
Nitrogen-rich fertilizer vs phosphorus-rich fertilizer Illustration
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers primarily boost leaf and stem growth by enhancing chlorophyll production, which is essential for photosynthesis and overall plant vigor. Phosphorus-rich fertilizers promote root development and flowering, playing a crucial role in energy transfer and genetic material synthesis within the plant. Selecting between nitrogen-rich and phosphorus-rich fertilizers depends on the specific growth stage and nutrient requirements of the crops to optimize yield and quality.
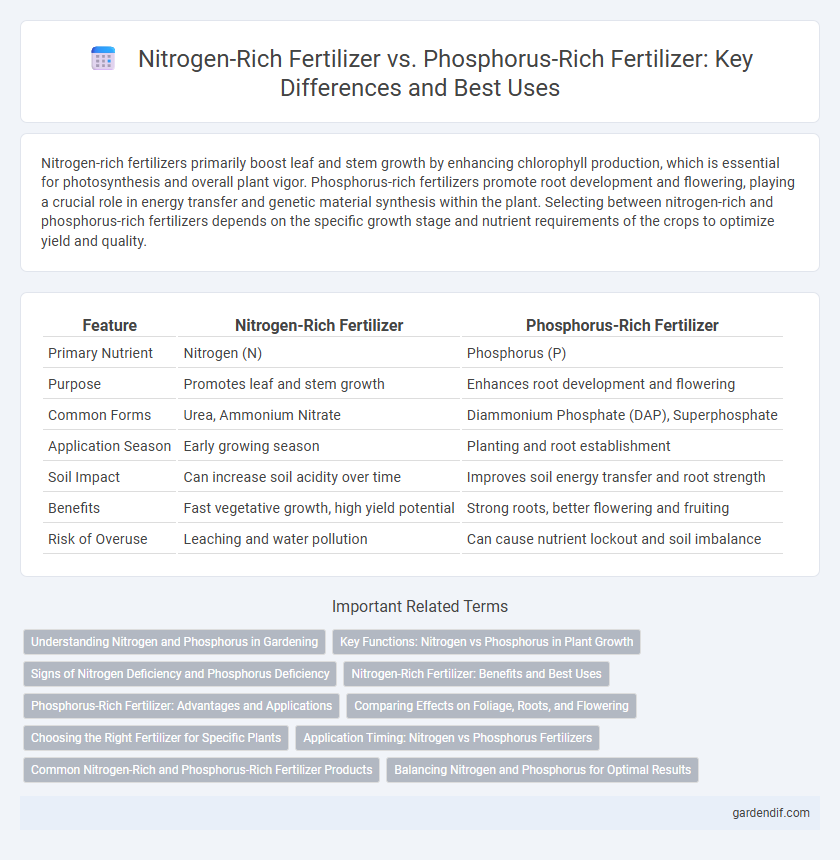
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nitrogen-Rich Fertilizer | Phosphorus-Rich Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Nutrient | Nitrogen (N) | Phosphorus (P) |
| Purpose | Promotes leaf and stem growth | Enhances root development and flowering |
| Common Forms | Urea, Ammonium Nitrate | Diammonium Phosphate (DAP), Superphosphate |
| Application Season | Early growing season | Planting and root establishment |
| Soil Impact | Can increase soil acidity over time | Improves soil energy transfer and root strength |
| Benefits | Fast vegetative growth, high yield potential | Strong roots, better flowering and fruiting |
| Risk of Overuse | Leaching and water pollution | Can cause nutrient lockout and soil imbalance |
Understanding Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Gardening
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers primarily promote lush, green foliage by enhancing chlorophyll production and overall plant growth, making them essential for leafy vegetables and lawns. Phosphorus-rich fertilizers support strong root development, flowering, and fruiting by facilitating energy transfer and cell division in plants. Balancing nitrogen and phosphorus levels according to soil tests optimizes plant health and maximizes crop yield in gardening.
Key Functions: Nitrogen vs Phosphorus in Plant Growth
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers promote vigorous leaf and stem development by enhancing chlorophyll production and photosynthesis efficiency, essential for rapid plant growth. Phosphorus-rich fertilizers contribute significantly to root system development, energy transfer through ATP, and overall flowering and fruiting processes. Both nutrients are critical, but nitrogen mainly supports vegetative growth while phosphorus drives reproductive success and root strength.
