
Overwintering vs Season Extension Illustration
Overwintering in a greenhouse involves protecting plants through cold seasons to ensure survival and growth despite harsh winter conditions. Season extension focuses on lengthening the growing period by modifying environmental factors such as temperature and light, enabling cultivation beyond traditional outdoor seasons. Both techniques maximize productivity but differ in their strategic approach to managing climate challenges.
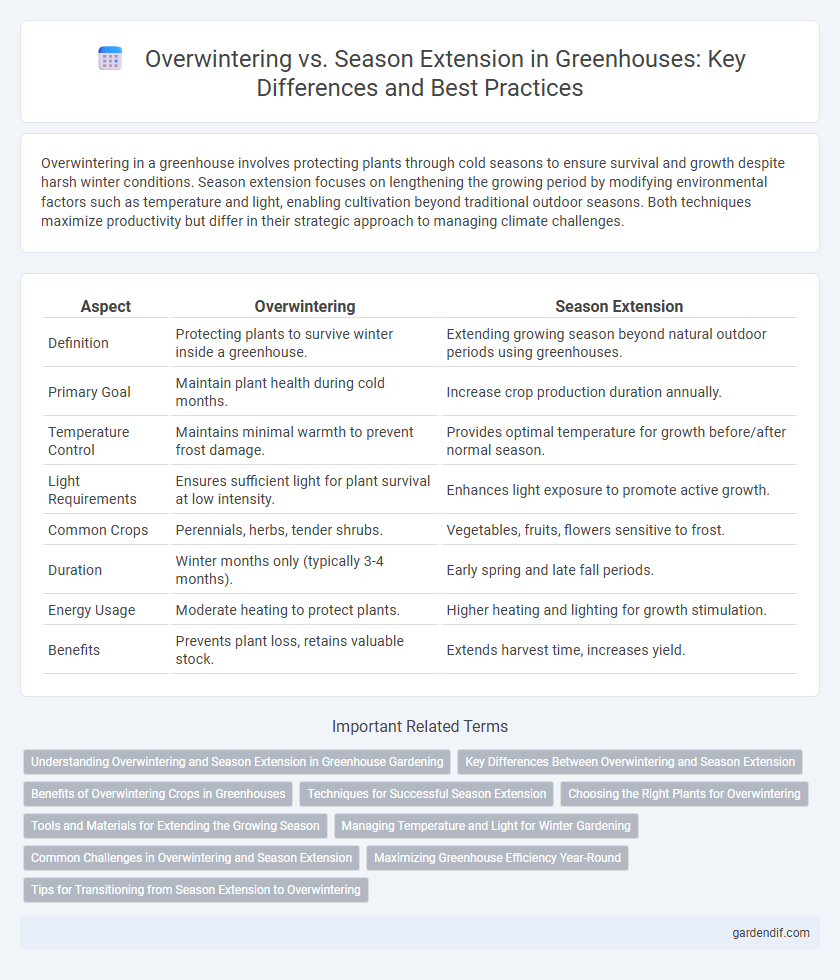
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Overwintering | Season Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protecting plants to survive winter inside a greenhouse. | Extending growing season beyond natural outdoor periods using greenhouses. |
| Primary Goal | Maintain plant health during cold months. | Increase crop production duration annually. |
| Temperature Control | Maintains minimal warmth to prevent frost damage. | Provides optimal temperature for growth before/after normal season. |
| Light Requirements | Ensures sufficient light for plant survival at low intensity. | Enhances light exposure to promote active growth. |
| Common Crops | Perennials, herbs, tender shrubs. | Vegetables, fruits, flowers sensitive to frost. |
| Duration | Winter months only (typically 3-4 months). | Early spring and late fall periods. |
| Energy Usage | Moderate heating to protect plants. | Higher heating and lighting for growth stimulation. |
| Benefits | Prevents plant loss, retains valuable stock. | Extends harvest time, increases yield. |
Understanding Overwintering and Season Extension in Greenhouse Gardening
Overwintering in greenhouse gardening involves protecting plants during the cold months to ensure their survival until the next growing season, often using insulation and controlled temperatures. Season extension focuses on lengthening the growing period beyond natural outdoor limits by maintaining optimal warmth, humidity, and light within the greenhouse environment. Effective management of temperature, ventilation, and humidity is crucial for both practices to maximize plant health and yield throughout colder periods.
