
Container Gardening vs Raised Bed Gardening Illustration
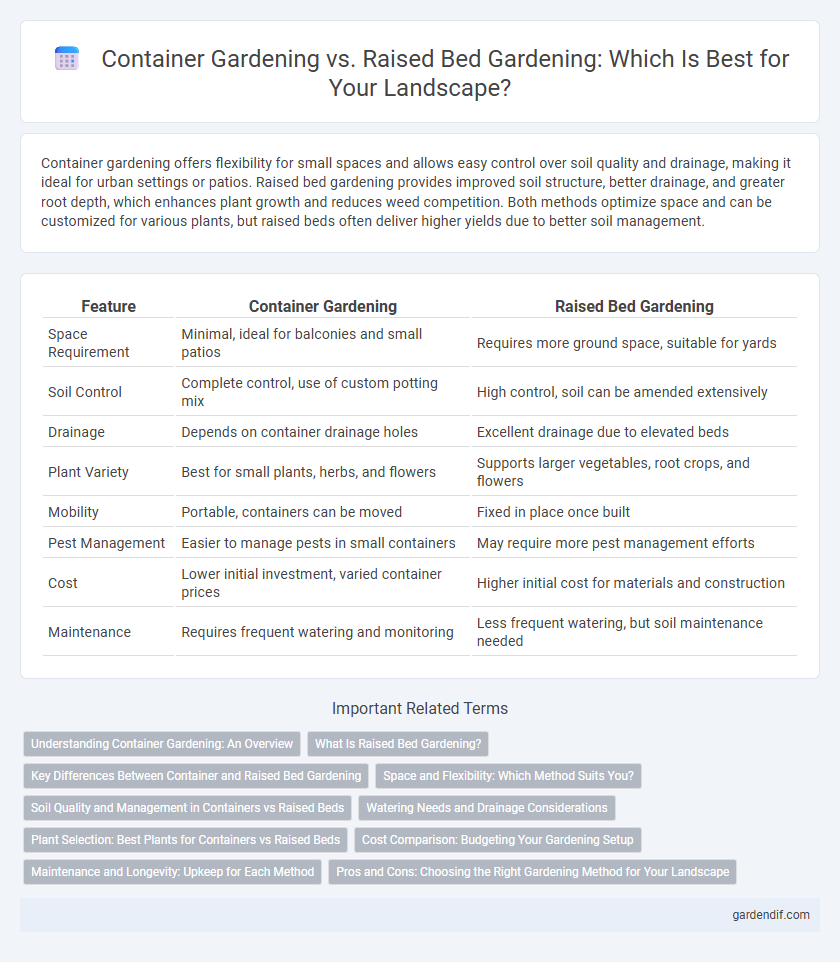
Container gardening offers flexibility for small spaces and allows easy control over soil quality and drainage, making it ideal for urban settings or patios. Raised bed gardening provides improved soil structure, better drainage, and greater root depth, which enhances plant growth and reduces weed competition. Both methods optimize space and can be customized for various plants, but raised beds often deliver higher yields due to better soil management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Container Gardening | Raised Bed Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Space Requirement | Minimal, ideal for balconies and small patios | Requires more ground space, suitable for yards |
| Soil Control | Complete control, use of custom potting mix | High control, soil can be amended extensively |
| Drainage | Depends on container drainage holes | Excellent drainage due to elevated beds |
| Plant Variety | Best for small plants, herbs, and flowers | Supports larger vegetables, root crops, and flowers |
| Mobility | Portable, containers can be moved | Fixed in place once built |
| Pest Management | Easier to manage pests in small containers | May require more pest management efforts |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, varied container prices | Higher initial cost for materials and construction |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent watering and monitoring | Less frequent watering, but soil maintenance needed |
Understanding Container Gardening: An Overview
Container gardening offers a flexible and space-efficient solution for growing plants, ideal for small patios, balconies, or urban settings. It involves planting in various pots or containers that provide controlled soil conditions, drainage, and mobility. This method supports diverse plant types, from herbs and vegetables to flowers, while allowing easy management of soil quality and pest control compared to traditional raised bed gardening.
