
Passive Solar Heating vs Electric Heating Illustration
Passive solar heating harnesses natural sunlight through windows and thermal mass materials, reducing energy costs and environmental impact by minimizing reliance on electricity. Electric heating offers precise temperature control and rapid heat distribution but often results in higher energy consumption and carbon emissions. Choosing passive solar heating supports sustainable energy use and lowers utility bills in greenhouse management.
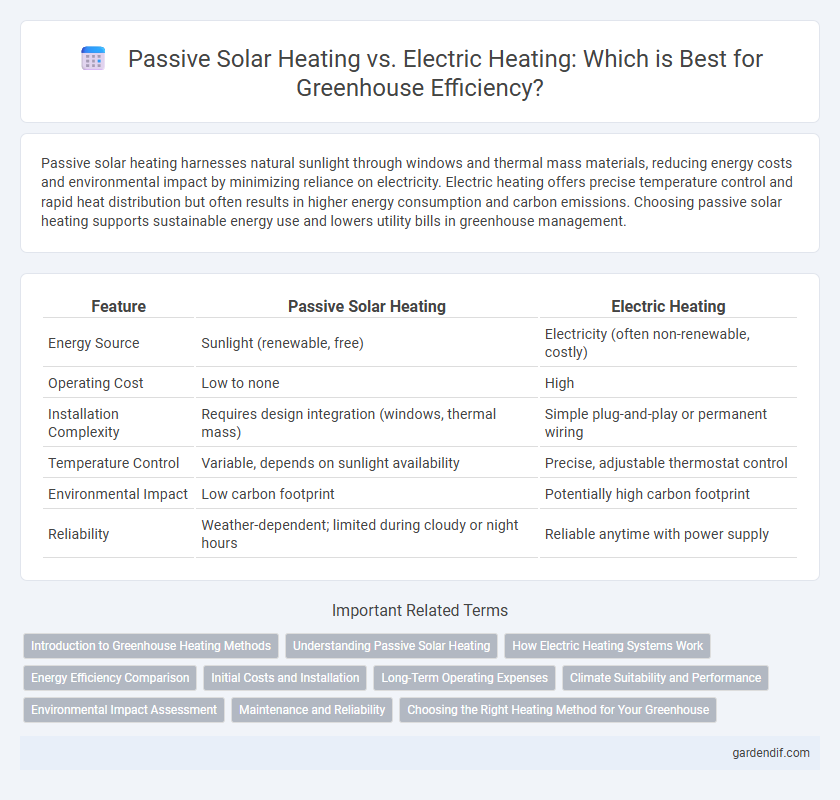
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Passive Solar Heating | Electric Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Sunlight (renewable, free) | Electricity (often non-renewable, costly) |
| Operating Cost | Low to none | High |
| Installation Complexity | Requires design integration (windows, thermal mass) | Simple plug-and-play or permanent wiring |
| Temperature Control | Variable, depends on sunlight availability | Precise, adjustable thermostat control |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint | Potentially high carbon footprint |
| Reliability | Weather-dependent; limited during cloudy or night hours | Reliable anytime with power supply |
Introduction to Greenhouse Heating Methods
Passive solar heating in greenhouses utilizes sunlight and thermal mass to naturally regulate temperature, reducing energy consumption and operational costs. Electric heating provides precise temperature control regardless of external weather, ensuring optimal growing conditions during colder periods. Choosing between these methods depends on factors such as climate, energy availability, and crop requirements for efficient greenhouse temperature management.
Understanding Passive Solar Heating
Passive solar heating in greenhouses utilizes sunlight absorbed through south-facing glass panels and thermal mass materials like concrete or water barrels, which store and slowly release heat to maintain stable temperatures. This method reduces reliance on electric heating systems, lowering energy costs and minimizing carbon emissions while promoting sustainable growing conditions. Understanding passive solar principles optimizes greenhouse design to maximize natural heat retention and improve plant growth efficiency.
How Electric Heating Systems Work
Electric heating systems in greenhouses utilize resistive heating elements to convert electrical energy into heat, efficiently raising the ambient temperature for plant growth. These systems are often combined with thermostats and timers to maintain consistent heat levels, ensuring optimal conditions regardless of external weather fluctuations. Unlike passive solar heating, electric heating provides precise temperature control and reliability during periods of low sunlight.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Passive solar heating in greenhouses harnesses natural sunlight through strategically placed glazing, reducing reliance on external energy sources and significantly cutting operational costs. Electric heating systems provide consistent temperature control but consume considerable electricity, leading to higher energy bills and a larger carbon footprint. Evaluations show passive solar systems can improve energy efficiency by up to 70% compared to traditional electric heaters, making them a sustainable choice for maintaining optimal growing conditions.
Initial Costs and Installation
Passive solar heating in greenhouses involves low upfront costs and simple installation, utilizing materials like south-facing glass and thermal mass to harness natural sunlight. In contrast, electric heating requires higher initial investment due to purchasing heaters, wiring, and potential modifications to the electrical system. Installation of electric systems is more complex, often needing professional expertise to ensure safety and system efficiency.
Long-Term Operating Expenses
Passive solar heating in greenhouses significantly reduces long-term operating expenses by harnessing natural sunlight and thermal mass to maintain temperature without ongoing energy costs. In contrast, electric heating systems incur continuous electricity expenses and require regular maintenance, leading to higher cumulative operating costs over time. Investing in passive solar design enhances energy efficiency and cost savings, making it the more economical choice for sustainable greenhouse management.
Climate Suitability and Performance
Passive solar heating in greenhouses harnesses natural sunlight, making it ideal for mild to moderate climates where solar radiation is sufficient to maintain optimal temperatures. Electric heating offers precise temperature control regardless of external weather conditions, proving advantageous in colder or variable climates where solar gain is inconsistent. Performance-wise, passive solar systems reduce energy costs but may require supplemental heating, while electric heaters provide reliable warmth at higher operational expenses.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Passive solar heating in greenhouses significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing natural sunlight and thermal mass for temperature regulation, minimizing reliance on fossil fuel-based electricity. Electric heating systems, often powered by grid electricity generated from non-renewable sources, contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions and increased environmental footprint. Life cycle assessments reveal passive solar heating as a sustainable alternative, enhancing energy efficiency and lowering overall environmental impact in greenhouse climate control.
Maintenance and Reliability
Passive solar heating requires minimal maintenance due to the absence of mechanical components, reducing repair costs and downtime. Electric heating systems demand regular inspections and component replacements to ensure efficiency and prevent electrical hazards. Reliability in passive solar heating is high as it depends on natural sunlight, whereas electric heating offers consistent temperature control but risks failures from power outages or equipment malfunctions.
Choosing the Right Heating Method for Your Greenhouse
Passive solar heating harnesses natural sunlight through greenhouse glazing, providing consistent warmth while significantly reducing energy costs and environmental impact. Electric heating offers precise temperature control, ideal for maintaining optimal growing conditions during periods of low sunlight or extreme cold. Selecting the right heating method depends on factors such as greenhouse size, climate, plant type, and budget, with many growers opting for a hybrid approach to maximize efficiency and plant health.
Passive Solar Heating vs Electric Heating Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com