
Fogging System vs Misting System Illustration
Fogging systems produce ultra-fine water droplets that quickly evaporate, increasing humidity levels without wetting plants, making them ideal for maintaining precise atmospheric conditions in a greenhouse. Misting systems release larger droplets that cool the surrounding air through evaporation but can leave foliage damp, potentially promoting disease in sensitive plants. Selecting between fogging and misting depends on the crop's humidity requirements and the need for cooling versus moisture control.
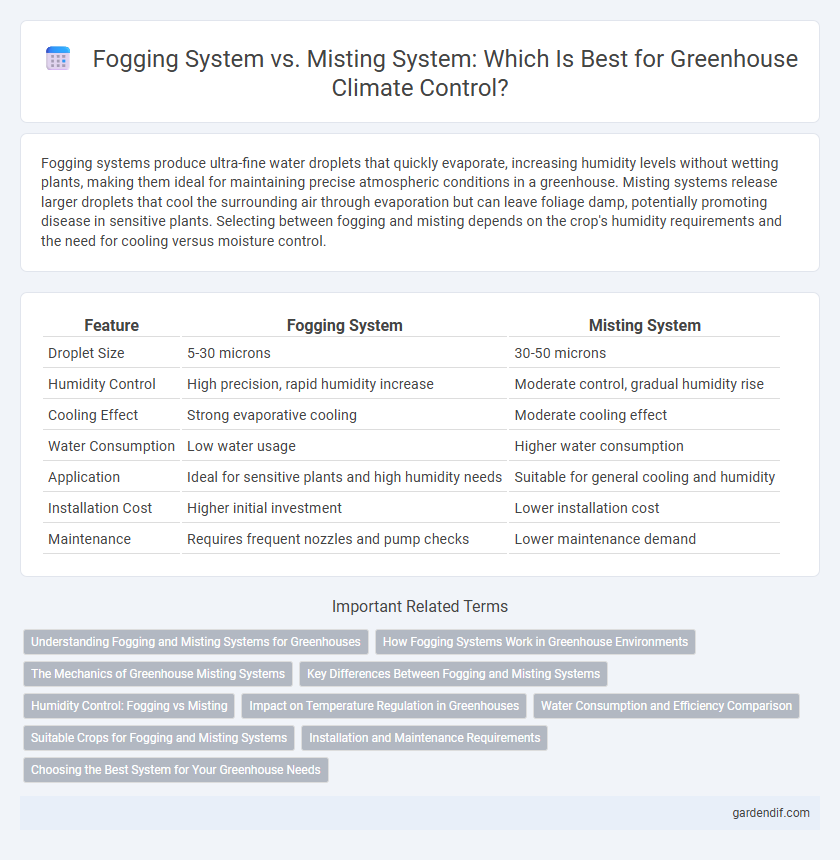
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fogging System | Misting System |
|---|---|---|
| Droplet Size | 5-30 microns | 30-50 microns |
| Humidity Control | High precision, rapid humidity increase | Moderate control, gradual humidity rise |
| Cooling Effect | Strong evaporative cooling | Moderate cooling effect |
| Water Consumption | Low water usage | Higher water consumption |
| Application | Ideal for sensitive plants and high humidity needs | Suitable for general cooling and humidity |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower installation cost |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent nozzles and pump checks | Lower maintenance demand |
Understanding Fogging and Misting Systems for Greenhouses
Fogging systems in greenhouses generate ultrafine water droplets that rapidly evaporate, increasing humidity and cooling the environment without wetting plants, making them ideal for delicate crops requiring precise humidity control. Misting systems produce larger droplets that settle more quickly, providing surface moisture to plants and soil, which helps reduce leaf temperature and dust but may increase the risk of fungal diseases if overused. Selecting between fogging and misting depends on crop type, climate conditions, and desired humidity levels, with fogging favored for high-humidity requirements and misting suited for evaporative cooling and light watering tasks.
