
Hoop House vs Glasshouse Illustration
Hoop houses use lightweight, flexible materials like plastic film to create affordable, energy-efficient growing environments, ideal for season extension and protecting crops from frost. Glasshouses offer superior light transmission and durability, making them suitable for year-round commercial production with precise climate control. Choosing between hoop house and glasshouse depends on budget, crop type, and desired growing conditions.
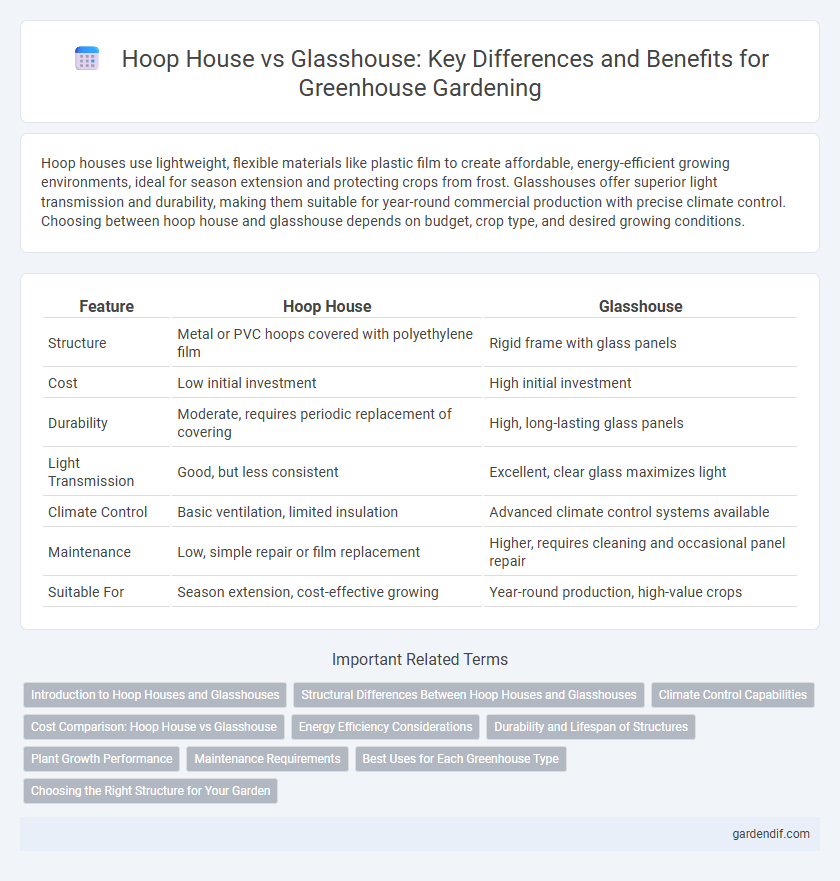
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hoop House | Glasshouse |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Metal or PVC hoops covered with polyethylene film | Rigid frame with glass panels |
| Cost | Low initial investment | High initial investment |
| Durability | Moderate, requires periodic replacement of covering | High, long-lasting glass panels |
| Light Transmission | Good, but less consistent | Excellent, clear glass maximizes light |
| Climate Control | Basic ventilation, limited insulation | Advanced climate control systems available |
| Maintenance | Low, simple repair or film replacement | Higher, requires cleaning and occasional panel repair |
| Suitable For | Season extension, cost-effective growing | Year-round production, high-value crops |
Introduction to Hoop Houses and Glasshouses
Hoop houses and glasshouses are two popular types of structures used for controlled-environment agriculture, each offering unique benefits for plant growth. Hoop houses, typically made with flexible plastic sheeting stretched over curved metal frames, provide cost-effective protection against weather and pests while allowing ample light penetration. In contrast, glasshouses utilize rigid glass panels and metal frameworks to create a stable, insulated environment, enabling year-round cultivation with precise control over temperature and humidity.
