
Passive Solar Greenhouse vs Active Solar Greenhouse Illustration
Passive solar greenhouses harness natural sunlight and heat retention materials to maintain temperature, requiring minimal energy input. Active solar greenhouses utilize mechanical systems such as fans, heaters, and solar panels to regulate climate more precisely and extend growing seasons. Choosing between passive and active solar greenhouse designs depends on energy availability, climate conditions, and desired control over the environment.
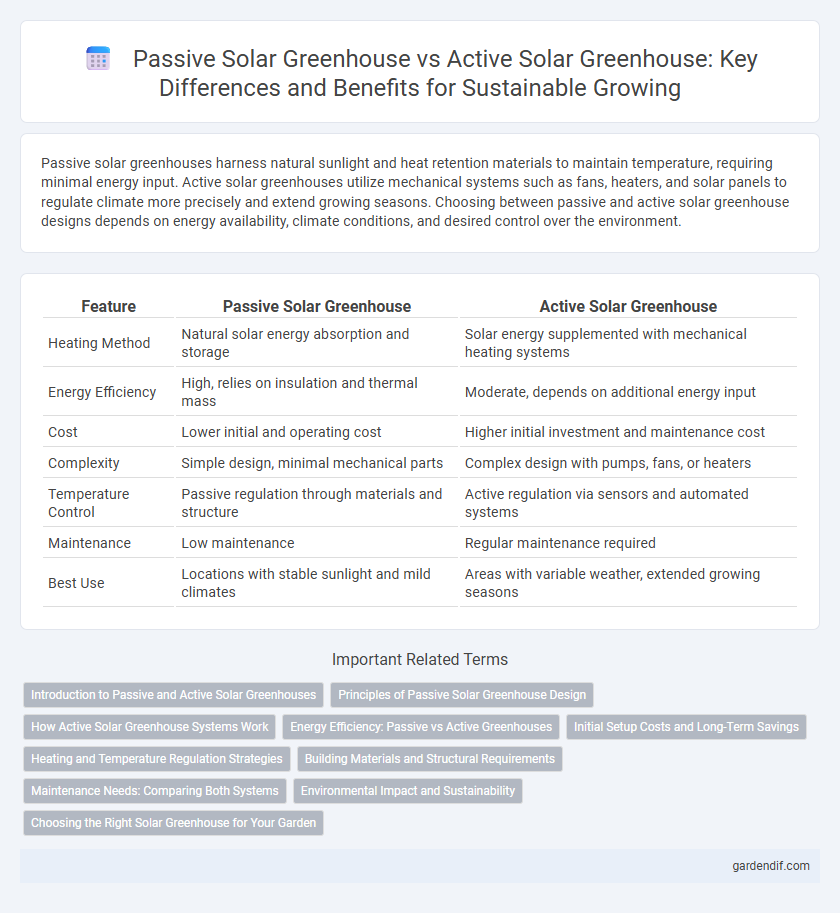
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Passive Solar Greenhouse | Active Solar Greenhouse |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Natural solar energy absorption and storage | Solar energy supplemented with mechanical heating systems |
| Energy Efficiency | High, relies on insulation and thermal mass | Moderate, depends on additional energy input |
| Cost | Lower initial and operating cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance cost |
| Complexity | Simple design, minimal mechanical parts | Complex design with pumps, fans, or heaters |
| Temperature Control | Passive regulation through materials and structure | Active regulation via sensors and automated systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Regular maintenance required |
| Best Use | Locations with stable sunlight and mild climates | Areas with variable weather, extended growing seasons |
Introduction to Passive and Active Solar Greenhouses
Passive solar greenhouses utilize materials like south-facing glass and thermal mass to naturally collect and store solar energy, minimizing external energy inputs. Active solar greenhouses incorporate mechanical systems such as fans, pumps, and solar panels to enhance temperature regulation and energy efficiency. Both designs optimize solar energy use but differ in complexity and reliance on technology for maintaining ideal growing conditions.
