
N-P-K ratio vs Micronutrient ratio Illustration
The N-P-K ratio in fertilizers indicates the proportions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium essential for plant growth, directly influencing root development, flowering, and overall yield. Micronutrient ratios, although present in smaller quantities, are critical for enzyme function, disease resistance, and chlorophyll synthesis, impacting plant health and productivity. Balancing both macronutrient N-P-K ratios and micronutrient levels ensures optimal fertilizer efficiency and sustainable crop performance.
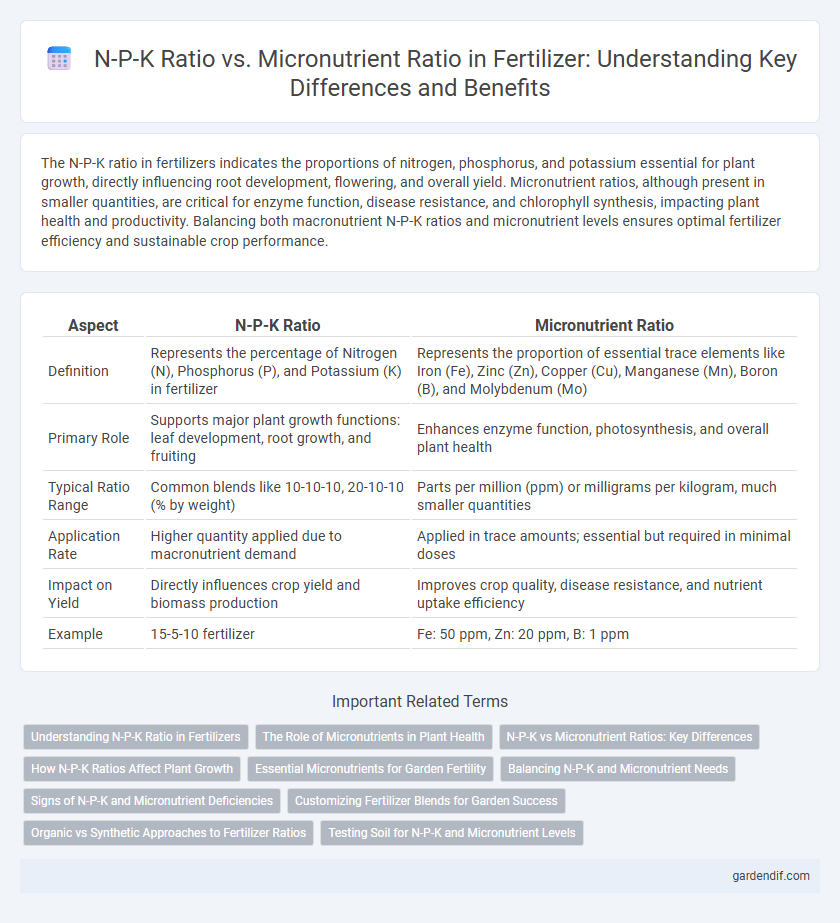
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | N-P-K Ratio | Micronutrient Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Represents the percentage of Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) in fertilizer | Represents the proportion of essential trace elements like Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn), Boron (B), and Molybdenum (Mo) |
| Primary Role | Supports major plant growth functions: leaf development, root growth, and fruiting | Enhances enzyme function, photosynthesis, and overall plant health |
| Typical Ratio Range | Common blends like 10-10-10, 20-10-10 (% by weight) | Parts per million (ppm) or milligrams per kilogram, much smaller quantities |
| Application Rate | Higher quantity applied due to macronutrient demand | Applied in trace amounts; essential but required in minimal doses |
| Impact on Yield | Directly influences crop yield and biomass production | Improves crop quality, disease resistance, and nutrient uptake efficiency |
| Example | 15-5-10 fertilizer | Fe: 50 ppm, Zn: 20 ppm, B: 1 ppm |
Understanding N-P-K Ratio in Fertilizers
The N-P-K ratio in fertilizers represents the percentage of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), the primary macronutrients essential for plant growth, root development, and overall crop health. While N-P-K addresses major nutrient needs, micronutrient ratios include elements like iron, zinc, and manganese, vital for enzymatic functions but required in smaller quantities. Optimizing N-P-K ratios ensures robust vegetative growth and yield, making it critical to balance with micronutrient availability for comprehensive soil fertility management.
