
Rain Garden vs Rock Garden Illustration
Rain gardens efficiently manage stormwater by capturing and filtering runoff through native plants and soil, promoting groundwater recharge and reducing erosion. Rock gardens emphasize aesthetic appeal with drought-tolerant plants arranged among stones, requiring minimal maintenance and water. Choosing between a rain garden and a rock garden depends on environmental goals, site conditions, and desired garden function.
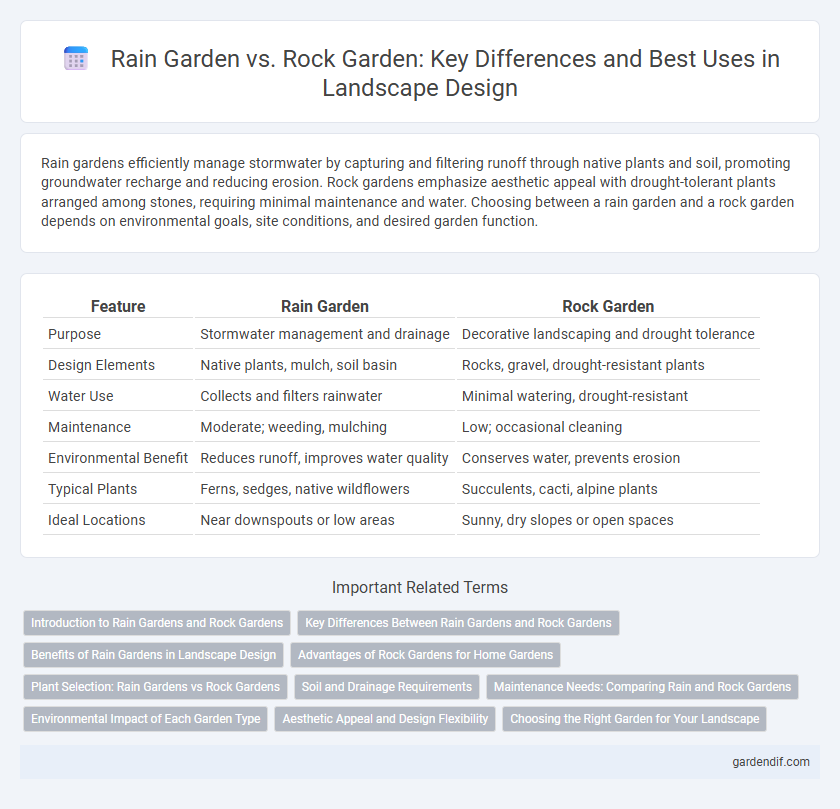
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rain Garden | Rock Garden |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Stormwater management and drainage | Decorative landscaping and drought tolerance |
| Design Elements | Native plants, mulch, soil basin | Rocks, gravel, drought-resistant plants |
| Water Use | Collects and filters rainwater | Minimal watering, drought-resistant |
| Maintenance | Moderate; weeding, mulching | Low; occasional cleaning |
| Environmental Benefit | Reduces runoff, improves water quality | Conserves water, prevents erosion |
| Typical Plants | Ferns, sedges, native wildflowers | Succulents, cacti, alpine plants |
| Ideal Locations | Near downspouts or low areas | Sunny, dry slopes or open spaces |
Introduction to Rain Gardens and Rock Gardens
Rain gardens are specially designed shallow depressions that capture and absorb rainwater runoff, promoting groundwater recharge and reducing stormwater pollution through native plants and engineered soil layers. Rock gardens, alternatively, emphasize aesthetic arrangements of rocks and drought-tolerant plants suited for arid environments, focusing on water conservation and minimal maintenance. Both garden types contribute to sustainable landscaping but serve different ecological functions and design purposes.
Key Differences Between Rain Gardens and Rock Gardens
Rain gardens are designed to capture and filter stormwater runoff using native plants that thrive in wet conditions, promoting environmental benefits like improved water quality and reduced erosion. Rock gardens emphasize aesthetic appeal through the strategic placement of rocks and drought-tolerant plants, requiring minimal water and maintenance. The primary difference lies in their function: rain gardens serve as eco-friendly stormwater management systems, while rock gardens focus on decorative landscaping in dry, well-drained areas.
Benefits of Rain Gardens in Landscape Design
Rain gardens improve stormwater management by capturing and filtering runoff, reducing erosion and water pollution. They support biodiversity by providing habitat for native plants and pollinators, enhancing ecological health and landscape aesthetics. Rain gardens also help recharge groundwater, making them a sustainable option for water conservation in urban and residential landscapes.
Advantages of Rock Gardens for Home Gardens
Rock gardens offer superior drought tolerance by using hardy, low-maintenance plants and stones that reduce water consumption, making them ideal for water-scarce regions. They provide excellent soil erosion control on slopes and uneven terrain through strategic rock placement and plant selection. Rock gardens also require less frequent upkeep compared to rain gardens, offering a long-lasting, visually appealing landscape feature that minimizes maintenance efforts.
Plant Selection: Rain Gardens vs Rock Gardens
Rain gardens feature water-tolerant plants like sedges, ferns, and native wildflowers that thrive in moist, nutrient-rich soils, effectively managing stormwater runoff. In contrast, rock gardens utilize drought-resistant species such as succulents, alpine plants, and ornamental grasses adapted to well-drained, rocky substrates with minimal water retention. Selecting plants based on moisture requirements and soil conditions ensures the ecological success and visual appeal of rain gardens versus rock gardens.
Soil and Drainage Requirements
Rain gardens require well-draining, porous soil to effectively capture and filter stormwater runoff, promoting infiltration and preventing erosion. In contrast, rock gardens thrive in sandy, gritty soil with excellent drainage, minimizing water retention around plant roots to avoid rot. Proper soil composition and drainage are critical for the success of both garden types, influencing plant health and water management.
Maintenance Needs: Comparing Rain and Rock Gardens
Rain gardens require regular upkeep such as removing debris, monitoring plant health, and ensuring proper water infiltration to prevent standing water and erosion. Rock gardens demand less frequent maintenance but benefit from occasional weeding, rock repositioning, and ensuring soil remains well-drained to avoid plant stress. Both garden types support sustainable landscaping but vary in time and effort based on plant species and environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact of Each Garden Type
Rain gardens significantly improve stormwater management by capturing and filtering runoff, reducing pollution and soil erosion while promoting groundwater recharge through native plant roots. Rock gardens, although low-maintenance and water-efficient, provide limited environmental benefits since they lack vegetation that supports biodiversity or effectively manages water flow. Choosing a rain garden enhances urban ecosystems and water quality, whereas rock gardens primarily conserve water but have minimal impact on local habitats.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Rain gardens offer a lush, vibrant aesthetic with diverse native plants and seasonal blooms that enhance ecological value and visual interest, while rock gardens provide a low-maintenance, sculptural appeal using stones, gravel, and drought-tolerant succulents. Design flexibility in rain gardens lies in their ability to accommodate water flow patterns and support wildlife habitat, contrasting with rock gardens that excel in architectural structure and minimalist beauty for arid environments. Both garden types can be customized to complement various landscape styles but differ significantly in texture, plant selection, and environmental function.
Choosing the Right Garden for Your Landscape
Rain gardens effectively manage stormwater runoff by using native plants and soil to absorb and filter rainwater, reducing erosion and improving local water quality. Rock gardens emphasize drought-tolerant plants and stones, offering low-maintenance beauty and excellent drainage for arid or sloped landscapes. Selecting the right garden depends on your climate, soil type, and water management needs to enhance both environmental benefits and aesthetic appeal.
Rain Garden vs Rock Garden Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com