
Native Plants vs Exotic Plants Illustration
Native plants thrive in local climates and soil conditions, requiring less water and maintenance than exotic plants. Exotic plants can introduce pests and diseases that disrupt native ecosystems and reduce biodiversity. Choosing native vegetation supports wildlife habitats and promotes ecological balance in landscaping.
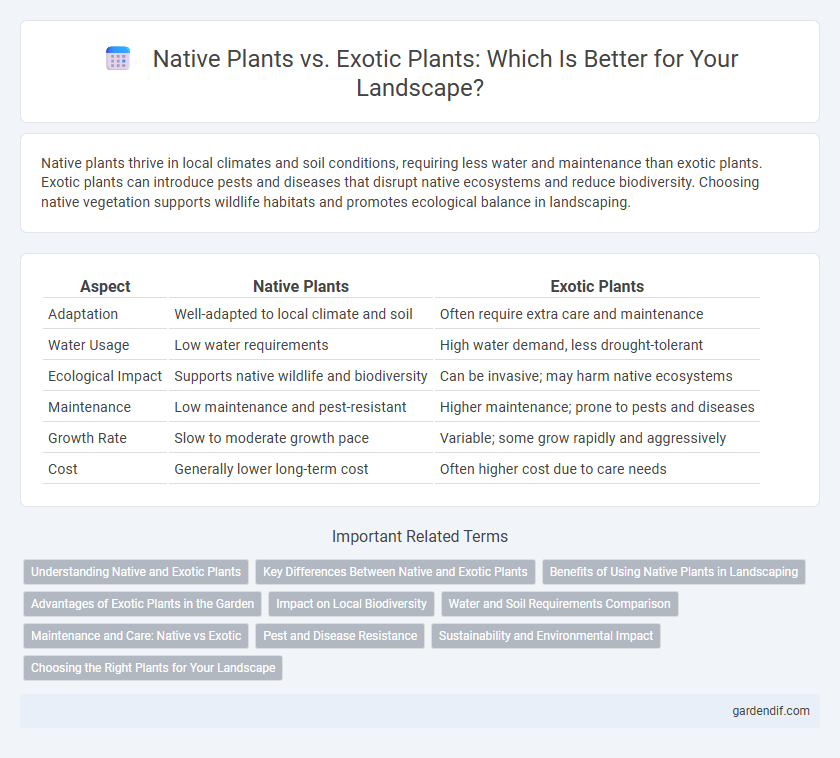
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Native Plants | Exotic Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptation | Well-adapted to local climate and soil | Often require extra care and maintenance |
| Water Usage | Low water requirements | High water demand, less drought-tolerant |
| Ecological Impact | Supports native wildlife and biodiversity | Can be invasive; may harm native ecosystems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance and pest-resistant | Higher maintenance; prone to pests and diseases |
| Growth Rate | Slow to moderate growth pace | Variable; some grow rapidly and aggressively |
| Cost | Generally lower long-term cost | Often higher cost due to care needs |
Understanding Native and Exotic Plants
Native plants have evolved naturally within specific regions, supporting local ecosystems, wildlife, and soil health, while requiring less water and maintenance. Exotic plants, introduced from different areas, may offer unique aesthetics but often risk becoming invasive and disrupting native biodiversity. Understanding the ecological roles, water needs, and growth patterns of both plant types is essential for sustainable landscape design.
Key Differences Between Native and Exotic Plants
Native plants are species that have evolved naturally in a specific region, adapting to local climate, soil, and wildlife, which enhances biodiversity and ecological balance. Exotic plants, introduced from different regions, often lack these adaptations, potentially disrupting ecosystems by competing with native species and altering habitats. Key differences include growth rates, water and soil nutrient needs, and their role in supporting pollinators and wildlife native to the area.
Benefits of Using Native Plants in Landscaping
Native plants enhance landscape sustainability by requiring less water, reducing maintenance needs, and supporting local ecosystems. Their deep root systems improve soil health and prevent erosion while providing essential habitat and food sources for native wildlife. Incorporating native plants into landscaping boosts biodiversity and promotes environmental resilience.
Advantages of Exotic Plants in the Garden
Exotic plants bring unique colors, textures, and seasonal interest that native plants might not offer, enhancing the garden's visual appeal and diversity. Many exotic species are drought-tolerant and pest-resistant, reducing maintenance needs and resource consumption. Their adaptability to different soil and climate conditions allows for creative landscaping designs that can thrive in varied environments.
Impact on Local Biodiversity
Native plants support local biodiversity by providing essential habitat and food sources for indigenous wildlife, including pollinators, birds, and insects. Exotic plants often disrupt ecosystems by outcompeting native species, reducing habitat availability and decreasing overall biodiversity. Maintaining native vegetation preserves ecological balance and promotes resilience against invasive species and environmental stresses.
Water and Soil Requirements Comparison
Native plants typically require less water due to their adaptation to local climate conditions, making them more water-efficient than exotic plants, which often demand higher irrigation. Soil requirements for native plants are usually minimal since they thrive in the existing soil composition, whereas exotic plants may need soil amendments to accommodate nutrient needs and pH levels. Selecting native species supports sustainable landscaping by reducing water use and preventing soil degradation commonly associated with exotic plant cultivation.
Maintenance and Care: Native vs Exotic
Native plants typically require less maintenance and care due to their adaptation to local soil, climate, and pest conditions. Exotic plants often demand more intensive watering, fertilizing, pruning, and pest control to thrive outside their natural habitat. Choosing native species can reduce long-term landscape maintenance costs and promote ecological balance.
Pest and Disease Resistance
Native plants exhibit superior pest and disease resistance due to their long-term adaptation to local environmental conditions and natural predators. In contrast, exotic plants often lack these evolutionary defenses, making them more vulnerable to infestations and diseases in non-native habitats. Selecting native species can reduce the need for chemical treatments, promoting healthier, more sustainable landscapes.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Native plants enhance sustainability by supporting local ecosystems, conserving water, and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Exotic plants often require more resources to thrive, potentially disrupting native biodiversity and increasing the risk of invasive species. Choosing native flora promotes ecological balance and long-term environmental health in landscaping projects.
Choosing the Right Plants for Your Landscape
Selecting native plants for your landscape enhances local biodiversity by supporting regional wildlife and requiring less water and maintenance compared to exotic plants. Exotic plants often bring vibrant colors and unique textures, but they can disrupt ecosystems and demand more resources to thrive. Prioritizing native species ensures sustainability, resilience to pests, and long-term harmony with the natural environment.
Native Plants vs Exotic Plants Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com