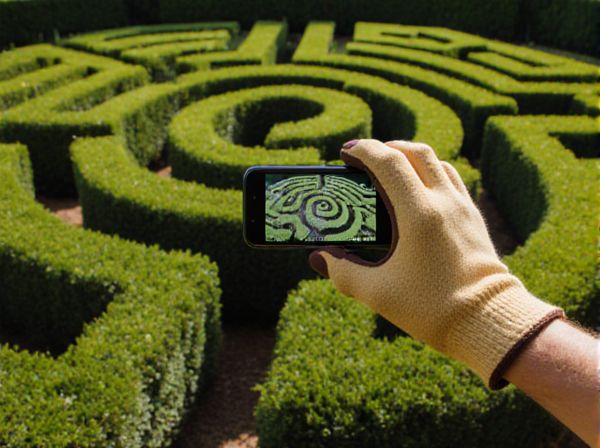

Hedge Maze vs Parterre Illustration
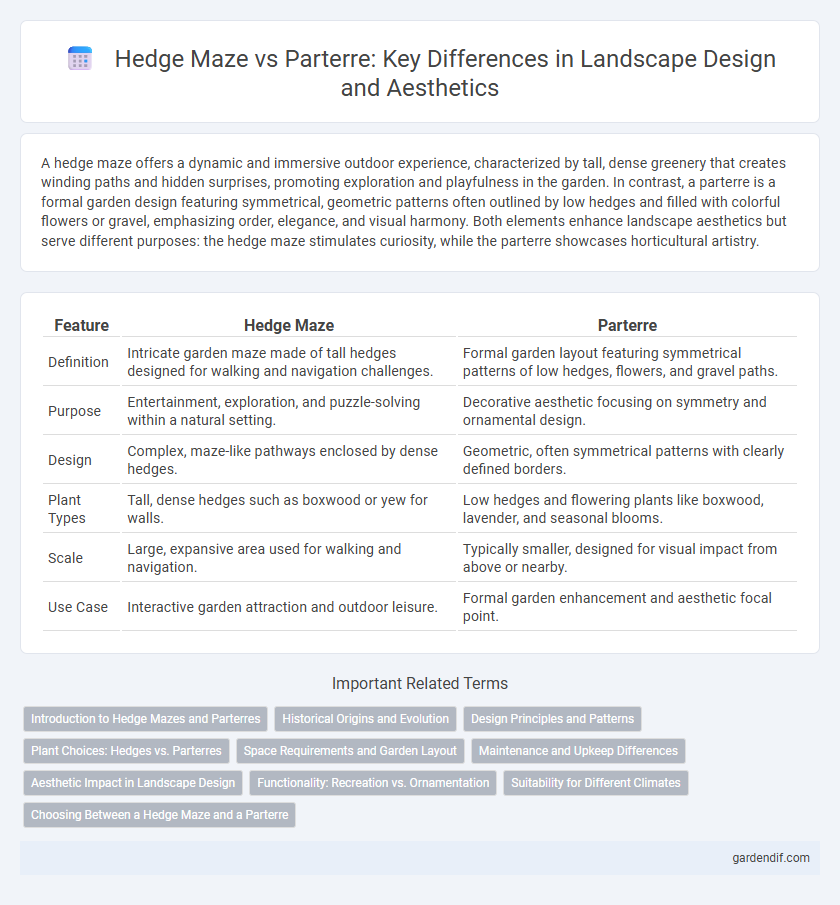
A hedge maze offers a dynamic and immersive outdoor experience, characterized by tall, dense greenery that creates winding paths and hidden surprises, promoting exploration and playfulness in the garden. In contrast, a parterre is a formal garden design featuring symmetrical, geometric patterns often outlined by low hedges and filled with colorful flowers or gravel, emphasizing order, elegance, and visual harmony. Both elements enhance landscape aesthetics but serve different purposes: the hedge maze stimulates curiosity, while the parterre showcases horticultural artistry.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hedge Maze | Parterre |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intricate garden maze made of tall hedges designed for walking and navigation challenges. | Formal garden layout featuring symmetrical patterns of low hedges, flowers, and gravel paths. |
| Purpose | Entertainment, exploration, and puzzle-solving within a natural setting. | Decorative aesthetic focusing on symmetry and ornamental design. |
| Design | Complex, maze-like pathways enclosed by dense hedges. | Geometric, often symmetrical patterns with clearly defined borders. |
| Plant Types | Tall, dense hedges such as boxwood or yew for walls. | Low hedges and flowering plants like boxwood, lavender, and seasonal blooms. |
| Scale | Large, expansive area used for walking and navigation. | Typically smaller, designed for visual impact from above or nearby. |
| Use Case | Interactive garden attraction and outdoor leisure. | Formal garden enhancement and aesthetic focal point. |
Introduction to Hedge Mazes and Parterres
Hedge mazes are intricate garden features created by planting tall, dense hedges in complex, labyrinthine patterns designed to challenge visitors' navigation skills, often serving both decorative and recreational purposes. Parterres are formal garden beds arranged in symmetrical, geometric patterns with low, trimmed hedges or flower borders, emphasizing aesthetic precision and order rather than maze complexity. Both elements highlight classic landscape design principles, with hedge mazes focusing on interactive exploration and parterres on visual harmony and structure.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Hedge mazes originated in European Renaissance gardens, designed as intricate labyrinths for entertainment and symbolic exploration, evolving from medieval hedge gardens that emphasized mystery and challenge. Parterres, tracing back to 16th-century French formal gardens, showcase symmetrical arrangements of low hedges and colorful flower beds that highlight geometric patterns and order. Both reflect evolving landscape aesthetics: hedge mazes focus on complexity and intrigue, while parterres emphasize precision and ornamental beauty.
