
Shading cloth vs whitewash Illustration
Shading cloth provides precise control over light intensity and can be adjusted or removed easily to protect plants from excessive heat or glare. Whitewash, a traditional method, reflects sunlight by coating greenhouse surfaces, reducing temperature but potentially limiting light penetration for photosynthesis. Choosing between shading cloth and whitewash depends on specific crop needs, climate conditions, and maintenance preferences for optimal greenhouse performance.
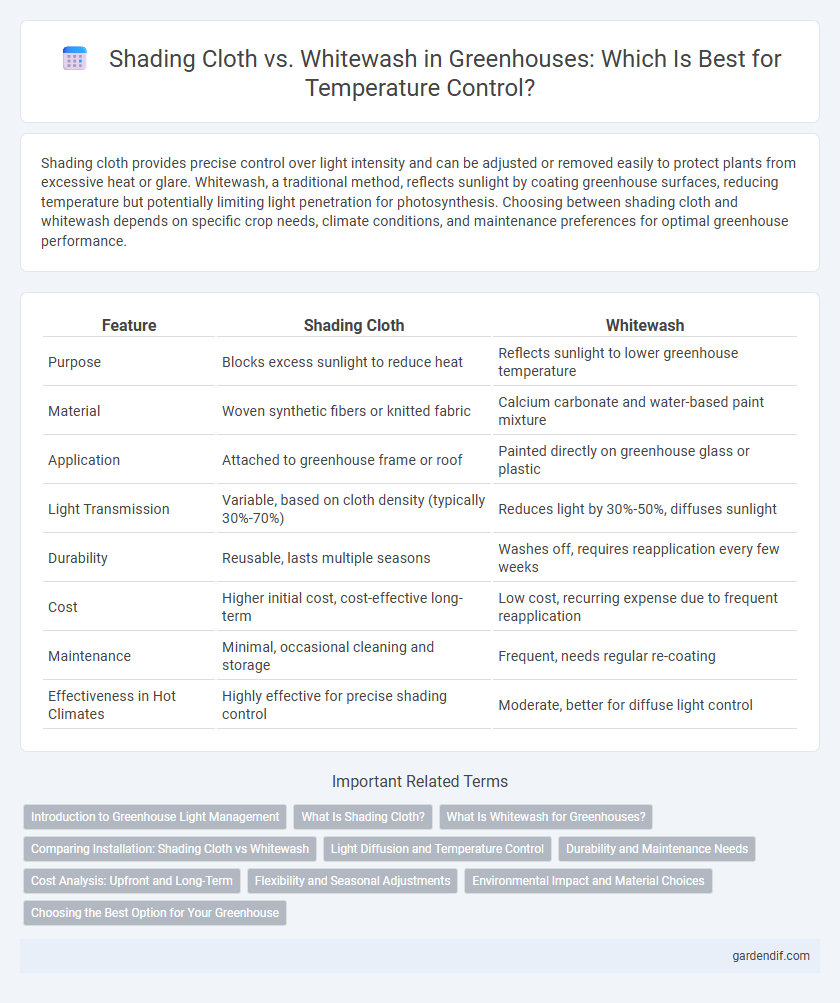
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shading Cloth | Whitewash |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Blocks excess sunlight to reduce heat | Reflects sunlight to lower greenhouse temperature |
| Material | Woven synthetic fibers or knitted fabric | Calcium carbonate and water-based paint mixture |
| Application | Attached to greenhouse frame or roof | Painted directly on greenhouse glass or plastic |
| Light Transmission | Variable, based on cloth density (typically 30%-70%) | Reduces light by 30%-50%, diffuses sunlight |
| Durability | Reusable, lasts multiple seasons | Washes off, requires reapplication every few weeks |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective long-term | Low cost, recurring expense due to frequent reapplication |
| Maintenance | Minimal, occasional cleaning and storage | Frequent, needs regular re-coating |
| Effectiveness in Hot Climates | Highly effective for precise shading control | Moderate, better for diffuse light control |
Introduction to Greenhouse Light Management
Shading cloth and whitewash are essential tools in greenhouse light management, each affecting light diffusion and intensity uniquely. Shading cloth provides adjustable light control by reducing solar radiation through fabric density, optimizing plant growth and temperature regulation. Whitewash reflects sunlight, lowering heat buildup but offers less precise control over light quality compared to shading cloth solutions.
