
Xeriscaping vs Rain Gardening Illustration
Xeriscaping conserves water by using drought-tolerant plants and efficient irrigation techniques, making it ideal for arid landscapes. Rain gardening collects and filters stormwater runoff, reducing erosion and improving water quality in wetter environments. Both practices promote sustainable landscaping by enhancing ecological balance and minimizing water waste.
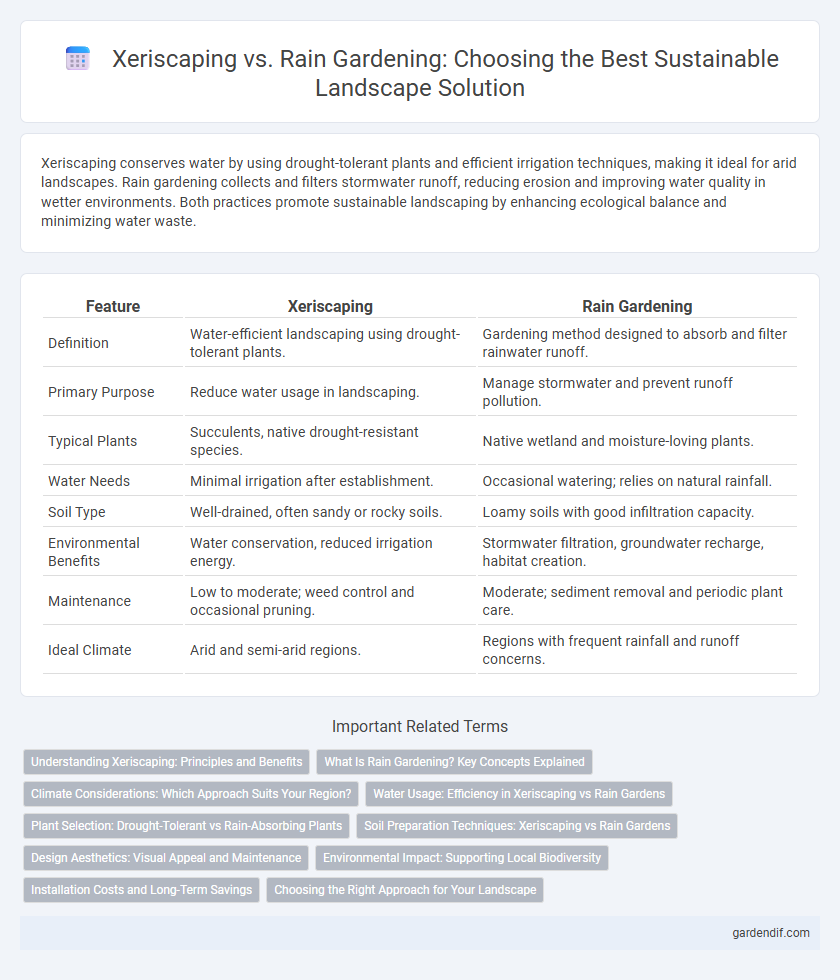
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Xeriscaping | Rain Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water-efficient landscaping using drought-tolerant plants. | Gardening method designed to absorb and filter rainwater runoff. |
| Primary Purpose | Reduce water usage in landscaping. | Manage stormwater and prevent runoff pollution. |
| Typical Plants | Succulents, native drought-resistant species. | Native wetland and moisture-loving plants. |
| Water Needs | Minimal irrigation after establishment. | Occasional watering; relies on natural rainfall. |
| Soil Type | Well-drained, often sandy or rocky soils. | Loamy soils with good infiltration capacity. |
| Environmental Benefits | Water conservation, reduced irrigation energy. | Stormwater filtration, groundwater recharge, habitat creation. |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate; weed control and occasional pruning. | Moderate; sediment removal and periodic plant care. |
| Ideal Climate | Arid and semi-arid regions. | Regions with frequent rainfall and runoff concerns. |
Understanding Xeriscaping: Principles and Benefits
Xeriscaping emphasizes water-efficient landscaping through principles such as soil analysis, strategic plant selection, and efficient irrigation techniques to reduce water consumption by up to 50%. This sustainable practice incorporates drought-resistant native plants, mulch for moisture retention, and minimal turf areas to enhance landscape resilience in arid climates. Benefits include lower water bills, reduced maintenance needs, and improved ecosystem health by conserving local water resources.