How Fogging Systems Work in Greenhouse Environments
Fogging systems in greenhouses operate by releasing ultra-fine water droplets, typically less than 10 microns in diameter, which rapidly evaporate to increase humidity without wetting plant surfaces. These systems utilize high-pressure pumps and specialized nozzles to create a consistent, uniform mist that enhances microclimate control crucial for crop growth. By maintaining optimal humidity levels, fogging systems improve transpiration, reduce plant stress, and prevent fungal diseases more effectively than traditional misting systems.
The Mechanics of Greenhouse Misting Systems
Greenhouse misting systems operate by releasing fine water droplets through high-pressure nozzles to increase humidity and regulate temperature efficiently. These systems rely on precise pump mechanisms and calibrated nozzles to ensure uniform droplet size and coverage, optimizing plant transpiration and growth conditions. Compared to fogging systems, misting systems deliver larger droplets that provide targeted cooling and hydration without oversaturating the air.
Key Differences Between Fogging and Misting Systems
Fogging systems produce ultra-fine water droplets, typically less than 10 microns, which rapidly evaporate to increase humidity without wetting plants, making them ideal for precise climate control in greenhouses. Misting systems release larger droplets around 30-50 microns that settle on plant surfaces, providing both humidity and surface cooling but potentially increasing the risk of disease due to surface moisture. The key distinction lies in droplet size and function: fogging optimizes ambient humidity with minimal wetting, while misting delivers direct leaf wetting along with temperature reduction.
Humidity Control: Fogging vs Misting
Fogging systems produce fine water droplets under 10 microns that rapidly evaporate, creating high humidity levels ideal for delicate plants in greenhouses. Misting systems release larger droplets, around 30-50 microns, providing moderate humidity increases while also cooling the area. For precise humidity control, fogging offers superior saturation without excessive wetting, whereas misting balances humidity with surface moisture for plants requiring less dense humidity.
Impact on Temperature Regulation in Greenhouses
Fogging systems provide fine water droplets that rapidly evaporate, enhancing cooling and maintaining optimal temperature levels within greenhouses. Misting systems release larger droplets that settle quickly, offering moderate temperature reduction but increased humidity compared to fogging. Effective temperature regulation depends on system choice, with fogging better suited for high-temperature control and misting preferred when balancing cooling with humidity management.
Water Consumption and Efficiency Comparison
Fogging systems in greenhouses consume significantly less water than misting systems, using fine droplets that evaporate quickly to maintain high humidity with minimal waste. Misting systems spray larger water droplets that often settle on plants and surfaces, resulting in higher water consumption and evaporative loss. Efficiency in humidity control favors fogging systems due to their ability to create a consistent microclimate while conserving water resources.
Suitable Crops for Fogging and Misting Systems
Fogging systems are ideal for delicate crops such as orchids and leafy greens that require high humidity and fine moisture distribution without waterlogging. Misting systems suit crops like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, where moderate humidity and periodic moisture help maintain plant health and reduce heat stress. Selecting the appropriate system enhances crop yield by matching humidity control to the specific transpiration rates and water needs of each plant type.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Fogging systems require precise installation involving high-pressure pumps and fine nozzles to generate ultra-fine droplets, ensuring uniform humidity without wetting plants, while misting systems utilize lower pressure and larger nozzles for coarser spray. Maintenance for fogging systems demands regular cleaning to prevent nozzle clogging and monitoring pump performance, whereas misting systems have simpler upkeep with less frequent filter changes and easier nozzle replacement. Proper installation and consistent maintenance directly impact system efficiency, plant health, and greenhouse climate control.
Choosing the Best System for Your Greenhouse Needs
Fogging systems produce ultra-fine droplets that quickly lower temperature and increase humidity, making them ideal for high-humidity, tropical greenhouse environments. Misting systems emit larger droplets, providing gentle cooling and moisture without over-saturating plants, suitable for greenhouses needing moderate humidity control. Selecting the best system depends on your crop type, climate conditions, and precise humidity and temperature requirements to optimize plant health and growth.
Fogging System vs Misting System Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com