
Edible Landscaping vs Ornamental Landscaping Illustration
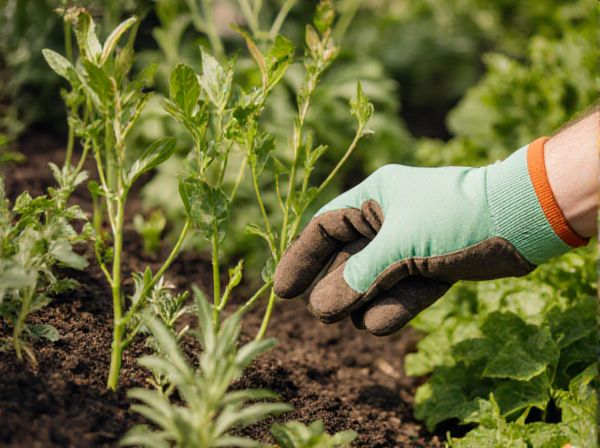
Edible landscaping transforms outdoor spaces by integrating fruits, vegetables, and herbs, providing both aesthetic appeal and practical harvests. Ornamental landscaping prioritizes visual beauty through decorative plants, flowers, and design elements without focusing on food production. Combining edible and ornamental landscaping enhances garden functionality while maintaining an attractive environment.
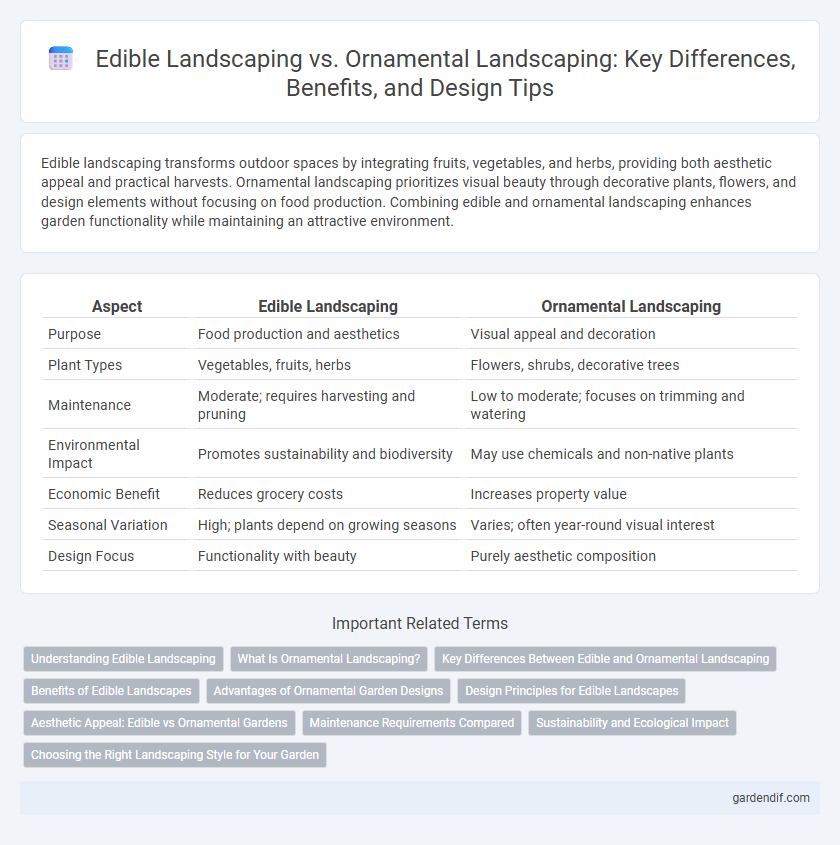
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Edible Landscaping | Ornamental Landscaping |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Food production and aesthetics | Visual appeal and decoration |
| Plant Types | Vegetables, fruits, herbs | Flowers, shrubs, decorative trees |
| Maintenance | Moderate; requires harvesting and pruning | Low to moderate; focuses on trimming and watering |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability and biodiversity | May use chemicals and non-native plants |
| Economic Benefit | Reduces grocery costs | Increases property value |
| Seasonal Variation | High; plants depend on growing seasons | Varies; often year-round visual interest |
| Design Focus | Functionality with beauty | Purely aesthetic composition |
Understanding Edible Landscaping
Edible landscaping integrates food-producing plants such as fruits, vegetables, and herbs into traditional garden designs, offering both aesthetic and nutritional benefits. Unlike ornamental landscaping, which prioritizes visual appeal through flowers and decorative plants, edible landscaping emphasizes sustainability and practical use by maximizing yield alongside beauty. This approach promotes biodiversity, reduces grocery costs, and encourages local, organic food production within residential and commercial landscapes.
