
Top Ventilation vs Side Ventilation Illustration
Top ventilation in greenhouses enhances heat dissipation by allowing hot air to escape through the roof, creating a natural airflow that cools the interior effectively. Side ventilation promotes cross-ventilation by drawing in cooler air from the sides and pushing warm air out, which helps maintain consistent temperature and humidity levels. Combining both can optimize airflow, but the choice depends on greenhouse design and climate conditions.
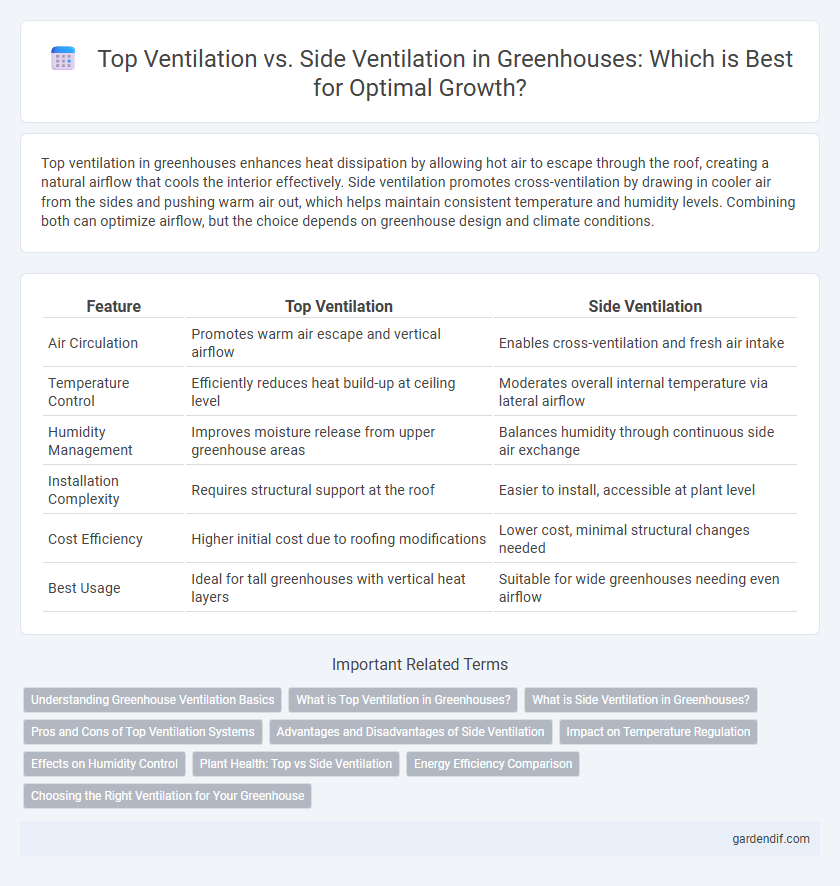
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Top Ventilation | Side Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Air Circulation | Promotes warm air escape and vertical airflow | Enables cross-ventilation and fresh air intake |
| Temperature Control | Efficiently reduces heat build-up at ceiling level | Moderates overall internal temperature via lateral airflow |
| Humidity Management | Improves moisture release from upper greenhouse areas | Balances humidity through continuous side air exchange |
| Installation Complexity | Requires structural support at the roof | Easier to install, accessible at plant level |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost due to roofing modifications | Lower cost, minimal structural changes needed |
| Best Usage | Ideal for tall greenhouses with vertical heat layers | Suitable for wide greenhouses needing even airflow |
Understanding Greenhouse Ventilation Basics
Top ventilation in greenhouses allows hot air to escape quickly, promoting better temperature regulation and reducing humidity levels effectively. Side ventilation facilitates fresh air intake at a lower level, creating a natural airflow that cools plants while supplying essential carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Combining both ventilation types ensures optimal air circulation, maintaining a stable environment for healthy plant growth.
What is Top Ventilation in Greenhouses?
Top ventilation in greenhouses refers to vents installed on the roof or upper sections to facilitate hot air escape and improve airflow. This method maximizes heat removal by leveraging the natural rise of warm air, maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels. Effective top ventilation supports plant health by preventing overheating and promoting even air distribution.
What is Side Ventilation in Greenhouses?
Side ventilation in greenhouses involves installing vents or windows along the sides of the structure to facilitate airflow and temperature regulation. This method allows fresh air to enter at plant level, promoting improved air circulation and reducing humidity buildup, which helps prevent diseases. Side ventilation is especially effective in maintaining a stable environment for plants by enhancing natural cooling and ensuring consistent CO2 exchange.
Pros and Cons of Top Ventilation Systems
Top ventilation systems in greenhouses enhance air circulation by allowing hot air to escape naturally, improving temperature regulation and reducing humidity levels. They are energy-efficient and reduce the risk of overheating during hot weather, but installation costs and maintenance can be higher compared to side ventilation. However, top ventilation may be less effective in areas with low wind speeds, limiting airflow and cooling capacity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Side Ventilation
Side ventilation in greenhouses offers improved air circulation by allowing fresh air to enter at plant level, reducing heat buildup and promoting healthier plant growth. It can be more effective in controlling humidity and preventing fungal diseases compared to top ventilation. However, side ventilation may be less efficient in hot climates due to limited vertical airflow and increased exposure to dust and pests.
Impact on Temperature Regulation
Top ventilation in greenhouses promotes efficient heat escape by allowing hot air to rise and exit, resulting in cooler internal temperatures. Side ventilation facilitates cross airflow, enhancing air circulation and reducing temperature gradients within the structure. Combining both methods optimizes temperature regulation by balancing heat removal and maintaining consistent airflow throughout the greenhouse.
Effects on Humidity Control
Top ventilation in greenhouses facilitates the release of warm, moist air rising from plants, effectively reducing humidity and preventing condensation buildup. Side ventilation promotes cross airflow, enhancing air circulation at plant canopy level and aiding in balanced humidity control throughout the greenhouse. Combining top and side ventilation systems optimizes moisture removal, creating a stable environment that minimizes fungal disease risks and supports plant health.
Plant Health: Top vs Side Ventilation
Top ventilation in greenhouses promotes efficient hot air escape, reducing humidity and preventing fungal diseases, which supports optimal plant health. Side ventilation ensures steady airflow at plant canopy level, enhancing CO2 circulation critical for photosynthesis and reducing heat stress on leaves. Combining both ventilation types optimizes temperature regulation and air quality, significantly improving plant growth and disease resistance.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Top ventilation in greenhouses promotes natural convection by allowing warm air to escape upwards, leading to more effective temperature regulation and reduced reliance on mechanical cooling systems. Side ventilation facilitates cross-ventilation by enabling air to flow horizontally, which can be less energy-efficient in maintaining uniform temperature, especially in larger structures. Studies indicate that integrating top vents with controlled side vents optimizes energy consumption by balancing heat removal and airflow, resulting in significant reductions in cooling energy costs.
Choosing the Right Ventilation for Your Greenhouse
Top ventilation in greenhouses enhances heat escape and air circulation, ideal for controlling temperature in hot climates. Side ventilation promotes cross-ventilation, improving airflow and humidity control, beneficial for greenhouses growing humidity-sensitive plants. Selecting ventilation depends on climate conditions, plant types, and greenhouse design to optimize growth and energy efficiency.
Top Ventilation vs Side Ventilation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com