
Waterborne Pests vs Soilborne Pests Illustration
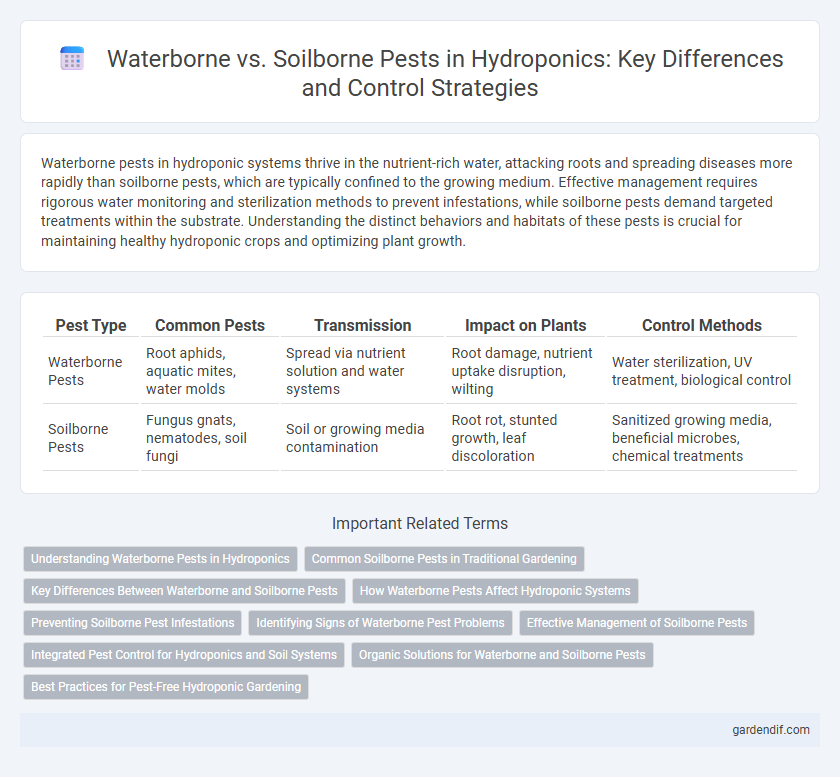
Waterborne pests in hydroponic systems thrive in the nutrient-rich water, attacking roots and spreading diseases more rapidly than soilborne pests, which are typically confined to the growing medium. Effective management requires rigorous water monitoring and sterilization methods to prevent infestations, while soilborne pests demand targeted treatments within the substrate. Understanding the distinct behaviors and habitats of these pests is crucial for maintaining healthy hydroponic crops and optimizing plant growth.
Table of Comparison
| Pest Type | Common Pests | Transmission | Impact on Plants | Control Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waterborne Pests | Root aphids, aquatic mites, water molds | Spread via nutrient solution and water systems | Root damage, nutrient uptake disruption, wilting | Water sterilization, UV treatment, biological control |
| Soilborne Pests | Fungus gnats, nematodes, soil fungi | Soil or growing media contamination | Root rot, stunted growth, leaf discoloration | Sanitized growing media, beneficial microbes, chemical treatments |
Understanding Waterborne Pests in Hydroponics
Waterborne pests in hydroponics primarily include algae, fungal water molds, and certain aquatic insect larvae that thrive in the nutrient-rich water environment. Unlike soilborne pests, which inhabit the growing medium, waterborne pests spread rapidly through the hydroponic solution, causing root damage and nutrient uptake disruption. Effective management involves maintaining water quality through regular filtration, UV sterilization, and monitoring pH and dissolved oxygen levels to inhibit pest proliferation.
Common Soilborne Pests in Traditional Gardening
Common soilborne pests in traditional gardening include root-knot nematodes, wireworms, and root maggots, which thrive in soil environments and damage plant roots by feeding on them. These pests cause reduced nutrient uptake, stunted growth, and increased susceptibility to diseases, significantly impacting crop yields. Managing soilborne pests often involves crop rotation, soil solarization, and the use of resistant plant varieties to minimize damage.
