
Container Gardening vs Window Box Gardening Illustration
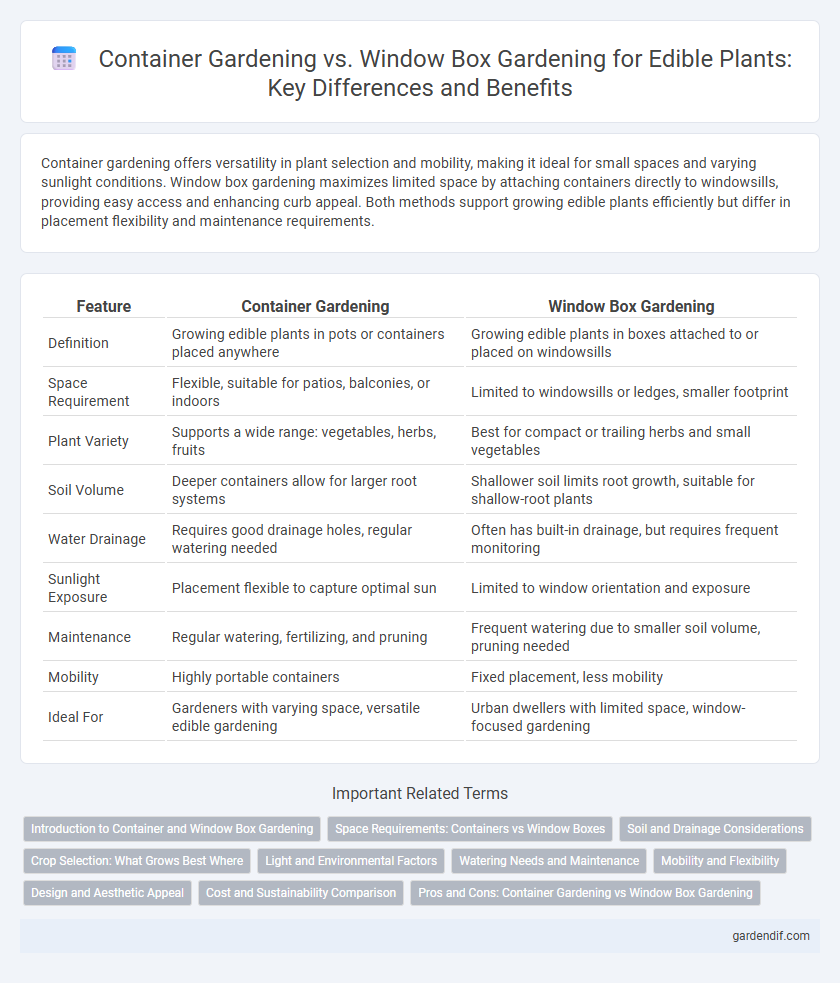
Container gardening offers versatility in plant selection and mobility, making it ideal for small spaces and varying sunlight conditions. Window box gardening maximizes limited space by attaching containers directly to windowsills, providing easy access and enhancing curb appeal. Both methods support growing edible plants efficiently but differ in placement flexibility and maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Container Gardening | Window Box Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing edible plants in pots or containers placed anywhere | Growing edible plants in boxes attached to or placed on windowsills |
| Space Requirement | Flexible, suitable for patios, balconies, or indoors | Limited to windowsills or ledges, smaller footprint |
| Plant Variety | Supports a wide range: vegetables, herbs, fruits | Best for compact or trailing herbs and small vegetables |
| Soil Volume | Deeper containers allow for larger root systems | Shallower soil limits root growth, suitable for shallow-root plants |
| Water Drainage | Requires good drainage holes, regular watering needed | Often has built-in drainage, but requires frequent monitoring |
| Sunlight Exposure | Placement flexible to capture optimal sun | Limited to window orientation and exposure |
| Maintenance | Regular watering, fertilizing, and pruning | Frequent watering due to smaller soil volume, pruning needed |
| Mobility | Highly portable containers | Fixed placement, less mobility |
| Ideal For | Gardeners with varying space, versatile edible gardening | Urban dwellers with limited space, window-focused gardening |
Introduction to Container and Window Box Gardening
Container gardening offers versatile options for growing edible plants in limited spaces, utilizing pots and containers of various sizes and materials to optimize soil quality and drainage. Window box gardening specializes in compact, decorative planters attached to windowsills, maximizing sunlight exposure and accessibility for herbs and small vegetables. Both methods enable urban gardeners to cultivate fresh produce efficiently while enhancing aesthetic appeal and space utilization.