Signs of Nitrogen Deficiency and Phosphorus Deficiency
Nitrogen deficiency in plants typically presents as yellowing leaves, especially older foliage, stunted growth, and reduced leaf size, reflecting impaired chlorophyll production and protein synthesis. In contrast, phosphorus deficiency manifests through dark green or purplish leaf discoloration, delayed maturity, and weak root development, indicative of its crucial role in energy transfer and root vitality. Understanding these distinct symptoms guides targeted fertilizer application to optimize plant health and crop yield.
Nitrogen-Rich Fertilizer: Benefits and Best Uses
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers significantly enhance plant growth by promoting lush, green foliage and increasing photosynthesis efficiency, making them ideal for crops like corn, wheat, and leafy vegetables. They improve soil fertility by supplying essential nitrogen, a crucial macronutrient that supports amino acid and protein synthesis in plants. Optimal use of nitrogen-rich fertilizers involves timed application during critical growth stages to maximize nutrient uptake and minimize environmental runoff.
Phosphorus-Rich Fertilizer: Advantages and Applications
Phosphorus-rich fertilizers are essential for promoting strong root development, flowering, and fruiting in plants by supplying adequate phosphorus, a key nutrient involved in energy transfer and photosynthesis. These fertilizers improve soil fertility and enhance crop yield quality, especially in phosphorus-deficient soils common in many agricultural regions. Applications include use in root vegetables, legumes, and flowering crops where phosphorus availability directly influences plant health and productivity.
Comparing Effects on Foliage, Roots, and Flowering
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers primarily promote lush, green foliage growth by enhancing chlorophyll production and leaf development, while phosphorus-rich fertilizers stimulate robust root systems and improve nutrient uptake efficiency. Phosphorus supports flowering and fruiting processes, leading to increased bloom size and quantity, whereas excess nitrogen can delay flowering and reduce bloom quality. Balanced application of nitrogen and phosphorus ensures optimal plant health by combining vigorous vegetative growth with strong root establishment and prolific flowering.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Specific Plants
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers are ideal for leafy vegetables and plants requiring robust green growth, as nitrogen promotes chlorophyll production and foliage development. Phosphorus-rich fertilizers support root development and flowering, making them essential for root crops, flowering plants, and fruit-bearing species. Selecting the right fertilizer depends on the plant's growth stage and nutrient requirements, ensuring optimal health and maximum yield.
Application Timing: Nitrogen vs Phosphorus Fertilizers
Nitrogen-rich fertilizers are most effective when applied during the early growth stages of crops to support rapid vegetative development, while phosphorus-rich fertilizers are best applied at planting to enhance root establishment and early vigor. Timing nitrogen application closer to periods of active growth reduces leaching and maximizes uptake efficiency, whereas phosphorus remains relatively immobile in soil, allowing for earlier application without significant loss. Proper synchronization of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer timing improves nutrient use efficiency and crop yield potential.
Common Nitrogen-Rich and Phosphorus-Rich Fertilizer Products
Common nitrogen-rich fertilizers include urea, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium sulfate, which are essential for promoting vigorous leaf and stem growth in crops. Phosphorus-rich fertilizers, such as superphosphate, triple superphosphate, and ammonium phosphate, play a critical role in root development and energy transfer within plants. The choice between nitrogen-rich and phosphorus-rich fertilizers depends on soil nutrient composition and specific crop requirements for optimal yield.
Balancing Nitrogen and Phosphorus for Optimal Results
Balancing nitrogen-rich and phosphorus-rich fertilizers is essential for maximizing crop yield and soil health, as nitrogen supports vegetative growth while phosphorus promotes root development and energy transfer. Overapplication of nitrogen can lead to nutrient imbalances, reducing phosphorus availability and causing environmental issues such as nitrate leaching. Optimizing the ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus according to soil test results ensures efficient nutrient uptake, enhances plant growth, and minimizes ecological impact.
Nitrogen-rich fertilizer vs phosphorus-rich fertilizer Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com