
Hardscaping vs Softscaping Illustration
Hardscaping involves the use of non-plant elements such as patios, walkways, retaining walls, and fountains that provide structure and durability to outdoor spaces. Softscaping focuses on living elements like trees, shrubs, flowers, and grass, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and ecological balance of a landscape. Combining hardscaping and softscaping creates a harmonious environment that balances functionality with natural beauty.
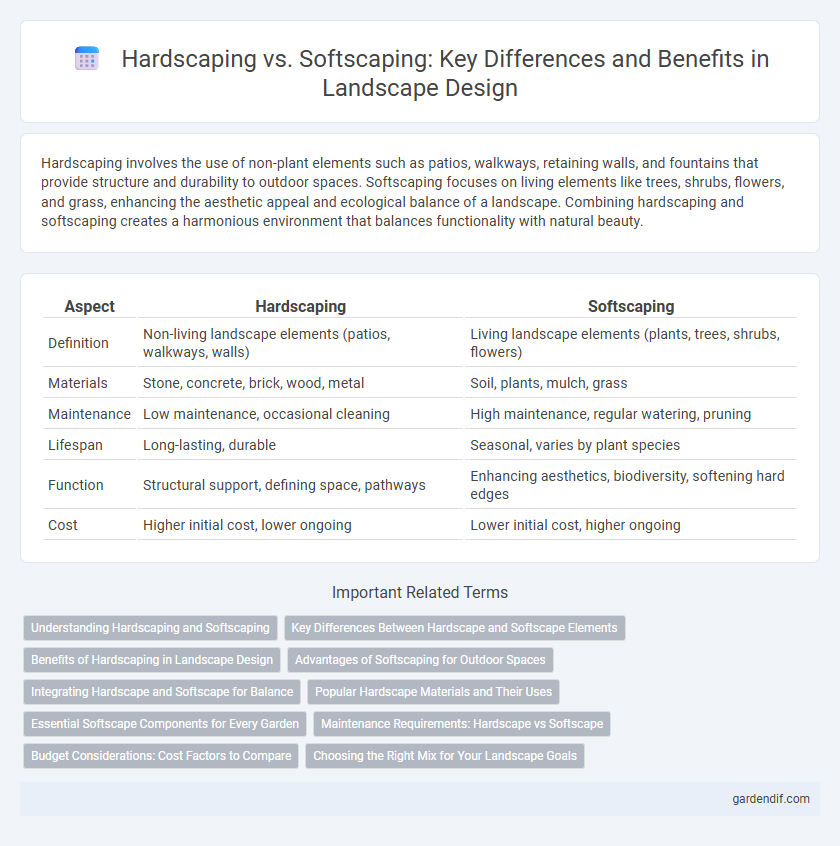
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hardscaping | Softscaping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-living landscape elements (patios, walkways, walls) | Living landscape elements (plants, trees, shrubs, flowers) |
| Materials | Stone, concrete, brick, wood, metal | Soil, plants, mulch, grass |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, occasional cleaning | High maintenance, regular watering, pruning |
| Lifespan | Long-lasting, durable | Seasonal, varies by plant species |
| Function | Structural support, defining space, pathways | Enhancing aesthetics, biodiversity, softening hard edges |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower ongoing | Lower initial cost, higher ongoing |
Understanding Hardscaping and Softscaping
Hardscaping involves the use of non-living elements such as patios, walkways, retaining walls, and decks, which provide structure and durability to outdoor spaces. Softscaping focuses on living components like trees, shrubs, flowers, and lawns that enhance biodiversity and aesthetic appeal. Combining these elements strategically optimizes landscape design, balancing functionality with natural beauty.
Key Differences Between Hardscape and Softscape Elements
Hardscape elements in landscaping consist of non-living materials such as stone, concrete, bricks, and wood used to create patios, walkways, retaining walls, and decks, providing structure and durability. Softscape involves living components like plants, trees, grass, flowers, and shrubs that contribute to aesthetic appeal, environmental benefits, and seasonal changes. The key differences lie in their materials, purpose, maintenance requirements, and impact on the overall landscape design, with hardscaping focusing on functionality and permanence, while softscaping emphasizes natural beauty and ecological health.
Benefits of Hardscaping in Landscape Design
Hardscaping in landscape design enhances outdoor spaces by providing durable, low-maintenance structures such as patios, walkways, and retaining walls that increase property value and usability. It offers erosion control, improved drainage, and defines garden areas, creating a visually appealing and functional environment. Incorporating hardscaping elements reduces water usage compared to extensive softscaping, supporting sustainable landscape practices.
Advantages of Softscaping for Outdoor Spaces
Softscaping enhances outdoor spaces by introducing natural elements such as trees, shrubs, flowers, and grasses that improve air quality and promote biodiversity. The flexible design options of softscaping allow for seasonal changes and ecological benefits like habitat creation and soil stabilization. Incorporating softscape features also supports sustainable water management through improved infiltration and reduced runoff.
Integrating Hardscape and Softscape for Balance
Integrating hardscape and softscape creates a balanced landscape that combines functional elements like patios, walkways, and retaining walls with natural features such as plants, trees, and lawns. Strategic placement of hardscape materials enhances soil stability and defines garden zones, while softscape adds texture, color, and seasonal interest, promoting ecological benefits and visual harmony. Achieving equilibrium between these components optimizes outdoor space usability and aesthetic appeal, increasing property value and environmental sustainability.
Popular Hardscape Materials and Their Uses
Popular hardscape materials include natural stone, concrete, brick, and pavers, each offering durability and aesthetic appeal for outdoor spaces. Natural stone is commonly used for patios and walkways due to its timeless look, while concrete provides a versatile and cost-effective solution for driveways and retaining walls. Brick and pavers are favored for creating intricate patterns in garden paths and courtyards, enhancing the overall landscape design with texture and color variation.
Essential Softscape Components for Every Garden
Essential softscape components for every garden include a variety of plants such as perennials, shrubs, and trees that provide structure, color, and texture throughout the seasons. Healthy soil preparation and proper irrigation systems are crucial for supporting plant growth and maintaining garden vitality. Incorporating mulch and ground covers helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and enhance the overall aesthetic appeal of the landscape.
Maintenance Requirements: Hardscape vs Softscape
Hardscaping, including materials such as stone, concrete, and pavers, demands lower maintenance with occasional cleaning and sealing to prevent cracks and erosion. Softscaping, involving plants, soil, and mulch, requires regular watering, pruning, fertilizing, and pest control to maintain plant health and aesthetics. Effective landscape design balances both hardscape durability and softscape vitality to optimize upkeep efforts and long-term sustainability.
Budget Considerations: Cost Factors to Compare
Hardscaping expenses typically involve materials like stone, concrete, and pavers, which have higher upfront costs but offer long-term durability and low maintenance, impacting the overall budget significantly. Softscaping costs vary based on plant selection, soil preparation, and irrigation systems, often requiring ongoing investment for upkeep and seasonal replacement. Comparing cost factors includes evaluating installation fees, maintenance expenses, and lifespan to balance initial outlay with sustainable landscape value.
Choosing the Right Mix for Your Landscape Goals
Selecting the ideal balance between hardscaping and softscaping hinges on your landscape goals, budget, and maintenance preferences. Hardscaping elements like patios, walkways, and retaining walls provide structure and durability, while softscaping incorporates plants, lawns, and trees to enhance aesthetic appeal and ecological benefits. A well-planned mix improves functionality, boosts property value, and creates a harmonious outdoor environment tailored to your lifestyle.
Hardscaping vs Softscaping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com