
Freestanding vs attached greenhouse Illustration
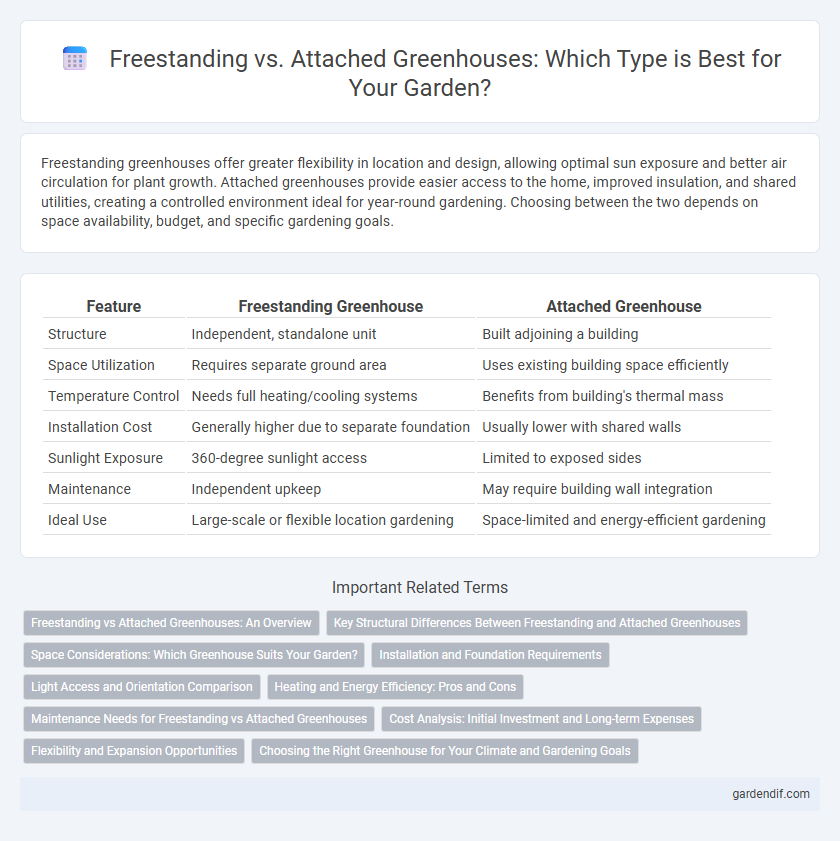
Freestanding greenhouses offer greater flexibility in location and design, allowing optimal sun exposure and better air circulation for plant growth. Attached greenhouses provide easier access to the home, improved insulation, and shared utilities, creating a controlled environment ideal for year-round gardening. Choosing between the two depends on space availability, budget, and specific gardening goals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Freestanding Greenhouse | Attached Greenhouse |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Independent, standalone unit | Built adjoining a building |
| Space Utilization | Requires separate ground area | Uses existing building space efficiently |
| Temperature Control | Needs full heating/cooling systems | Benefits from building's thermal mass |
| Installation Cost | Generally higher due to separate foundation | Usually lower with shared walls |
| Sunlight Exposure | 360-degree sunlight access | Limited to exposed sides |
| Maintenance | Independent upkeep | May require building wall integration |
| Ideal Use | Large-scale or flexible location gardening | Space-limited and energy-efficient gardening |
Freestanding vs Attached Greenhouses: An Overview
Freestanding greenhouses stand independently and allow for greater flexibility in location, maximizing sunlight exposure and airflow, while attached greenhouses are connected to an existing structure, benefiting from shared heating and easier access. Freestanding designs typically vary in size and shape, offering versatile options for garden customization, whereas attached greenhouses often utilize the wall of the house to enhance thermal efficiency. The choice between freestanding and attached greenhouses depends on space availability, budget, and specific gardening needs such as temperature control and structural support.