Key Differences Between Waterborne and Soilborne Pests
Waterborne pests primarily infest hydroponic systems by thriving in nutrient-rich water solutions, causing root rot and rapid spread of diseases like Pythium and Phytophthora. Soilborne pests reside in traditional soil environments, targeting plant roots with nematodes, fungi, and insects that cause wilting and nutrient deficiencies. Understanding these key differences helps optimize pest management strategies tailored for hydroponic versus soil cultivation, improving plant health and yield.
How Waterborne Pests Affect Hydroponic Systems
Waterborne pests in hydroponic systems primarily spread through the nutrient solution, rapidly affecting plant roots and causing diseases like root rot and fungal infections. These pests compromise oxygen availability and nutrient uptake, leading to stunted growth and reduced yields. Effective management requires continuous monitoring of water quality and use of biological control agents to prevent infestations and maintain system health.
Preventing Soilborne Pest Infestations
Preventing soilborne pest infestations in hydroponic systems involves maintaining sterile growing media and using pathogen-free seedlings to reduce harmful nematodes, fungi, and bacteria. Implementing crop rotation with resistant varieties and utilizing biological controls like beneficial microorganisms minimizes pest populations without chemical dependency. Proper sanitation of equipment and continuous monitoring further ensure early detection and containment of soilborne pests, safeguarding plant health and productivity.
Identifying Signs of Waterborne Pest Problems
Waterborne pest problems in hydroponic systems are often identified by signs such as slimy biofilms on roots, stunted plant growth, and yellowing or wilting leaves despite adequate nutrient levels. Common waterborne pests include root aphids, fungus gnats larvae, and water molds, which thrive in the nutrient solution and degrade root health. Monitoring root zones for discoloration, unusual odors, or the presence of small mobile pests helps early detection and effective management of these waterborne threats.
Effective Management of Soilborne Pests
Soilborne pests in hydroponic systems, such as root-knot nematodes and fungal pathogens like Pythium, cause significant root damage leading to reduced plant growth and yield. Effective management includes sterilizing growing media, implementing crop rotation with non-host plants, and using biocontrol agents like beneficial fungi and bacteria to suppress pest populations. Regular monitoring and maintaining optimal nutrient and pH levels also enhance plant resistance against soilborne pests, ensuring healthier hydroponic crops.
Integrated Pest Control for Hydroponics and Soil Systems
Waterborne pests in hydroponic systems often include pathogens like Pythium and Phytophthora, which thrive in nutrient-rich water and require constant monitoring through water filtration and biological controls such as beneficial microbes. Soilborne pests like nematodes and root-knot worms in traditional soil systems demand integrated pest management strategies combining crop rotation, organic amendments, and targeted biopesticides to suppress infestations. Implementing integrated pest control in both hydroponic and soil environments involves combining cultural, biological, and chemical methods tailored to the unique ecosystems, ensuring effective pest suppression and sustainable crop production.
Organic Solutions for Waterborne and Soilborne Pests
Waterborne pests such as root aphids and fungus gnats can be effectively managed using organic treatments like beneficial nematodes and Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti), which specifically target larval stages in hydroponic systems. Soilborne pests including root knot nematodes and fungal pathogens respond well to organic soil amendments like neem oil, compost teas, and mycorrhizal fungi that enhance plant resistance and disrupt pest life cycles. Implementing these organic solutions ensures pest control without synthetic chemicals, maintaining the sustainability and environmental benefits of hydroponic cultivation.
Best Practices for Pest-Free Hydroponic Gardening
Waterborne pests in hydroponic systems, such as algae and root aphids, thrive in nutrient-rich water, while soilborne pests like root-knot nematodes and fungus gnats typically infiltrate traditional soil gardens. Best practices for pest-free hydroponic gardening include maintaining optimal water pH and temperature, implementing regular water filtration and sterilization, and using biological controls such as beneficial nematodes or predatory insects. Preventative measures like sanitizing equipment, monitoring plant health frequently, and avoiding overwatering reduce the risk of pest infestation and ensure sustainable crop growth.
Waterborne Pests vs Soilborne Pests Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com