
shade garden vs sun garden Illustration
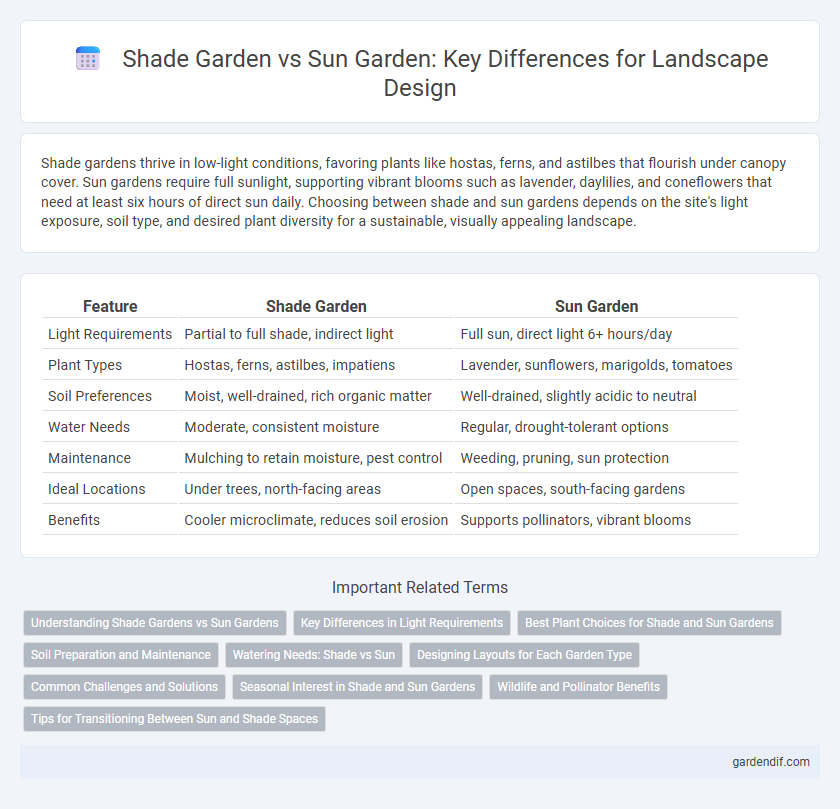
Shade gardens thrive in low-light conditions, favoring plants like hostas, ferns, and astilbes that flourish under canopy cover. Sun gardens require full sunlight, supporting vibrant blooms such as lavender, daylilies, and coneflowers that need at least six hours of direct sun daily. Choosing between shade and sun gardens depends on the site's light exposure, soil type, and desired plant diversity for a sustainable, visually appealing landscape.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shade Garden | Sun Garden |
|---|---|---|
| Light Requirements | Partial to full shade, indirect light | Full sun, direct light 6+ hours/day |
| Plant Types | Hostas, ferns, astilbes, impatiens | Lavender, sunflowers, marigolds, tomatoes |
| Soil Preferences | Moist, well-drained, rich organic matter | Well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral |
| Water Needs | Moderate, consistent moisture | Regular, drought-tolerant options |
| Maintenance | Mulching to retain moisture, pest control | Weeding, pruning, sun protection |
| Ideal Locations | Under trees, north-facing areas | Open spaces, south-facing gardens |
| Benefits | Cooler microclimate, reduces soil erosion | Supports pollinators, vibrant blooms |
Understanding Shade Gardens vs Sun Gardens
Shade gardens thrive in areas with limited direct sunlight, typically under trees or structures, favoring plants like hostas, ferns, and astilbes that require low to moderate light levels. Sun gardens demand ample sunlight, usually six or more hours per day, supporting heat- and drought-tolerant species such as lavender, coneflowers, and daylilies. Selecting between shade and sun gardens depends on site-specific light conditions and plant adaptability, influencing garden design, maintenance, and overall plant health.