What Is Rain Gardening? Key Concepts Explained
Rain gardening is a sustainable landscaping technique designed to manage stormwater runoff by directing it into shallow, vegetated basins that capture and filter rainwater. Key concepts include using native plants adapted to wet and dry conditions, improving soil infiltration, and reducing pollutants before they reach waterways. This method enhances water conservation, minimizes erosion, and supports local biodiversity by creating natural habitats.
Climate Considerations: Which Approach Suits Your Region?
Xeriscaping is ideal for arid and drought-prone regions, utilizing drought-tolerant plants and minimal water requirements to conserve resources. Rain gardening suits areas with moderate rainfall, designed to capture and filter stormwater runoff, reducing erosion and improving groundwater recharge. Evaluating local precipitation patterns, soil types, and water availability helps determine the most sustainable landscaping approach for your climate zone.
Water Usage: Efficiency in Xeriscaping vs Rain Gardens
Xeriscaping utilizes drought-tolerant plants and efficient irrigation methods, reducing water consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional landscaping. Rain gardens capture and absorb stormwater runoff, minimizing the need for supplemental watering while improving groundwater recharge. Both techniques optimize water use by adapting to local climate and soil conditions, promoting sustainable landscape water management.
Plant Selection: Drought-Tolerant vs Rain-Absorbing Plants
Xeriscaping prioritizes drought-tolerant plants such as succulents, native grasses, and cacti, which require minimal water and thrive in arid conditions, reducing irrigation needs. Rain gardening focuses on rain-absorbing plants like blue flag iris, swamp milkweed, and sedges that effectively capture and filter stormwater runoff, improving groundwater recharge. Selecting the right plant types ensures sustainable water management while enhancing landscape resilience and biodiversity.
Soil Preparation Techniques: Xeriscaping vs Rain Gardens
Xeriscaping soil preparation prioritizes soil amendment with organic matter and the addition of porous materials like sand or gravel to enhance drainage and reduce water retention. Rain gardening soil preparation emphasizes creating a layered soil profile with a blend of compost-rich topsoil and sand to maximize water infiltration and support native, water-tolerant plants. Both techniques require soil testing to assess pH levels and nutrient content, ensuring optimal plant health and water management in sustainable landscaping.
Design Aesthetics: Visual Appeal and Maintenance
Xeriscaping emphasizes drought-tolerant plants and minimal irrigation, creating sleek, low-maintenance landscapes with a natural, desert-inspired aesthetic. Rain gardening incorporates native plants designed to manage stormwater, blending vibrant textures and seasonal blooms for dynamic visual interest. Both approaches offer sustainable beauty, but xeriscaping favors simplicity and longevity, while rain gardening provides ecological benefits and evolving floral variety.
Environmental Impact: Supporting Local Biodiversity
Xeriscaping conserves water by using drought-tolerant plants, reducing irrigation needs and minimizing strain on local water resources. Rain gardening captures and filters stormwater runoff, preventing pollutants from reaching waterways and providing habitat for native species. Both approaches support local biodiversity by promoting native plants and creating sustainable ecosystems adapted to regional climates.
Installation Costs and Long-Term Savings
Xeriscaping typically involves lower installation costs due to the use of drought-resistant plants and minimal irrigation infrastructure, reducing water expenses significantly over time. Rain gardening may have moderate upfront costs linked to soil amendments and drainage systems but offers long-term savings by managing stormwater and reducing runoff fees. Both methods promote sustainability, with xeriscaping emphasizing water conservation and rain gardening enhancing groundwater recharge, impacting overall landscape maintenance budgets.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Landscape
Xeriscaping emphasizes drought-tolerant plants and water-efficient landscaping techniques, ideal for arid regions with limited water supply. Rain gardening focuses on capturing and filtering stormwater runoff through native, moisture-loving plants to improve water quality and reduce erosion. Selecting the right approach depends on your local climate, soil conditions, and water availability to create a sustainable and visually appealing landscape.
Xeriscaping vs Rain Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com