What Is Raised Bed Gardening?
Raised bed gardening involves cultivating plants in soil that is elevated above the surrounding ground, typically enclosed by a frame made of wood, stone, or composite materials. This gardening method improves soil drainage, reduces soil compaction, and allows for better control over soil quality and nutrients. Raised beds also facilitate easier access for planting, weeding, and harvesting, making them ideal for gardeners seeking efficient and organized cultivation in limited spaces.
Key Differences Between Container and Raised Bed Gardening
Container gardening offers mobility and control over soil quality, ideal for small spaces and urban environments, while raised bed gardening provides improved drainage, root growth, and larger planting areas suited for extensive vegetable cultivation. Containers tend to heat up faster and dry out more quickly, requiring more frequent watering compared to raised beds that retain moisture longer and support deeper root systems. Cost-effective setup and flexibility favor container gardens, whereas raised beds often demand permanent construction but enhance soil structure and yield potential.
Space and Flexibility: Which Method Suits You?
Container gardening offers exceptional flexibility for limited spaces such as balconies and patios, allowing easy rearrangement and mobility. Raised bed gardening maximizes soil depth and supports larger plant varieties, making it ideal for more permanent garden setups with ample space. Assess the available area and desired garden scale to determine which approach aligns best with your space constraints and gardening goals.
Soil Quality and Management in Containers vs Raised Beds
Container gardening offers precise control over soil quality by allowing gardeners to customize soil mixes for optimal drainage and nutrient content, minimizing risks of compaction and poor aeration. Raised bed gardening enhances soil management by improving drainage and reducing soil compaction while allowing amending native soil with organic matter for sustained fertility. Both methods require regular monitoring of moisture levels and nutrient replenishment to maintain healthy plant growth, but containers often demand more frequent watering and fertilization due to limited soil volume.
Watering Needs and Drainage Considerations
Container gardening demands frequent watering due to limited soil volume, leading to faster drying, while raised bed gardening retains moisture longer with better soil depth and aeration. Proper drainage in containers requires selecting pots with ample drainage holes and using well-draining soil mixes to prevent root rot, whereas raised beds benefit from elevated soil that naturally improves water runoff and reduces waterlogging risks. Efficient water management in both methods hinges on understanding each system's unique drainage properties and adjusting irrigation schedules accordingly.
Plant Selection: Best Plants for Containers vs Raised Beds
Container gardening suits compact, shallow-rooted plants like herbs, lettuce, and small flowers, thriving in limited soil with controlled drainage. Raised bed gardening supports a wider range, including deep-rooted vegetables such as tomatoes, carrots, and potatoes, benefiting from improved soil depth and aeration. Selecting plants based on root depth and growth habits optimizes yield and health in each gardening method.
Cost Comparison: Budgeting Your Gardening Setup
Container gardening typically demands lower initial costs, with basic pots and soil priced around $20 to $50 per setup, making it ideal for small spaces and beginners. Raised bed gardening requires a higher investment, often ranging from $150 to $500 depending on materials like cedar or composite wood, plus soil amendments, but offers enhanced soil control and durability. Budget-conscious gardeners should weigh upfront expenses against long-term maintenance and productivity when choosing between these popular landscaping methods.
Maintenance and Longevity: Upkeep for Each Method
Container gardening requires regular watering and fertilizing due to limited soil volume, with containers needing replacement or repair every few years to prevent deterioration. Raised bed gardening demands periodic soil enrichment and weed control, offering greater longevity as beds can last over a decade with durable materials like cedar or composite wood. Maintenance for raised beds is less frequent but involves seasonal soil amendments, while containers offer flexibility but higher ongoing upkeep.
Pros and Cons: Choosing the Right Gardening Method for Your Landscape
Container gardening offers flexibility and mobility, ideal for small spaces and urban settings, but requires frequent watering and limited root growth. Raised bed gardening improves soil drainage and root development, supports larger plants, and reduces weed pressure, yet demands more initial setup and space. Selecting between these methods depends on your landscape size, soil quality, and maintenance preferences to achieve optimal plant health and yield.
Container Gardening vs Raised Bed Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com