Key Differences in Light Requirements
Shade gardens thrive in indirect or filtered sunlight, requiring less than four hours of direct sun daily, which supports plants adapted to low-light conditions. Sun gardens demand full sun exposure, typically six or more hours of direct sunlight, favoring sun-loving species that need intense light for photosynthesis. Understanding these light requirements is crucial for selecting appropriate plants and ensuring healthy growth in either shade or sun garden environments.
Best Plant Choices for Shade and Sun Gardens
Shade gardens thrive with hostas, ferns, and astilbes that flourish in low-light conditions, providing rich texture and vibrant foliage despite limited sun exposure. Sun gardens excel with lavender, coneflowers, and black-eyed Susans, plants that require full sun to produce abundant blooms and maintain drought tolerance. Selecting native, sun-loving species for bright areas and shade-tolerant perennials for darker spots ensures optimal growth and landscape sustainability.
Soil Preparation and Maintenance
Shade gardens require rich, well-draining soil with high organic matter to retain moisture and support shade-tolerant plants, while sun gardens benefit from nutrient-rich, well-aerated soil that can sustain higher evaporation rates. Regular mulching in shade gardens conserves soil moisture and prevents compaction, whereas sun gardens need frequent watering and periodic soil amendments to replenish nutrients lost through intense sun exposure. Proper soil pH adjustment and tailored fertilizer application promote optimal growth in both shade and sun garden environments.
Watering Needs: Shade vs Sun
Shade gardens typically require less frequent watering due to lower evaporation rates and cooler soil temperatures, conserving moisture for plants like ferns and hostas. Sun gardens demand more frequent and deeper watering to support sun-loving species such as lavender and salvia, which thrive in drier, well-drained conditions. Efficient irrigation strategies should be tailored to the distinct moisture retention characteristics of shade versus sun garden environments.
Designing Layouts for Each Garden Type
Designing layouts for shade gardens involves selecting plants with low light requirements such as ferns, hostas, and astilbe, and arranging them to create layered textures and varying heights that thrive in filtered light environments. Sun garden layouts prioritize sun-loving plants like lavender, coneflowers, and ornamental grasses, emphasizing open spaces that maximize sun exposure while considering soil drainage and heat tolerance. Strategic placement of pathways, seating areas, and focal points enhances both garden types by promoting accessibility and aesthetic harmony tailored to their unique growing conditions.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Shade gardens often struggle with limited sunlight, resulting in slower plant growth and fewer flowering options compared to sun gardens. Common challenges include dealing with poor soil drainage and selecting shade-tolerant species like hostas, ferns, and astilbes to ensure healthy foliage. Sun gardens face heat stress and moisture loss, so solutions involve mulching, drought-resistant plants such as lavender and sedum, and efficient irrigation systems to maintain vibrant blooms.
Seasonal Interest in Shade and Sun Gardens
Shade gardens thrive with plants like hostas, ferns, and astilbes that provide year-round texture and vibrant foliage during spring through fall. Sun gardens, featuring sun-loving species such as lavender, coneflowers, and black-eyed Susans, offer dynamic seasonal blooms that attract pollinators from late spring to early autumn. Incorporating a variety of perennials and shrubs ensures continuous color and structural interest across all seasons in both garden types.
Wildlife and Pollinator Benefits
Shade gardens provide a vital habitat for shade-loving wildlife such as certain butterflies, moths, and amphibians, promoting biodiversity in cooler, sheltered areas. Sun gardens attract a wider range of pollinators like bees, hummingbirds, and butterflies by offering abundant flowering plants that require full sunlight for nectar production. Both garden types support ecosystems by supplying food and shelter, but sun gardens generally enhance pollinator activity, boosting plant reproduction and local wildlife diversity.
Tips for Transitioning Between Sun and Shade Spaces
To successfully transition between sun and shade garden spaces, select plants adaptable to varying light conditions, such as hostas for shade and daylilies for sun. Gradually adjust watering schedules, as sun gardens typically require more frequent irrigation than shade areas. Use mulch to retain soil moisture and regulate temperature, ensuring both sun and shade plants thrive during periods of change.
shade garden vs sun garden Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com