Design Principles and Patterns
A hedge maze emphasizes complexity and exploration through winding pathways and dense greenery, creating an immersive experience with strategic sightlines and enclosed spaces. Parterres prioritize symmetrical patterns and geometric precision, utilizing low, clipped hedges and ornamental plantings to form visually striking, formal garden designs. Both designs rely on balance and repetition, but hedge mazes focus on mystery and movement, while parterres highlight order and aesthetic harmony.
Plant Choices: Hedges vs. Parterres
Hedge mazes primarily use dense, fast-growing shrubs such as boxwood, yew, and privet to create tall, structured walls that define intricate pathways and enclosures. Parterres emphasize low-growing, colorful plants like ornamental herbs, flowering annuals, and ground covers arranged in symmetrical patterns to highlight geometric designs. Selecting appropriate plants for hedges ensures privacy and height, while parterre vegetation focuses on texture, color contrast, and seasonal interest within a flat, ornamental framework.
Space Requirements and Garden Layout
Hedge mazes require significant space, often spanning several acres to accommodate intricate pathways and high hedges, making them suitable for large estate gardens. Parterres are more compact and geometric, designed for smaller, formal garden layouts with symmetrical patterns and low, decorative plantings that emphasize visual elegance. The layout of a hedge maze prioritizes complexity and exploration, while parterres focus on order and aesthetic balance within limited garden areas.
Maintenance and Upkeep Differences
Hedge mazes demand intensive maintenance, including regular trimming, pest control, and frequent inspections to ensure pathways remain clear and hedges retain their shape. Parterres generally require less upkeep, focusing on seasonal planting, weeding, and soil care to maintain intricate floral patterns and symmetry. The labor and costs associated with hedge maze maintenance are significantly higher due to the complexity and living structure involvement compared to the primarily botanical upkeep of parterres.
Aesthetic Impact in Landscape Design
Hedge mazes create dynamic, interactive landscapes with vertical greenery that guides movement and sparks curiosity, enhancing garden exploration and offering a playful aesthetic. Parterres deliver visually striking, symmetrical patterns through low, clipped hedges and colorful plantings, emphasizing formal elegance and order in outdoor spaces. Both elements contribute distinctly to landscape design by balancing complexity and refinement to elevate the overall visual impact.
Functionality: Recreation vs. Ornamentation
Hedge mazes provide an interactive recreational experience, engaging visitors in exploration and problem-solving within a garden setting. Parterres primarily serve ornamental purposes, showcasing intricate patterns of low-growing plants designed to enhance aesthetic appeal. While hedge mazes invite physical movement and adventure, parterres emphasize visual artistry and structured elegance in landscape design.
Suitability for Different Climates
Hedge mazes thrive in temperate climates with sufficient rainfall, as dense, resilient shrubs like boxwood or yew require consistent moisture to maintain their structure and lush appearance. Parterres, featuring low-growing, ornamental plants and gravel pathways, are highly adaptable to arid and Mediterranean climates due to their drought-tolerant plant selections and efficient drainage systems. Selecting between a hedge maze and a parterre depends largely on local climate conditions, soil type, and water availability to ensure long-term garden health and visual appeal.
Choosing Between a Hedge Maze and a Parterre
Selecting between a hedge maze and a parterre depends on desired garden functionality and aesthetic goals; hedge mazes offer interactive, playful pathways enhancing spatial experience, while parterres emphasize symmetrical, ornamental flower beds that showcase intricate patterns. Hedge mazes require more maintenance due to dense shrub growth and frequent trimming, compared to the relatively low upkeep of parterres where focus is primarily on maintaining plant health and design clarity. Consider available space and visitor engagement when choosing, as hedge mazes thrive in larger areas inviting exploration, whereas parterres suit formal gardens emphasizing visual elegance and order.
Hedge Maze vs Parterre Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com