
Greenhouse hydroponics vs traditional soil gardening Illustration
Greenhouse hydroponics offers precise nutrient control and faster plant growth compared to traditional soil gardening, which relies on natural soil conditions and is more susceptible to pests and diseases. Hydroponic systems in greenhouses use less water and space, making them ideal for urban or resource-limited environments, while soil gardening supports beneficial microbial life and organic matter that enhance soil health. Choosing between the two depends on factors like crop type, environmental control, and sustainability goals.
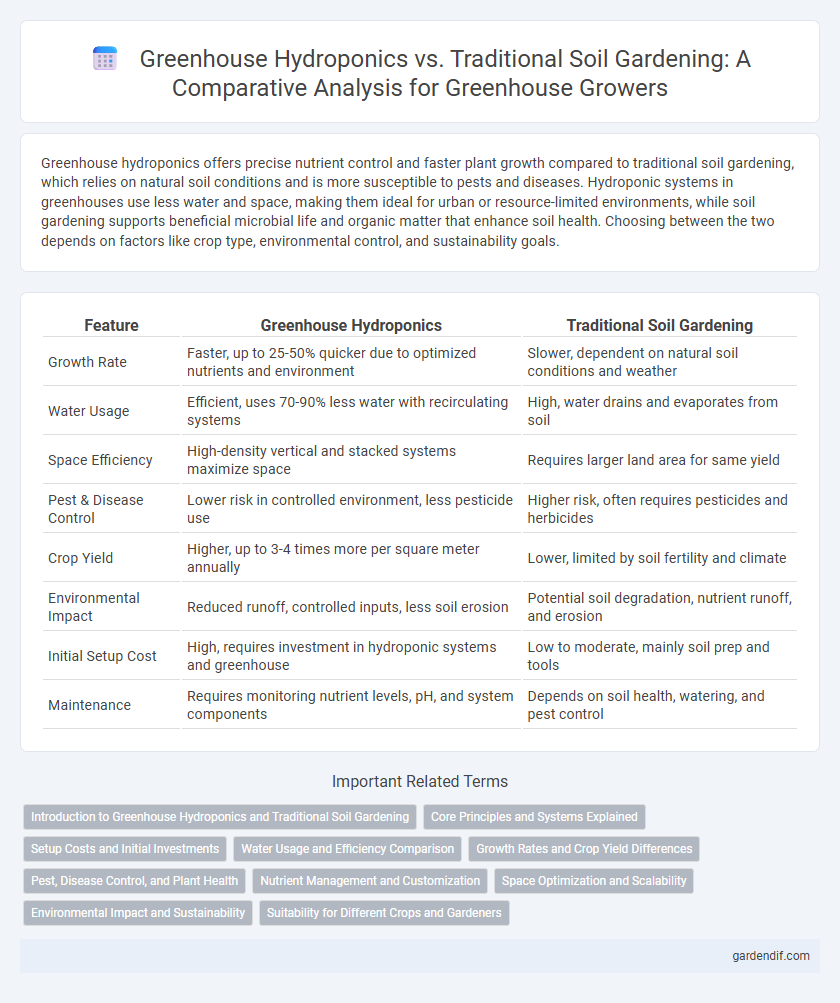
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Greenhouse Hydroponics | Traditional Soil Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Faster, up to 25-50% quicker due to optimized nutrients and environment | Slower, dependent on natural soil conditions and weather |
| Water Usage | Efficient, uses 70-90% less water with recirculating systems | High, water drains and evaporates from soil |
| Space Efficiency | High-density vertical and stacked systems maximize space | Requires larger land area for same yield |
| Pest & Disease Control | Lower risk in controlled environment, less pesticide use | Higher risk, often requires pesticides and herbicides |
| Crop Yield | Higher, up to 3-4 times more per square meter annually | Lower, limited by soil fertility and climate |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced runoff, controlled inputs, less soil erosion | Potential soil degradation, nutrient runoff, and erosion |
| Initial Setup Cost | High, requires investment in hydroponic systems and greenhouse | Low to moderate, mainly soil prep and tools |
| Maintenance | Requires monitoring nutrient levels, pH, and system components | Depends on soil health, watering, and pest control |
Introduction to Greenhouse Hydroponics and Traditional Soil Gardening
Greenhouse hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, enabling precise control over environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light within the greenhouse environment. Traditional soil gardening relies on soil as a growth medium, depending on natural soil composition, irrigation, and climate conditions, which can vary significantly and affect plant health and yield. Hydroponic systems in greenhouses often result in faster growth rates and higher crop productivity compared to conventional soil gardening due to optimized resource management and reduced pest exposure.
