
Hardscape vs Softscape Illustration
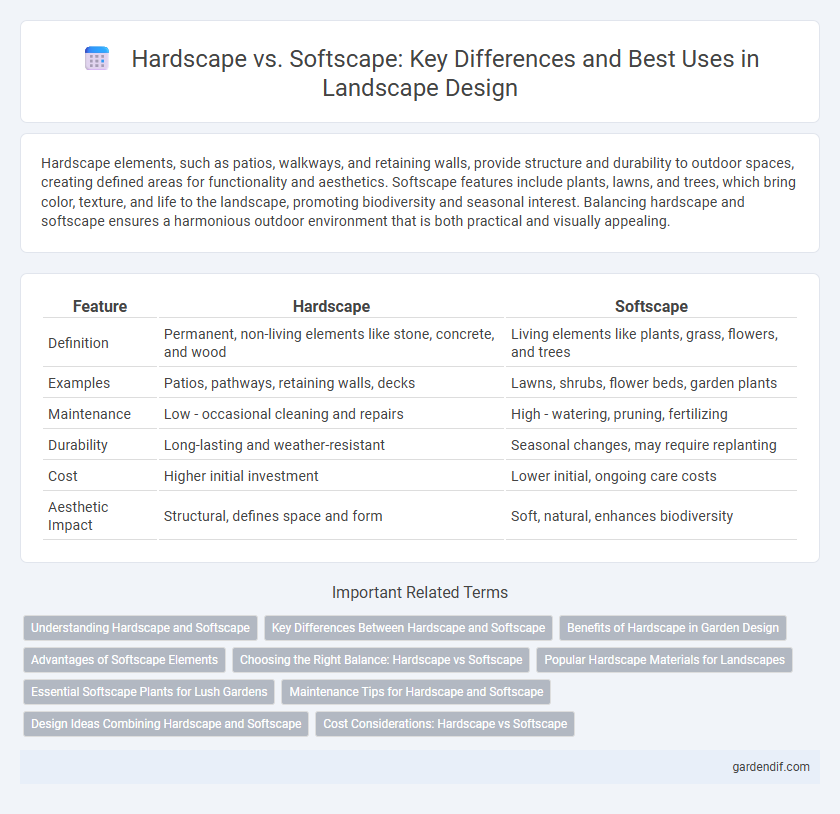
Hardscape elements, such as patios, walkways, and retaining walls, provide structure and durability to outdoor spaces, creating defined areas for functionality and aesthetics. Softscape features include plants, lawns, and trees, which bring color, texture, and life to the landscape, promoting biodiversity and seasonal interest. Balancing hardscape and softscape ensures a harmonious outdoor environment that is both practical and visually appealing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hardscape | Softscape |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent, non-living elements like stone, concrete, and wood | Living elements like plants, grass, flowers, and trees |
| Examples | Patios, pathways, retaining walls, decks | Lawns, shrubs, flower beds, garden plants |
| Maintenance | Low - occasional cleaning and repairs | High - watering, pruning, fertilizing |
| Durability | Long-lasting and weather-resistant | Seasonal changes, may require replanting |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial, ongoing care costs |
| Aesthetic Impact | Structural, defines space and form | Soft, natural, enhances biodiversity |
Understanding Hardscape and Softscape
Hardscape comprises the non-living elements of landscaping such as patios, walkways, retaining walls, and decks, crafted from materials like stone, concrete, wood, and metal to provide structure and function. Softscape involves the living components, including plants, trees, shrubs, grass, and flowers, which enhance aesthetics, promote biodiversity, and contribute to environmental benefits like air purification and soil stabilization. Understanding the balance between hardscape and softscape is essential for creating harmonious, sustainable, and visually appealing outdoor spaces.
Key Differences Between Hardscape and Softscape
Hardscape refers to the non-living elements in a landscape design, such as patios, walkways, retaining walls, and decks, which provide structure and durability. Softscape includes living components like plants, trees, lawns, and flowers that enhance aesthetic appeal and promote ecological benefits. The key differences lie in material composition, functionality, and maintenance requirements, with hardscape offering permanence and hardiness, while softscape delivers adaptability and seasonal variation.
Benefits of Hardscape in Garden Design
Hardscape elements in garden design offer durable, low-maintenance surfaces that enhance functionality and aesthetic appeal, providing structure and definition to outdoor spaces. Materials such as stone, concrete, and wood create pathways, patios, and retaining walls that improve drainage and prevent soil erosion, contributing to sustainable landscape management. Incorporating hardscape features increases usable outdoor living areas, supports diverse planting schemes by delineating zones, and adds year-round visual interest regardless of seasonal changes.
Advantages of Softscape Elements
Softscape elements such as plants, trees, and shrubs enhance biodiversity and improve air quality by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. They provide natural aesthetics, creating seasonal interest with varying colors, textures, and fragrances that hardscape materials cannot replicate. Softscape also promotes soil health, supports local wildlife habitats, and aids in water absorption, reducing runoff and erosion.
Choosing the Right Balance: Hardscape vs Softscape
Achieving the ideal balance between hardscape and softscape enhances both functionality and aesthetic appeal in landscape design. Hardscape elements such as patios, pathways, and retaining walls provide structure and durability, while softscape components like plants, trees, and lawns contribute natural beauty and seasonal interest. Prioritizing site-specific factors like climate, soil conditions, and intended usage ensures harmony between these elements, creating a sustainable and visually pleasing outdoor environment.
Popular Hardscape Materials for Landscapes
Popular hardscape materials for landscapes include natural stone, concrete, brick, and pavers, each offering durability and aesthetic appeal. Natural stone provides a timeless, organic look, while concrete allows for versatile shapes and finishes, making it ideal for patios and walkways. Brick and pavers are favored for their classic appearance and ease of installation, contributing to both functional and decorative outdoor spaces.
Essential Softscape Plants for Lush Gardens
Essential softscape plants for lush gardens include variations of ornamental grasses, flowering shrubs like azaleas and hydrangeas, and ground covers such as creeping thyme or hostas. These plants enhance soil health, provide vibrant colors, and improve overall texture, creating a dynamic contrast to hardscape elements like stone pathways or retaining walls. Incorporating diverse softscape species promotes biodiversity and sustains a healthy garden ecosystem.
Maintenance Tips for Hardscape and Softscape
Hardscape maintenance involves regular cleaning to prevent staining and debris accumulation, sealing surfaces to protect against weather damage, and inspecting structural elements like retaining walls for cracks or erosion. Softscape care requires consistent watering schedules, pruning to promote healthy growth, and soil conditioning to improve nutrient availability and drainage. Combining these practices ensures longevity and aesthetic appeal in landscaping projects.
Design Ideas Combining Hardscape and Softscape
Integrating hardscape features such as stone pathways, retaining walls, and patios with softscape elements like flowering plants, shrubs, and trees creates a balanced and visually appealing landscape design. Strategic placement of these components enhances outdoor functionality while providing texture and color contrast that elevates the overall aesthetic. Incorporating natural materials and native vegetation promotes sustainability and ensures seamless harmony between built structures and organic surroundings.
Cost Considerations: Hardscape vs Softscape
Hardscape elements such as patios, retaining walls, and pathways generally require higher upfront costs due to materials like stone, concrete, and labor-intensive installation. Softscape components, including plants, trees, and grass, involve lower initial expenses but may incur ongoing maintenance costs like watering, pruning, and fertilization. Budget planning for landscaping should balance these factors, considering both immediate investment and long-term upkeep to optimize overall expense management.
Hardscape vs Softscape Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com