Structural Differences Between Hoop Houses and Glasshouses
Hoop houses use flexible metal or PVC pipes covered with polyethylene film, creating a curved structure that is lightweight and easy to assemble, while glasshouses feature rigid frames typically made of aluminum or steel with glass panels offering durability and superior light transmission. The hoop house's semi-circular shape allows quick ventilation adjustments but provides less insulation and protection compared to the robust, weather-resistant glasshouse design. Glasshouses support complex climate control systems, making them ideal for year-round cultivation, whereas hoop houses are preferred for seasonal crop protection due to their cost-effectiveness and simpler structure.
Climate Control Capabilities
Hoop houses provide basic climate control by using plastic covers that trap heat and protect crops from wind and light frost but offer limited temperature regulation and ventilation options. Glasshouses feature superior climate control with advanced heating, cooling, and ventilation systems, allowing precise management of temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels year-round. This high level of environmental control in glasshouses supports enhanced plant growth, extended growing seasons, and increased crop yields compared to hoop houses.
Cost Comparison: Hoop House vs Glasshouse
Hoop houses typically cost between $3 and $8 per square foot, making them a more economical option for small to medium-scale growers compared to glasshouses, which can range from $20 to $50 or more per square foot due to higher material and construction expenses. Maintenance costs for hoop houses are generally lower because they use lightweight polyethylene films instead of glass panels, which require more frequent cleaning and repair. While initial investment is significantly less with hoop houses, long-term durability and climate control in glasshouses can justify higher upfront costs for commercial growers seeking to optimize crop production year-round.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Hoop houses utilize polyethylene coverings that provide effective insulation while allowing flexibility in temperature control, resulting in lower initial energy costs compared to glasshouses. Glasshouses, constructed with glass panels, offer superior light transmission and durability but often require higher heating energy to maintain optimal growing temperatures, especially in colder climates. Energy efficiency in hoop houses is enhanced by their ability to retain heat passively, whereas glasshouses benefit from integrating supplemental heating systems and advanced glazing technologies.
Durability and Lifespan of Structures
Hoop houses typically feature galvanized steel frames with polyethylene covers, offering moderate durability and a lifespan of 5 to 7 years under optimal conditions. Glasshouses utilize aluminum or steel frames combined with glass panels, providing superior robustness and longevity, often exceeding 20 years with proper maintenance. The choice depends on balancing initial costs with long-term structural integrity and environmental resistance.
Plant Growth Performance
Hoop houses provide a flexible, cost-effective environment that enhances plant growth by maintaining warmer temperatures and higher humidity levels compared to open fields. Glasshouses, with their superior light transmission and precise climate control systems, optimize photosynthesis and encourage faster, more uniform plant development. Both structures improve plant growth performance, but glasshouses generally deliver higher yields due to better environmental regulation and protection from pests.
Maintenance Requirements
Hoop houses require minimal maintenance due to their simple structure and use of plastic covers that can be easily replaced or repaired. Glasshouses demand more maintenance, including regular cleaning of glass panels to maximize light transmission and checking the structural integrity to prevent leaks and damage. Both structures benefit from periodic inspections, but glasshouses typically involve higher ongoing labor and cost for upkeep.
Best Uses for Each Greenhouse Type
Hoop houses excel in extending growing seasons for vegetables and herbs due to their cost-effective design and flexibility in temperature control. Glasshouses provide superior light transmission and climate regulation, making them ideal for cultivating high-value crops like flowers, tropical plants, and delicate seedlings. Selecting the appropriate greenhouse type depends on crop requirements, budget constraints, and desired durability.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Garden
Hoop houses offer a cost-effective, lightweight structure ideal for extending the growing season with flexible plastic coverings, while glasshouses provide superior durability, light transmission, and temperature control for year-round cultivation. Consider your budget, climate, and crop requirements when choosing between the affordable, easily assembled hoop house and the energy-efficient, permanent glasshouse. Effective garden management depends on selecting a structure that balances insulation, ventilation, and space to maximize plant growth.
Hoop House vs Glasshouse Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com