Core Principles and Systems Explained
Greenhouse hydroponics relies on soilless cultivation, using nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots, enhancing growth efficiency and resource use. Traditional soil gardening depends on soil as a natural medium for root support and nutrient supply, with plants relying on soil biology for nutrient cycling and retention. Hydroponic systems in greenhouses, such as nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC), optimize environmental control, reduce pests, and enable higher yield densities compared to traditional soil-based methods.
Setup Costs and Initial Investments
Greenhouse hydroponics requires a higher initial investment due to the need for specialized equipment such as nutrient delivery systems, grow lights, and climate control technology, whereas traditional soil gardening generally involves lower setup costs with basic tools and soil amendments. The cost of hydroponic systems varies widely but typically exceeds that of soil gardening infrastructure, reflecting its advanced technology and water efficiency benefits. Despite higher upfront expenses, hydroponics offers faster crop cycles and higher yields, which can offset initial investments over time.
Water Usage and Efficiency Comparison
Greenhouse hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil gardening by recycling nutrient solutions and minimizing evaporation. This method delivers water directly to plant roots, significantly reducing wastage compared to soil-based systems. Efficient water management in hydroponics supports sustainable agriculture, especially in regions facing water scarcity.
Growth Rates and Crop Yield Differences
Greenhouse hydroponics offers significantly faster growth rates compared to traditional soil gardening due to optimized nutrient delivery and controlled environmental conditions. Crop yields in hydroponic systems within greenhouses are typically higher, achieving up to 30-50% increased productivity per square meter. This efficiency stems from precise water and nutrient management, reducing plant stress and enhancing photosynthesis.
Pest, Disease Control, and Plant Health
Greenhouse hydroponics significantly reduces pest infestations by eliminating soil-borne insects and diseases common in traditional gardening, promoting healthier plant growth. Controlled environments limit exposure to pathogens, decreasing the need for chemical pesticides and enhancing plant resilience. This method fosters improved nutrient uptake and disease resistance, resulting in higher yields and superior plant health compared to soil-based cultivation.
Nutrient Management and Customization
Greenhouse hydroponics offers precise nutrient management by delivering a balanced mix of essential minerals directly to plant roots, ensuring optimal growth and reducing nutrient waste compared to traditional soil gardening. Customization in hydroponic systems allows growers to tailor nutrient concentrations and pH levels for specific crops, resulting in higher yields and faster growth cycles. Traditional soil gardening relies on variable soil composition, making nutrient control less consistent and customization more challenging, often leading to nutrient deficiencies or excesses.
Space Optimization and Scalability
Greenhouse hydroponics maximizes space utilization by enabling vertical stacking and dense plant arrangements, which traditional soil gardening cannot achieve due to root space and soil requirements. This method supports scalability through modular system expansion and controlled environment parameters, allowing consistent crop production regardless of outdoor conditions. Efficient resource use and precise nutrient delivery in hydroponics further enhance productivity per square meter compared to conventional soil-based greenhouses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Greenhouse hydroponics significantly reduces water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional soil gardening, making it a more sustainable choice for water-scarce regions. This method minimizes land use and prevents soil degradation, thereby maintaining soil health and biodiversity. The controlled environment also reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, lowering chemical runoff and promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices.
Suitability for Different Crops and Gardeners
Greenhouse hydroponics offers superior suitability for growing leafy greens, herbs, and vine crops due to precise nutrient control and faster growth cycles, making it ideal for commercial growers and tech-savvy gardeners. Traditional soil gardening excels with root vegetables, fruit trees, and crops requiring extensive soil ecosystems, preferred by hobbyists and those valuing natural cultivation methods. Both methods accommodate diverse gardening goals, but hydroponics provides higher yield efficiency for space-limited environments while soil gardening supports biodiversity and long-term soil health.
Greenhouse hydroponics vs traditional soil gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com