The Role of Micronutrients in Plant Health
Micronutrients such as zinc, iron, manganese, and copper play a crucial role in plant health by supporting enzyme function, chlorophyll production, and overall metabolic processes, which are not addressed by the primary N-P-K ratio that focuses on nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Deficiencies in micronutrients can lead to stunted growth, chlorosis, and reduced crop yields despite optimal N-P-K fertilization. Balanced fertilization strategies that incorporate both N-P-K and essential micronutrients ensure improved nutrient uptake, stress resistance, and enhanced plant productivity.
N-P-K vs Micronutrient Ratios: Key Differences
N-P-K ratio represents the primary macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium essential for plant growth, while micronutrient ratios include trace elements like zinc, iron, and manganese required in smaller quantities. N-P-K ratios primarily influence overall plant vigor, root development, and fruit production, whereas micronutrient ratios affect specialized physiological functions such as chlorophyll synthesis and enzyme activation. Precision in balancing N-P-K and micronutrient ratios is crucial for optimizing crop yield and nutrient efficiency in fertilization management.
How N-P-K Ratios Affect Plant Growth
N-P-K ratios indicate the proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) essential for plant growth, influencing root development, flowering, and overall plant health. A balanced N-P-K ratio ensures optimal nutrient uptake, improving photosynthesis, cell division, and stress resistance. Micronutrient ratios, while crucial for enzymatic functions and chlorophyll production, support fine-tuning but have less direct impact on primary growth stages compared to N-P-K ratios.
Essential Micronutrients for Garden Fertility
Essential micronutrients such as iron, manganese, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and boron play a critical role in achieving optimal garden fertility beyond the primary N-P-K ratio. While nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium support major growth functions, micronutrient balance ensures enzymatic activity, photosynthesis efficiency, and overall plant health. Maintaining precise micronutrient ratios alongside N-P-K levels promotes robust root development, disease resistance, and higher crop yields in nutrient-demanding garden soils.
Balancing N-P-K and Micronutrient Needs
Balancing N-P-K and micronutrient ratios is essential for optimal plant growth, as macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium support primary metabolic processes while micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese are crucial for enzymatic functions. A well-formulated fertilizer maintains appropriate N-P-K ratios--commonly 10-10-10 or 20-20-20--while ensuring micronutrient levels meet crop-specific demands to prevent deficiencies and toxicities. Precision in nutrient management through soil testing and targeted supplementation enhances nutrient uptake efficiency and overall crop yield quality.
Signs of N-P-K and Micronutrient Deficiencies
Signs of N-P-K deficiencies include stunted growth, yellowing leaves (chlorosis), and poor fruit development, indicating insufficient nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium levels respectively. Micronutrient deficiencies often manifest as interveinal chlorosis, necrotic spots, or distorted leaf shapes due to lack of elements like iron, zinc, or manganese. Accurate diagnosis of deficiencies through visual symptoms and soil testing is essential for proper nutrient management and optimal crop yield.
Customizing Fertilizer Blends for Garden Success
Customizing fertilizer blends requires balancing the primary N-P-K ratio with essential micronutrient ratios to enhance plant growth and soil health effectively. Optimizing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels addresses major nutrient needs, while integrating tailored micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese supports specific crop requirements and corrects soil deficiencies. Precise N-P-K and micronutrient adjustments improve nutrient uptake efficiency and maximize garden productivity.
Organic vs Synthetic Approaches to Fertilizer Ratios
Organic fertilizers typically offer balanced N-P-K ratios combined with essential micronutrients in naturally occurring proportions, enhancing soil health and microbial activity. Synthetic fertilizers provide precise N-P-K formulations but often lack micronutrient diversity, requiring additional supplementation to prevent nutrient imbalances. Combining organic matter with tailored synthetic inputs can optimize nutrient availability and support sustainable plant growth.
Testing Soil for N-P-K and Micronutrient Levels
Testing soil for N-P-K levels provides crucial data on the primary macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium that support plant growth, while analyzing micronutrient ratios identifies essential trace elements like iron, zinc, and manganese that influence crop health and yield. Accurate soil testing enables tailored fertilizer applications that optimize nutrient availability, prevent deficiencies, and avoid environmental damage caused by over-fertilization. Integrating N-P-K and micronutrient analysis ensures balanced nutrient management for sustainable agricultural productivity.
N-P-K ratio vs Micronutrient ratio Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com