Key Structural Differences Between Freestanding and Attached Greenhouses
Freestanding greenhouses are independent structures with self-supporting frames, typically featuring four solid walls and a roof, allowing placement anywhere in a garden. Attached greenhouses share one or more walls with an existing building, relying on the building's structure for support, which helps conserve space and maintain heat more efficiently. The choice between freestanding and attached greenhouses depends on space availability, structural stability, and heat retention needs.
Space Considerations: Which Greenhouse Suits Your Garden?
Freestanding greenhouses offer flexible placement options, ideal for larger gardens with ample space, allowing maximum sunlight exposure and airflow. Attached greenhouses save space by utilizing existing structures, making them perfect for smaller gardens or areas with limited yard room. Evaluating garden size and available space helps determine whether a freestanding or attached greenhouse best fits your gardening needs.
Installation and Foundation Requirements
Freestanding greenhouses require a sturdy, level foundation such as concrete or compacted gravel to support the entire structure independently, ensuring stability against wind and weather. Attached greenhouses can utilize the existing building's foundation and wall, simplifying installation and reducing the need for extensive groundwork. Proper anchoring and sealing are critical for both types to prevent heat loss and maintain structural integrity.
Light Access and Orientation Comparison
Freestanding greenhouses provide 360-degree light access, allowing optimal sunlight exposure throughout the day, while attached greenhouses have limited light access on the wall side due to building shadows. Orientation flexibility is higher in freestanding models, enabling growers to position the structure for maximum solar gain, unlike attached greenhouses which must align with the existing building facade. Light intensity and duration are generally superior in freestanding greenhouses, enhancing plant growth rates and yield.
Heating and Energy Efficiency: Pros and Cons
Freestanding greenhouses offer superior heating efficiency due to their standalone structure, allowing for controlled temperature regulation and better insulation options with glass or polycarbonate panels. Attached greenhouses benefit from shared wall heat retention with the main building, reducing heating costs and energy consumption by utilizing residual heat from living spaces. However, freestanding designs demand more energy for heating, while attached greenhouses may face limitations in natural light and airflow, impacting overall energy efficiency.
Maintenance Needs for Freestanding vs Attached Greenhouses
Freestanding greenhouses, being completely separate structures, often require more extensive maintenance, including foundation upkeep, exterior surface care, and weatherproofing to withstand environmental elements. Attached greenhouses benefit from shared walls with the main building, reducing exposure and often lowering heating, cooling, and structural maintenance demands. Both types need regular inspection for pests, glazing integrity, and ventilation system functionality to maintain optimal growing conditions.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Expenses
Freestanding greenhouses typically require a higher initial investment due to foundation costs and full structural framing, while attached greenhouses benefit from shared walls, reducing material and construction expenses. Long-term expenses for freestanding greenhouses include greater heating and cooling costs because they are fully exposed to environmental conditions, whereas attached greenhouses often enjoy energy savings by utilizing the thermal mass of the connected building. Maintenance costs can be higher for freestanding structures as they face more exposure to weather elements, impacting durability and repair frequency.
Flexibility and Expansion Opportunities
Freestanding greenhouses offer greater flexibility in placement and design, allowing for optimal sunlight exposure and customizable sizes independent of existing structures. Attached greenhouses benefit from shared walls, reducing construction costs and enhancing energy efficiency, but limit expansion options due to structural constraints. Choosing between freestanding and attached greenhouses depends on long-term goals for spatial flexibility and potential growth in cultivation capacity.
Choosing the Right Greenhouse for Your Climate and Gardening Goals
Freestanding greenhouses offer greater flexibility and can be positioned anywhere with optimal sunlight, making them ideal for diverse climates and extensive gardening projects. Attached greenhouses conserve space and maintain warmer internal temperatures by sharing a wall with an existing structure, which benefits gardeners in cooler regions or those seeking easy access to indoor facilities. Evaluating local climate conditions and specific gardening objectives ensures the selection of a greenhouse type that maximizes plant growth and energy efficiency.
Freestanding vs attached greenhouse Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com