability and potential to leach harmful chemicals into the soil. Choosing organic mulch aligns with eco-friendly goals by minimizing pollution and supporting soil biodiversity, while synthetic options may contribute to long-term soil degradation and landfill waste.
Cost Comparison: Organic and Synthetic Mulch
Organic mulch, such as wood chips and straw, generally costs between $20 to $60 per cubic yard and requires more frequent replacement due to decomposition, increasing long-term expenses. Synthetic mulch, like rubber or plastic mulch, typically ranges from $50 to $100 per cubic yard with higher initial costs but lower maintenance and longer durability. Evaluating total cost over time reveals synthetic mulch can be more cost-effective despite upfront investment, while organic mulch offers environmental benefits and soil enrichment.
Application and Maintenance Tips
Organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, improves soil health by decomposing and adding nutrients while requiring periodic replenishment every season for optimal effectiveness. Synthetic mulch, typically made from plastic or rubber, offers long-lasting weed control and moisture retention but demands careful installation to prevent soil overheating and occasional cleaning to remove debris. Proper application involves spreading organic mulch in a 2-4 inch layer around plants, whereas synthetic mulch needs secure anchoring and must be monitored for damage or wear over time.
Best Uses for Organic Mulch in the Garden
Organic mulch, such as wood chips, straw, and compost, excels in improving soil fertility by breaking down and adding essential nutrients. It is best used around vegetable gardens, flower beds, and trees to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and enhance soil structure. Organic mulch also supports beneficial microorganisms, promoting a healthy, sustainable garden ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Organic Garden
Organic mulch, made from natural materials like wood chips, straw, and compost, enriches soil health by enhancing microbial activity and improving moisture retention in organic gardens. Synthetic mulch, typically composed of plastic or rubber, provides effective weed control and temperature regulation but lacks nutrient contributions and biodegradability. Choosing the right mulch for your organic garden depends on prioritizing soil fertility, environmental impact, and long-term sustainability goals, with organic mulch generally favored for supporting ecological balance.
Organic Mulch vs Synthetic Mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com