Key Differences Between Overwintering and Season Extension
Overwintering in a greenhouse involves protecting plants through the cold months by maintaining stable temperatures and minimizing growth, ensuring survival until spring. Season extension focuses on prolonging the growing period beyond typical outdoor limitations by controlling temperature, light, and humidity to promote continuous plant development. The key difference lies in overwintering prioritizing plant dormancy and survival, whereas season extension emphasizes active growth and harvest extension.
Benefits of Overwintering Crops in Greenhouses
Overwintering crops in greenhouses preserves valuable plant varieties through harsh winter conditions, ensuring continuous yield and reducing the need for replanting each season. This method maximizes space utilization and energy efficiency by maintaining stable microclimates, which supports early spring harvests and improves overall crop quality. Overwintering also protects against pests and diseases prevalent in outdoor environments, enhancing crop health and boosting long-term sustainability for growers.
Techniques for Successful Season Extension
Techniques for successful season extension in greenhouses include the use of thermal mass, row covers, and supplemental heating to maintain optimal temperature and protect crops from frost. Employing passive solar design elements and ventilation strategies helps regulate humidity and airflow, reducing plant stress and disease risk. Integrating these methods enables growers to maximize yield beyond the traditional growing season while conserving energy.
Choosing the Right Plants for Overwintering
Selecting the right plants for overwintering in a greenhouse involves prioritizing cold-hardy varieties such as kale, spinach, and chard, which maintain productivity in lower temperatures. Understanding plant hardiness zones and microclimate conditions within the greenhouse ensures optimal survival and growth during winter months. Overwintering crops often require less supplemental heating compared to season extension, making plant choice crucial for energy-efficient and successful cold season cultivation.
Tools and Materials for Extending the Growing Season
Overwintering in greenhouses relies heavily on insulated coverings, thermal mass materials like water barrels, and supplemental heating systems to protect plants from freezing temperatures. Season extension tools include row covers, cold frames, and high tunnels made from lightweight, durable materials such as polyethylene film and UV-resistant plastics. Efficient use of grow lights, soil heaters, and frost cloths enhances temperature regulation and plant survival during colder months.
Managing Temperature and Light for Winter Gardening
Overwintering in greenhouses involves maintaining stable temperatures around 45-55degF and providing supplemental lighting of 8-12 hours daily to support plant dormancy and survival. Season extension techniques focus on raising temperatures to 60-70degF and increasing light exposure to 12-16 hours through LED grow lights, promoting active growth and harvest during colder months. Effective temperature regulation via heaters and thermal curtains, combined with automated lighting systems, ensures optimal photosynthesis and reduces frost damage in winter gardening.
Common Challenges in Overwintering and Season Extension
Overwintering and season extension in greenhouses face common challenges such as temperature regulation, pest management, and maintaining adequate light levels. Frost protection and energy efficiency are critical to prevent crop loss during harsh winter conditions, while minimizing heating costs is essential for sustainable production. Proper ventilation and humidity control also play vital roles in preventing disease outbreaks and ensuring healthy plant growth throughout extended growing periods.
Maximizing Greenhouse Efficiency Year-Round
Overwintering preserves plant health during cold months by maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels inside the greenhouse, ensuring crop survival and productivity. Season extension techniques, such as adding thermal screens and supplemental lighting, boost plant growth beyond the natural growing season. Combining both strategies maximizes greenhouse efficiency year-round by stabilizing environmental conditions and extending usable growing periods.
Tips for Transitioning from Season Extension to Overwintering
To successfully transition from season extension to overwintering in a greenhouse, prioritize insulation improvements such as adding thermal curtains or bubble wrap to retain heat during colder months. Implementing supplemental heating systems and monitoring soil temperature ensures plant survival through winter. Regularly adjusting ventilation helps maintain optimal humidity levels, preventing mold and promoting healthy growth throughout the extended period.
Overwintering vs Season Extension Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com