What Is Shading Cloth?
Shading cloth is a specialized fabric used in greenhouses to reduce sunlight intensity and control temperature, enhancing plant growth by preventing excessive heat and light stress. Unlike whitewash, which is a temporary paint applied directly to greenhouse glass, shading cloth offers reusable, adjustable coverage that allows for precise regulation of light transmission. This material typically consists of woven polyethylene or polypropylene, providing durability and UV protection while maintaining airflow and visibility within the greenhouse.
What Is Whitewash for Greenhouses?
Whitewash for greenhouses is a water-based coating applied to glass or plastic surfaces to diffuse sunlight, reducing heat buildup and preventing plant scorching. It creates a translucent film that scatters light evenly, improving photosynthesis while maintaining ventilation. Compared to shading cloth, whitewash is cost-effective, easy to apply, and requires reapplication after rain or cleaning.
Comparing Installation: Shading Cloth vs Whitewash
Shading cloth offers quick and precise installation, typically requiring simple frame attachments or clips that can be easily adjusted or removed as needed. Whitewash demands thorough surface preparation and uniform application using brushes or sprayers, making it more labor-intensive with drying time considerations. Both methods provide effective temperature control, but shading cloth allows greater flexibility for seasonal adjustments without structural alterations.
Light Diffusion and Temperature Control
Shading cloth provides superior light diffusion by evenly dispersing sunlight, reducing harsh shadows and preventing plant stress, while enhancing temperature control through consistent heat reduction. Whitewash reflects sunlight more directly, which can lead to uneven light distribution and potential overheating in certain areas of the greenhouse. Optimizing greenhouse microclimate with shading cloth improves photosynthesis efficiency and minimizes temperature fluctuations better than whitewash.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Shading cloth offers superior durability compared to whitewash, with many products lasting up to 5-7 years under continuous exposure to sunlight and weather conditions. Maintenance for shading cloth is minimal, requiring occasional cleaning to remove dust and debris, whereas whitewash demands frequent reapplication every few months due to washing off from rain or deteriorating under UV rays. The long-term cost-effectiveness of shading cloth makes it a preferred choice for greenhouse growers seeking low-maintenance and lasting shading solutions.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Shading cloth entails a higher initial investment compared to whitewash, but it offers durability and consistent performance over multiple seasons, reducing replacement costs. Whitewash presents a low upfront cost but requires frequent reapplication, increasing labor and material expenses in the long term. Analyzing lifecycle costs, shading cloth proves more cost-effective for intensive greenhouse operations seeking durability and consistent thermal regulation.
Flexibility and Seasonal Adjustments
Shading cloth offers superior flexibility and allows precise control over light intensity, enabling easy seasonal adjustments to optimize plant growth in greenhouses. Unlike whitewash, which provides a permanent and uniform shading effect, shading cloth can be quickly installed, removed, or adjusted to suit changing weather conditions. This adaptability ensures optimal photosynthesis throughout the year, improving crop yield and energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Material Choices
Shading cloth and whitewash differ significantly in environmental impact and material composition; shading cloth, typically made from UV-stabilized polyethylene or polypropylene, is reusable and recyclable, reducing waste and the need for frequent replacement. Whitewash, composed mainly of lime or calcium hydroxide, is biodegradable and non-toxic but requires repeated application, potentially increasing labor and resource use over time. Selecting shading cloth minimizes chemical runoff and enhances durability, while whitewash promotes eco-friendly biodegradation and soil conditioning.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Greenhouse
Shading cloth offers precise control over light intensity and duration, making it ideal for protecting delicate plants and optimizing photosynthesis in greenhouses. Whitewash provides a cost-effective, reflective coating that diffuses sunlight evenly, reducing heat buildup but may require frequent reapplication. Selecting the best option depends on your greenhouse's crop sensitivity, budget, and climate conditions to ensure optimal growth and energy efficiency.
Shading cloth vs whitewash Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com