What Is Ornamental Landscaping?
Ornamental landscaping emphasizes aesthetic appeal through the use of decorative plants, flowers, shrubs, and trees designed to enhance the visual beauty of outdoor spaces. This type of landscaping prioritizes color, texture, and form to create visually pleasing environments rather than producing food or edible plants. Common features include flowering plants, sculpted hedges, garden statues, and water features, which contribute to the overall design and ambiance of a property.
Key Differences Between Edible and Ornamental Landscaping
Edible landscaping integrates fruits, vegetables, and herbs into garden designs to provide both aesthetic appeal and food production, emphasizing functionality and sustainability. Ornamental landscaping prioritizes visual beauty using flowers, shrubs, and trees that typically do not produce food, focusing on color, texture, and form for decorative purposes. Key differences include plant selection, maintenance requirements, and the dual-purpose nature of edible landscapes versus the purely decorative intent of ornamental landscapes.
Benefits of Edible Landscapes
Edible landscaping enhances sustainability by integrating fruit trees, vegetable beds, and herbs directly into garden designs, promoting fresh, nutrient-rich food production on-site. This approach reduces grocery expenses and carbon footprints while attracting pollinators that benefit overall garden health. Incorporating edible plants also boosts biodiversity and offers therapeutic gardening opportunities that improve mental well-being through hands-on, purposeful interaction with nature.
Advantages of Ornamental Garden Designs
Ornamental landscaping enhances property value through visually appealing plant arrangements and seasonal color variety, boosting curb appeal significantly. It promotes biodiversity by attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies, creating environmentally sustainable ecosystems. Maintenance flexibility allows for tailored care levels suited to different climates and homeowner lifestyles, ensuring long-term garden health and aesthetics.
Design Principles for Edible Landscapes
Edible landscaping integrates food-producing plants with aesthetic design principles to create visually appealing and functional outdoor spaces. Key design principles include selecting diverse plant species that offer seasonal interest, optimizing spatial arrangement for sunlight and accessibility, and incorporating companion planting to enhance growth and pest control. Prioritizing both beauty and productivity ensures sustainable and attractive edible landscapes that blend seamlessly with ornamental elements.
Aesthetic Appeal: Edible vs Ornamental Gardens
Edible landscaping combines visual beauty with functional taste, integrating fruit trees, herbs, and vegetables that offer vibrant colors and textures alongside fresh produce. Ornamental landscaping prioritizes purely aesthetic elements such as flowers, shrubs, and decorative plants selected for their shapes, colors, and seasonal blooms to create visually striking garden designs. While ornamental gardens emphasize form and color consistency, edible landscapes provide a dynamic interplay of foliage and harvestable items, enhancing both beauty and utility.
Maintenance Requirements Compared
Edible landscaping demands consistent maintenance, including regular watering, pruning, fertilizing, and pest control to ensure healthy fruit and vegetable production. Ornamental landscaping typically requires less intensive care, focusing mainly on seasonal pruning, mulching, and occasional fertilization to maintain aesthetic appeal. The higher maintenance frequency in edible landscaping reflects the need to sustain plant productivity and prevent diseases, contrasting with the generally lower upkeep of ornamental plants designed primarily for visual enhancement.
Sustainability and Ecological Impact
Edible landscaping integrates fruit trees, vegetables, and herbs into garden designs, promoting sustainability by reducing food miles and reliance on commercial agriculture, which lowers carbon emissions and supports biodiversity. Ornamental landscaping primarily emphasizes aesthetic appeal using non-edible plants, often requiring significant water, fertilizers, and pesticides, which can negatively impact local ecosystems. Choosing edible plants enhances ecological impact by providing habitat for pollinators, improving soil health, and fostering resilient urban food systems.
Choosing the Right Landscaping Style for Your Garden
Edible landscaping integrates fruits, vegetables, and herbs into traditional garden designs, maximizing both aesthetic appeal and food production. Ornamental landscaping prioritizes visual beauty through decorative plants, flowers, and trees without a focus on consumption. Selecting the right landscaping style depends on goals like food sustainability, maintenance levels, and desired garden aesthetics.
Edible Landscaping vs Ornamental Landscaping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com