Space Requirements: Containers vs Window Boxes
Container gardening offers flexible space options, accommodating a wide range of sizes from small pots to large barrels, making it ideal for varying garden dimensions. Window box gardening requires narrower, elongated containers that fit securely on window sills or ledges, optimizing limited horizontal space. Both methods support edible plant growth, but container gardening provides more volume for root development, while window boxes maximize space efficiency in compact areas.
Soil and Drainage Considerations
Container gardening requires well-draining soil mixes rich in organic matter to prevent waterlogging and root rot. Window box gardening demands lightweight, fast-draining soil blends to accommodate limited space and ensure adequate aeration. Proper drainage holes in both containers and window boxes are essential to maintain optimal moisture levels for edible plant health.
Crop Selection: What Grows Best Where
Container gardening thrives with versatile crops like tomatoes, peppers, and herbs such as basil and mint, which adapt well to deeper soil and ample space. Window box gardening suits compact, shallow-rooted plants like lettuce, radishes, and strawberries that require minimal soil depth and benefit from direct sunlight. Choosing crops according to container depth and light exposure ensures optimal growth and harvest success in both gardening styles.
Light and Environmental Factors
Container gardening offers flexibility in adjusting to varying light conditions, allowing placement in optimal sunlight throughout the day, which benefits light-loving edible plants such as tomatoes and peppers. Window box gardening typically exposes plants to limited and often indirect light, requiring selection of shade-tolerant crops like leafy greens and herbs. Environmental factors such as airflow and temperature fluctuations also differ; containers can be moved to protect from extreme weather, while window boxes are fixed and may experience microclimate effects from the building's interior.
Watering Needs and Maintenance
Container gardening typically requires more frequent watering due to larger soil volume and better drainage, which prevents waterlogging but increases evaporation rates. Window box gardening demands consistent moisture monitoring as limited soil depth causes quicker drying, necessitating daily watering in warm climates. Maintenance in container gardening often involves root pruning and soil replenishment, while window boxes require regular fertilization and pest control to sustain plant health.
Mobility and Flexibility
Container gardening offers superior mobility by allowing edible plants to be easily relocated for optimal sunlight exposure or seasonal changes, enhancing growth conditions. Window box gardening, while limited in size, provides flexibility for small spaces but restricts plant movement and variety due to fixed installation. Prioritizing mobility, container gardening supports diverse edible crops with adaptable positioning, making it ideal for changing environments and maximizing harvest potential.
Design and Aesthetic Appeal
Container gardening offers versatile design options with a wide range of pot shapes, sizes, and materials, allowing for customized arrangements that complement various outdoor spaces. Window box gardening enhances curb appeal by adding vibrant color and greenery directly to the home's facade, creating a charming, integrated look that maximizes limited space. Both methods provide aesthetic benefits, but window boxes emphasize vertical visual interest, while container gardens allow for flexible placement and layered design.
Cost and Sustainability Comparison
Container gardening typically requires larger pots and more soil, leading to higher initial costs, while window box gardening uses smaller, often reusable containers that reduce expenses. Window boxes maximize space efficiency and often utilize rainwater more effectively, promoting sustainability compared to container gardens that might necessitate frequent watering and soil replacement. Both methods support urban agriculture, but window box gardening tends to offer a more eco-friendly and cost-efficient approach.
Pros and Cons: Container Gardening vs Window Box Gardening
Container gardening offers flexibility with a wider variety of edible plants, allowing gardeners to move containers for optimal sunlight and space utilization; however, it requires more frequent watering and can be heavier to manage. Window box gardening maximizes small urban spaces with easy access and aesthetic appeal, but limits root growth and plant size due to space constraints. Both methods provide fresh produce but differ in maintenance, plant selection, and placement adaptability.
Container Gardening vs Window Box Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com