Principles of Passive Solar Greenhouse Design
Passive solar greenhouse design relies on natural energy flows to regulate temperature, using materials like thermal mass to absorb and store solar heat during the day and release it at night. Strategic orientation and insulation minimize heat loss while maximizing solar gain, with south-facing glazing capturing sunlight effectively in northern hemispheres. Ventilation and shading techniques maintain airflow and prevent overheating, ensuring a stable microclimate without mechanical systems.
How Active Solar Greenhouse Systems Work
Active solar greenhouse systems use mechanical devices such as fans, pumps, and heaters to regulate temperature and optimize energy efficiency throughout the day and night. These systems integrate solar panels and thermal storage to actively collect, store, and distribute heat, ensuring consistent climate control regardless of external weather conditions. Sensors and automated controls adjust heating, ventilation, and shading, maximizing plant growth by maintaining ideal environmental parameters.
Energy Efficiency: Passive vs Active Greenhouses
Passive solar greenhouses maximize energy efficiency by using natural sunlight and thermal mass to retain heat without mechanical systems, reducing energy consumption significantly. Active solar greenhouses incorporate fans, heaters, and automated systems to regulate temperature, which increases energy use but allows for more precise climate control. Balancing insulation quality and system automation impacts overall energy efficiency in both passive and active greenhouse designs.
Initial Setup Costs and Long-Term Savings
Passive solar greenhouses require lower initial setup costs due to simpler construction and reliance on natural heat retention through materials like insulated glazing and thermal mass. Active solar greenhouses demand higher initial investments for mechanical systems such as solar panels, heaters, and automated controls that optimize energy use. Long-term savings are generally greater in passive systems because they minimize energy expenses, while active systems offer more precise climate control, potentially reducing crop losses and operational inefficiencies.
Heating and Temperature Regulation Strategies
Passive solar greenhouses utilize materials with high thermal mass such as stone or water barrels to absorb and slowly release heat, maintaining stable temperatures without mechanical input. Active solar greenhouses rely on supplemental systems like fans, vents, and heaters powered by electricity or solar panels to regulate temperature more precisely. While passive designs maximize natural solar gain and insulation for heating, active systems ensure consistent climate control during fluctuating or extreme conditions.
Building Materials and Structural Requirements
Passive solar greenhouses rely heavily on materials with high thermal mass like concrete, brick, and stone to absorb and store solar energy, minimizing the need for mechanical systems. Active solar greenhouses incorporate advanced structural components such as metal framing and automated glazing systems to optimize energy capture and circulation, often requiring integrated heating and ventilation equipment. The choice of building materials and structural complexity directly impacts energy efficiency, cost, and climate control capabilities in both greenhouse types.
Maintenance Needs: Comparing Both Systems
Passive solar greenhouses require minimal maintenance due to their reliance on natural sunlight and thermal mass for heat regulation, reducing the need for mechanical components. Active solar greenhouses involve more complex systems like fans, pumps, and automated controls, which demand regular servicing and monitoring to ensure optimal performance. Choosing between the two depends on the gardener's willingness to manage maintenance tasks and the local climate conditions for energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Passive solar greenhouses leverage natural sunlight and thermal mass to regulate temperature, minimizing energy consumption and reducing carbon footprint. Active solar greenhouses incorporate mechanical systems like fans and pumps powered by renewable energy, which can increase energy efficiency but require more resources for maintenance and operation. Both designs promote sustainability, though passive systems generally offer lower environmental impact due to reduced reliance on external energy inputs.
Choosing the Right Solar Greenhouse for Your Garden
Passive solar greenhouses rely on natural sunlight and thermal mass to regulate temperature, requiring minimal energy input and lower maintenance costs. Active solar greenhouses incorporate mechanical systems such as fans, heaters, or solar panels to enhance climate control, offering greater flexibility and year-round growing potential. Selecting the right solar greenhouse depends on your garden's size, budget, and climate conditions, with passive designs suited for mild environments and active systems ideal for colder regions or intensive cultivation.
Passive Solar Greenhouse vs Active Solar Greenhouse Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com