
Chiller vs Heater Illustration
A hydroponic chiller maintains optimal nutrient solution temperatures by cooling water, preventing root stress and promoting healthy plant growth. In contrast, a hydroponic heater raises nutrient solution temperatures to avoid chilling roots, especially in colder environments. Choosing between a chiller or heater depends on climate conditions and desired root zone temperatures for maximizing yield in hydroponic systems.
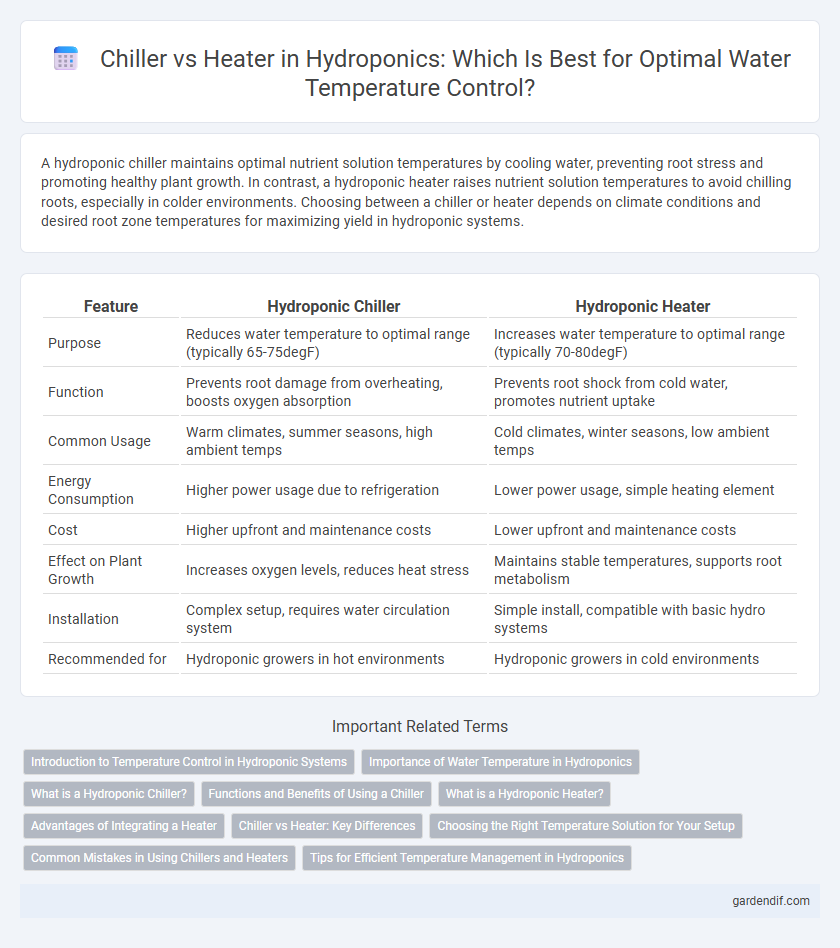
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydroponic Chiller | Hydroponic Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces water temperature to optimal range (typically 65-75degF) | Increases water temperature to optimal range (typically 70-80degF) |
| Function | Prevents root damage from overheating, boosts oxygen absorption | Prevents root shock from cold water, promotes nutrient uptake |
| Common Usage | Warm climates, summer seasons, high ambient temps | Cold climates, winter seasons, low ambient temps |
| Energy Consumption | Higher power usage due to refrigeration | Lower power usage, simple heating element |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs | Lower upfront and maintenance costs |
| Effect on Plant Growth | Increases oxygen levels, reduces heat stress | Maintains stable temperatures, supports root metabolism |
| Installation | Complex setup, requires water circulation system | Simple install, compatible with basic hydro systems |
| Recommended for | Hydroponic growers in hot environments | Hydroponic growers in cold environments |
Introduction to Temperature Control in Hydroponic Systems
Temperature control in hydroponic systems is essential for maintaining optimal root development and nutrient uptake. Chillers lower water temperature to prevent root diseases and reduce oxygen depletion, while heaters maintain warmth in cooler environments to promote nutrient absorption and plant growth. Precise regulation using chillers and heaters ensures stable water temperatures, directly impacting plant health and crop yield.
Importance of Water Temperature in Hydroponics
Maintaining optimal water temperature is crucial in hydroponics to ensure nutrient uptake and root health, with chillers preventing overheating by keeping temperatures between 65-75degF and heaters avoiding drops below 60degF that can stunt plant growth. Chillers reduce the risk of oxygen depletion and pathogen proliferation by controlling temperature in recirculating systems, while heaters promote root development in colder environments by stabilizing thermal conditions. Precise temperature management using chillers and heaters directly impacts plant yields, nutrient absorption efficiency, and overall system stability in hydroponic cultivation.
What is a Hydroponic Chiller?
A hydroponic chiller is a specialized cooling device designed to regulate the temperature of nutrient solutions in hydroponic systems, ensuring optimal root zone conditions. By maintaining consistent water temperatures, typically between 65-75degF (18-24degC), it prevents root diseases and promotes vigorous plant growth. Unlike heaters, chillers actively reduce water temperature, which is crucial in warmer climates or indoor setups where heat buildup can stress plants.
Functions and Benefits of Using a Chiller
Hydroponic chillers regulate nutrient solution temperature by cooling water to optimal ranges between 65-75degF, preventing root damage and promoting healthy plant growth. Using a chiller enhances oxygen levels and slows harmful bacterial growth, directly improving nutrient uptake and crop yield. Unlike heaters that raise temperature, chillers maintain consistent cool conditions essential for heat-sensitive crops and high-temperature environments.
What is a Hydroponic Heater?
A hydroponic heater is a device designed to regulate water temperature in hydroponic systems, ensuring optimal root zone warmth for plant growth. Unlike chillers that cool nutrient solutions to prevent overheating and root damage, heaters maintain consistent temperatures in colder environments, promoting nutrient uptake and preventing thermal shock. Efficient hydroponic heaters improve root health and maximize yield by stabilizing the nutrient reservoir's thermal conditions.
Advantages of Integrating a Heater
Integrating a heater in a hydroponic system ensures optimal root zone temperatures, promoting faster nutrient uptake and robust plant growth. Maintaining consistent warmth reduces plant stress and prevents root diseases caused by cold water conditions. Heaters enhance system efficiency by stabilizing environmental conditions, crucial for maximizing crop yield in cooler climates or during colder seasons.
Chiller vs Heater: Key Differences
Chillers regulate nutrient solution temperature by cooling it, preventing root zone overheating and promoting optimal oxygen levels for hydroponic plants. Heaters increase the temperature of the nutrient solution to maintain stable warmth in cooler environments, ensuring root growth and nutrient uptake. The key difference lies in their function: chillers reduce temperature to avoid heat stress, while heaters raise temperature to prevent chilling stress in hydroponic systems.
Choosing the Right Temperature Solution for Your Setup
Selecting the ideal temperature control system for hydroponic setups depends on the specific climate and crop requirements, with chillers providing consistent cooling for preventing root zone overheating and heaters maintaining optimal warmth during colder periods. Efficient chillers stabilize nutrient solution temperatures between 65-75degF, enhancing oxygen levels and nutrient uptake, while heaters ensure roots stay within the 70-80degF range to promote growth and prevent stress. Evaluating energy consumption, maintenance needs, and environmental conditions helps optimize plant health and maximize yield in hydroponic systems.
Common Mistakes in Using Chillers and Heaters
Common mistakes in using chillers and heaters in hydroponic systems include improper temperature calibration, which can lead to fluctuating root zone temperatures that stress plants and reduce nutrient uptake. Over-reliance on heaters without adequate ventilation may cause excessive humidity and promote fungal growth, while using chillers without considering ambient room temperature can result in energy inefficiency and inadequate cooling. Neglecting regular maintenance such as cleaning coils and checking coolant levels often reduces system performance and shortens equipment lifespan.
Tips for Efficient Temperature Management in Hydroponics
Maintaining precise temperature control in hydroponics requires balancing the use of chillers and heaters to optimize nutrient solution temperature, ideally between 65-75degF (18-24degC) for most crops. Employing insulated reservoirs and circulation pumps enhances thermal consistency, preventing temperature fluctuations that can stress plant roots and reduce oxygen levels. Monitoring with digital thermometers and automated control systems allows timely adjustments, promoting healthy growth and maximizing yield.
Chiller vs Heater Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com